Introduction
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely recognized in the food packaging industry for its exceptional strength, durability, and versatility. As one of the most commonly used materials for food containers and trays, PP food trays play a vital role in ensuring food safety, convenience, and environmental sustainability. This article delves into the multifaceted world of PP food trays, exploring their benefits, applications, sustainability concerns, and market trends from various perspectives.

1. What Are PP Food Trays?
Definition of PP Food Trays
Polypropylene food trays are made from polypropylene (PP), a thermoplastic polymer used in a range of foodservice applications. PP trays are typically used for packaging prepared meals, snacks, takeout orders, and catering services due to their strength and versatility.
PP is known for being a high-performance plastic with a unique combination of properties that makes it an ideal choice for packaging in the food industry. These trays are available in various sizes, colors, and shapes, and can be molded into different designs to suit specific foodservice requirements.
Key Characteristics:
-
Durability and Strength: PP trays are incredibly strong and resistant to breakage. They can withstand rough handling, making them ideal for high-traffic environments like fast food restaurants and catering services.
-
Heat and Chemical Resistance: PP has a high melting point, allowing it to endure hot food without warping or leaching chemicals into the food. This is particularly important for foods that need to be heated in a microwave or oven.
-
Lightweight: Despite their strength, PP trays are lightweight, reducing transportation costs and making them easy to handle for both customers and foodservice workers.

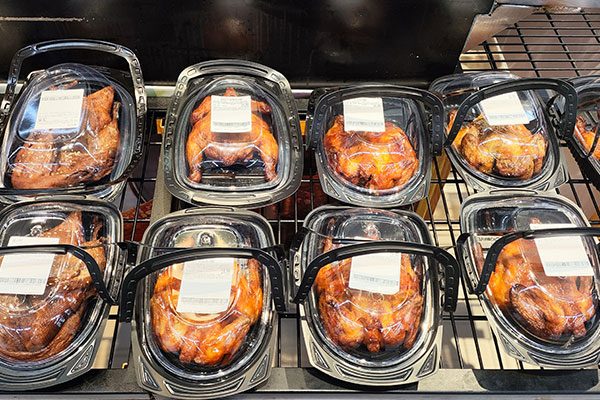
2. Benefits of PP Food Trays
Durability and Strength
The most prominent feature of PP food trays is their durability. They offer a significant advantage over other food packaging materials such as polystyrene (PS), PLA, and PVC due to their ability to resist cracking and breaking. This makes PP trays ideal for both industrial and home use, as they maintain their integrity even under stress.
Heat and Cold Resistance
Polypropylene stands out for its heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 120°C without distortion. This makes it suitable for use with hot foods, whether they are freshly prepared or reheated. It can also be used for cold food storage, as PP does not become brittle at low temperatures, unlike other materials such as polystyrene (PS).
-
Hot Food Applications: PP food trays are commonly used to package hot dishes like pizzas, baked goods, and pre-cooked meals. These trays can safely be microwaved and heated without risk of damaging the tray or affecting the food quality.
-
Cold Food Applications: They also maintain their structural integrity when used for cold foods like salads, fruits, and sandwiches, making them versatile for both hot and cold packaging.
Chemical Resistance
Unlike polystyrene or PVC, which can react with acidic foods and cause chemical leaching, PP food trays offer excellent chemical resistance. They can withstand exposure to oils, sauces, and acids without degrading or releasing harmful substances. This is a critical benefit for food safety, ensuring that the food remains uncontaminated by the packaging.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to other plastics, PP is relatively inexpensive to produce. This makes PP food trays a cost-effective solution for foodservice businesses, especially in high-volume settings like takeout restaurants, fast food chains, and catering services. The affordability of PP trays makes them an attractive alternative to more expensive packaging materials, such as PLA and PET.

3. The Market for PP Food Trays
Global Market Trends
In recent years, the demand for PP food trays has surged due to the growing popularity of takeout, delivery services, and ready-to-eat meals. With the global shift toward convenience foods, particularly post-pandemic, PP food trays have become essential in the foodservice industry.
-
Food Delivery Services: The rise of food delivery platforms such as UberEats, GrubHub, and Deliveroo has driven the demand for PP trays. These platforms require packaging that is both practical for transport and capable of preserving food quality.
-
Fast Food Chains and Quick-Service Restaurants (QSR): PP trays are often used in fast food restaurants for packaging sandwiches, burgers, fries, and other quick-service meals.
-
Catering Industry: PP trays are widely used in catering services, where large quantities of food need to be transported safely. These trays are customizable, allowing catering companies to use different tray sizes and configurations depending on their needs.
Consumer Preferences for Sustainable Packaging
As consumers become increasingly concerned about environmental issues, there is a growing demand for eco-friendly packaging. This trend has prompted many foodservice companies to seek sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic packaging. PP is a recyclable material, making it a more sustainable option compared to non-recyclable plastics like PS. However, it is important to note that while PP trays are recyclable, they are not biodegradable, which remains a limitation in their environmental impact.
-
Recyclability: PP is accepted by most recycling programs worldwide, and PP food trays can be recycled into new products. However, the recycling rates for PP are still lower than for other materials such as PET or PLA.
-
Eco-Conscious Consumer Demand: Many consumers now demand transparency about the sustainability of their food packaging. Companies that use PP food trays may benefit from highlighting their recyclability and commitment to sustainability.

4. Comparing PP with Other Food Tray Materials
PP vs. PLA
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable plastic made from renewable resources like cornstarch and sugarcane. However, PLA trays are less durable and more vulnerable to heat than PP trays. PLA is not suitable for high-temperature applications, as it can deform when exposed to heat above 50°C. On the other hand, PP can withstand higher temperatures, making it more versatile.
-
PP Advantages: PP trays are better suited for hot foods, microwaving, and extended storage without losing integrity. They are also more durable and resistant to breakage than PLA trays.
-
PLA Advantages: PLA trays are compostable and made from renewable resources, making them a more environmentally friendly option when disposal is a concern. However, they are not ideal for high-heat food applications.
PP vs. PS (Polystyrene)
While PS trays are often used for food packaging, PP trays offer superior strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. PS is more brittle and can easily crack or break under pressure, making it less suitable for certain food packaging needs.
-
PP Advantages: PP is more robust, flexible, and resistant to cracking than PS. It is also more heat-resistant, which makes it ideal for both hot and cold food applications.
-
PS Advantages: PS trays are often cheaper to produce than PP trays, but the tradeoff is in the material’s durability and heat resistance.

5. PP Food Trays in Sustainable Food Packaging
Sustainability Benefits of PP Trays
Although PP is not biodegradable, it is one of the most recyclable plastics in the market. This makes PP food trays a more sustainable choice compared to other materials like PVC, which is not recyclable in many regions. Additionally, the durability of PP means that it has a longer lifespan than other packaging materials, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
-
Longer Lifespan: The durability of PP food trays contributes to their sustainability. Unlike materials that crack and degrade easily, PP trays can be reused multiple times before needing to be replaced.
-
Energy Efficiency in Production: The production process of PP is energy-efficient compared to other materials like PLA or PET, making it a more eco-friendly choice from a manufacturing standpoint.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
PP trays are lightweight, which reduces the amount of energy required for transportation. Their low weight contributes to lower carbon emissions during transit, which is a significant advantage when compared to heavier materials.
-
Lower Transportation Costs: Due to their light weight, PP trays can reduce fuel consumption and costs associated with shipping, especially in high-volume settings.
-
Sustainability through Efficiency: The efficiency of PP in both production and transportation contributes to its overall sustainability.
6. Innovations in PP Food Tray Design
Customizable Designs
The flexibility of PP allows for a wide range of customizations, which is one of the key reasons why it is widely used in the food packaging industry. Whether it’s a simple single-compartment tray or a complex multi-compartment design, PP trays can be tailored to meet specific requirements.
-
Size and Shape Customization: PP trays can be manufactured in various sizes and shapes to fit different food portions. From square trays to rectangular ones, foodservice providers can create packaging that suits their specific menu items.
-
Design Innovation: Some companies have developed PP trays with enhanced features, such as airtight seals, stackability, and easy-to-handle designs. Custom features like these allow for improved functionality and convenience.
Enhanced Branding Opportunities
Custom PP trays also provide an opportunity for businesses to incorporate branding into their packaging. Logos, designs, and promotional messages can be printed directly on the surface of the trays, turning them into a powerful marketing tool.

7. Future of PP Food Trays: Innovations and Trends
Biodegradable Additives
Researchers are working on incorporating biodegradable additives into PP trays, which would allow these trays to break down more rapidly once discarded. This innovation would make PP a more environmentally friendly material while retaining its durability and heat resistance.
Increased Recycling Rates
As global recycling infrastructure continues to improve, the rate of PP recycling is expected to rise. This would reduce the amount of PP packaging that ends up in landfills and improve its sustainability profile.
8. Conclusion: The Role of PP Food Trays in the Future of Packaging
PP food trays have long been an essential part of the food packaging industry, offering a combination of durability, heat resistance, and recyclability. As consumer demand for sustainable and convenient packaging grows, PP trays will continue to play a significant role in providing foodservice solutions. Their versatility, customization options, and sustainability features make them an indispensable choice for businesses worldwide.
FAQ
-
What are the benefits of using PP food trays?
-
PP food trays are durable, heat-resistant, and chemical-resistant, making them perfect for hot and cold food packaging.
-
-
Can PP food trays be recycled?
-
Yes, PP food trays are fully recyclable, which helps reduce their environmental impact when properly disposed of.
-
-
What is the difference between PP and PLA trays?
-
PP trays are more heat-resistant and durable than PLA trays, which are biodegradable but have limitations in temperature tolerance.
-
-
Are PP food trays safe for microwaving?
-
Yes, PP food trays are microwave-safe and can handle high temperatures without deforming.
-
-
What are the environmental benefits of PP trays?
-
PP trays are recyclable, which helps reduce waste, and their production process is energy-efficient.
-
References
-
Thompson, R. C., Moore, C. J., Saal, F. S. V., & Swan, S. H. (2009). Plastics, the environment and human health: Current consensus and future trends. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364(1526), 2153-2166.
URL: https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rstb.2009.0053 -
Geyer, R., Jambeck, J. R., & Law, K. L. (2017). Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Science Advances, 3(7), e1700782.
URL: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.1700782 -
Kang, H. J., & Kim, H. J. (2019). Polypropylene-based packaging: Properties, uses, and sustainable recycling approaches. Packaging Technology and Science, 32(6), 276-295.
URL: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/pts.2394 -
Wang, S., & Zhang, J. (2021). Polypropylene Food Packaging: Innovation and Sustainability. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58(5), 1429-1440.
URL: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11483-021-01472-9
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.