Quick Summary
This article provides a comprehensive overview of PET packaging, covering its material properties, recyclability advantages, manufacturing technology, global market trends, and safety compliance. It also explains why PET has become the preferred choice for foodservice, beverages, and fresh food packaging worldwide, supported by data, expert insights, and industry references.
I. Introduction: Why PET Still Leads the Global Packaging Market
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) has been the backbone of global food packaging for more than four decades.
Today, even as new bioplastics such as PLA and PHA emerge and policies push for sustainable packaging, PET remains the dominant material in beverage cups, salad boxes, deli containers, fruit packaging, bakery clamshells, and tamper-evident food boxes.
According to Euromonitor, PET accounts for over 55% of all rigid plastic food packaging globally, and its consumption continues to grow—driven by safety, clarity, recyclability, and performance requirements that competing materials cannot fully replace.
This article delivers an expert-level, data-backed, helping brands, retailers, and packaging importers understand:
-
Why PET retains strong market dominance
-
How global regulations influence PET adoption
-
How thermoforming and RPET technologies are reshaping the industry
-
What buyers should verify when selecting PET suppliers
-
How manufacturers like DASHAN support global compliance and sustainability
-
What the future looks like for PET vs. PLA vs. PP
This is an authoritative guide created for global procurement teams, sustainability managers, distributors, QSR chains, and food packaging manufacturers.
II. The Scientific Foundation: Why PET Works for Food Packaging
PET began its life not as a packaging material but as a textile fiber in the 1940s. Its transition into food-grade packaging began in the 1970s, driven by its unique combination of:
-
High clarity
-
Excellent mechanical strength
-
Lightweight
-
Gas-barrier performance
-
Safety and global food-contact recognition
Below is a scientific breakdown for decision-makers.
1. Material Properties That Give PET Its Advantage
PET is a thermoplastic polyester formed through condensation polymerization of ethylene glycol (EG) and terephthalic acid (PTA).

Key material strengths include:
| Property | PET Value | Industry Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Transition Temperature | ~70–80°C | Maintains rigidity for cold/room temp foods |
| Melting Point | ~245–265°C | Enables high-precision thermoforming |
| Density | 1.38 g/cm³ | Lightweight yet stronger than PP/PLA |
| Impact Resistance | High | Ideal for salad boxes, drink cups, deli packs |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent | Enhances shelf visibility |
| Gas Barrier | Strong | Extends shelf life of cold foods |
How these properties matter for buyers:
-
PET protects product freshness in retail and cold chain logistics.
-
PET provides premium visual presentation for fruits, salads, bakery items.
-
PET offers the best strength-to-weight performance compared with PP and PLA.
2. Food Safety and International Compliance
PET is globally accepted for direct food contact under:
-
FDA 21 CFR Regulations (USA)
-
EU Regulation No. 10/2011
-
Japan Food Sanitation Act
-
South American food-contact standards (Chile, Colombia, Peru, Brazil)
Because PET does not require plasticizers and contains no endocrine disruptors, it is considered one of the safest plastics for cold beverages and ready-to-eat foods.
III. Global Regulatory Environment and Its Impact on PET Demand
Governments worldwide are restricting single-use plastics, but PET is often exempt or favored because it is recyclable and has strong existing recovery systems.
PET is considered a “preferred compliance material” in many regions.
1. Europe: PET as a Compliant Material
The EU’s Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD) targets non-recyclable plastics such as:
-
PS (polystyrene)
-
PVC
-
Non-recyclable laminated plastics
PET, especially RPET, is strongly supported because of its:
-
High recycling rate
-
Circular economy potential
-
Existing bottle-to-bottle infrastructure
France and Germany are leading examples where PET containers remain legal and widely used, provided they meet recycled content requirements.
2. North America: PET as the Most Practical Recyclable Material
The U.S. has no federal plastic ban, but state laws (California, Washington, Oregon) require:
-
Recycled content in beverage bottles
-
Progressively increasing RPET ratios
Because PET is one of the only plastics with a mature recycling ecosystem, it remains the top choice for medium-to-large food brands.
3. Latin America: PET’s Rapid Market Expansion
Countries like Chile, Colombia, and Peru are pushing strong EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) policies.
PET packaging is favored because:
-
It is widely recyclable
-
It supports producer compliance
-
It reduces plastic tax burdens (e.g., Colombia’s tax on non-recyclable plastics)
IV. PET vs. PLA vs. PP: Technical and Market Comparison
To help procurement teams evaluate their options, here is an expert-level comparison.
1. Performance Comparison Table
| Property | PET | PP | PLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clarity | ★★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ |
| Impact Strength | ★★★★★ | ★★★★ | ★★ |
| Heat Resistance | ★★★ | ★★★★ | ★★ |
| Compostability | No | No | Yes (industrial) |
| Recyclability | Excellent | Moderate | Limited |
| Cost Stability | Stable | Stable | Fluctuating |
| Global Acceptance | Very High | High | Moderate |
Conclusion:
PET remains the best option for cold foods, beverages, salads, bakery, deli, and display packaging.
V. Market Data: Why PET Demand Continues to Grow
Below are suggested chart integration points.
PET packaging demand is projected to grow from USD 79 billion in 2024 to USD 112 billion by 2030, driven by:
-
Cold beverage growth
-
Food delivery and takeaway expansion
-
Preference for clear packaging
-
Recycled PET (RPET) incentives
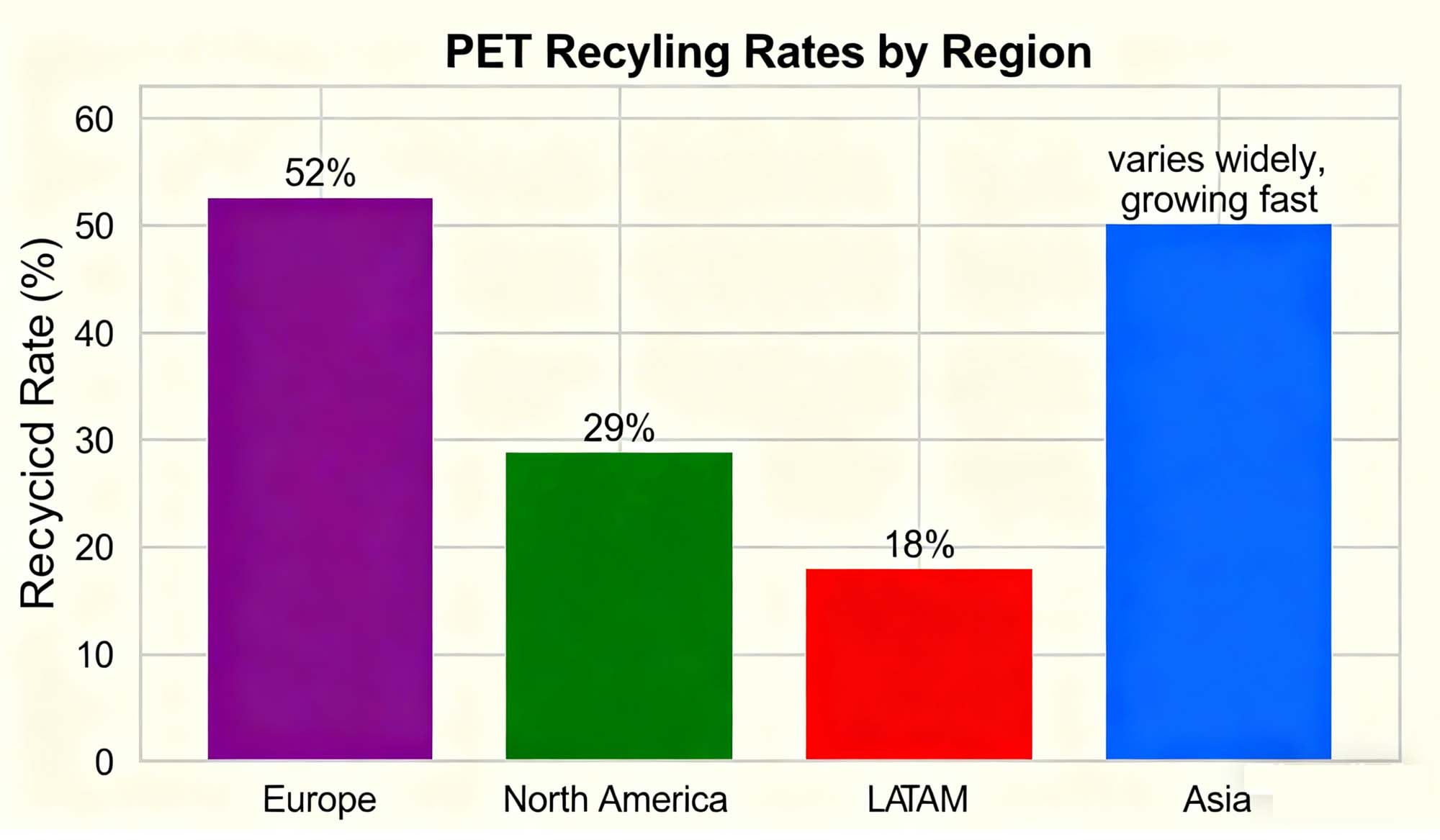
Europe leads with ~52% PET recycling rate, followed by:
-
North America: ~29%
-
LATAM: ~18%
-
Asia: varies widely, growing fast
VI. Advanced Thermoforming Technology and How It Improves PET Quality
PET performance depends heavily on thermoforming.
Key benefits include:
-
Consistent wall thickness
-
Enhanced clarity
-
Reinforced structural stability
-
Lower defect rates
-
Reduced material waste
How thermoforming affects PET cup quality:
-
Proper drying avoids yellowing
-
Controlled heating prevents warping
-
Uniform pressure avoids weak points
-
Precision molds improve sealing performance
VII. Adding DASHAN Into the Picture
As global buyers demand higher quality and reliable compliance, manufacturers like DASHAN have strengthened the PET supply chain through:
1. Certified Quality Systems

DASHAN maintains:
-
ISO 9001 Quality Management Certification
-
ISO 14001 Environmental Management Certification
-
FDA Food Contact Compliance
-
EU 10/2011 Food-Contact Compliance
These certifications ensure every PET cup, lid, clamshell, and tamper-evident salad box meets global expectations for safety and performance.
2. Advanced PET Thermoforming Facilities
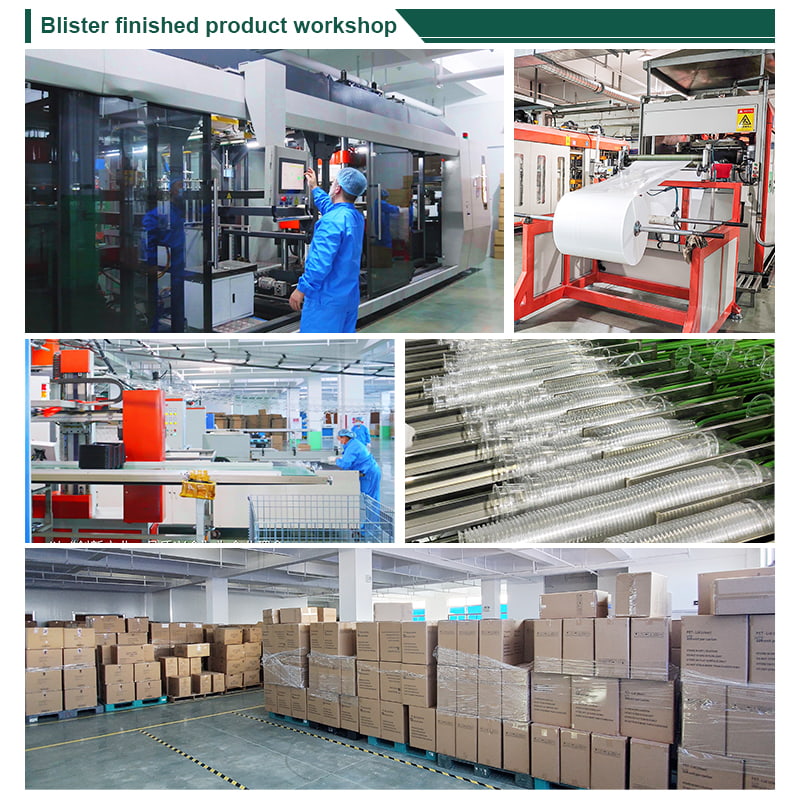

DASHAN operates modern production lines equipped with:
-
Automated PET sheet extrusion
-
High-precision thermoforming
-
In-line trimming and stacking
-
Optical clarity monitoring
-
Raw-material traceability systems
This allows the company to produce PET packaging with:
-
Crystal-clear transparency
-
Excellent structural strength
-
Superior consistency
-
Food-safe production standards
3. Proven Export Experience

DASHAN products are exported to:
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Southeast Asia
-
The Middle East
-
North America
And the company has exhibited in:
-
Dubai
-
Malaysia
-
Russia
-
Thailand
-
China International Packaging Expo
These global exhibitions reinforce DASHAN’s credibility and market recognition.
VIII. PET Tamper-Evident Boxes: A Fast-Growing Segment
With the rise of food delivery and ready-to-eat markets, tamper-evident PET salad boxes are growing rapidly.
Why restaurants and retailers prefer PET tamper-evident boxes:
-
They clearly show product freshness
-
They prevent contamination during delivery
-
They offer high stacking strength
-
They meet many “anti-tampering” requirements
-
They are compatible with RPET upgrades
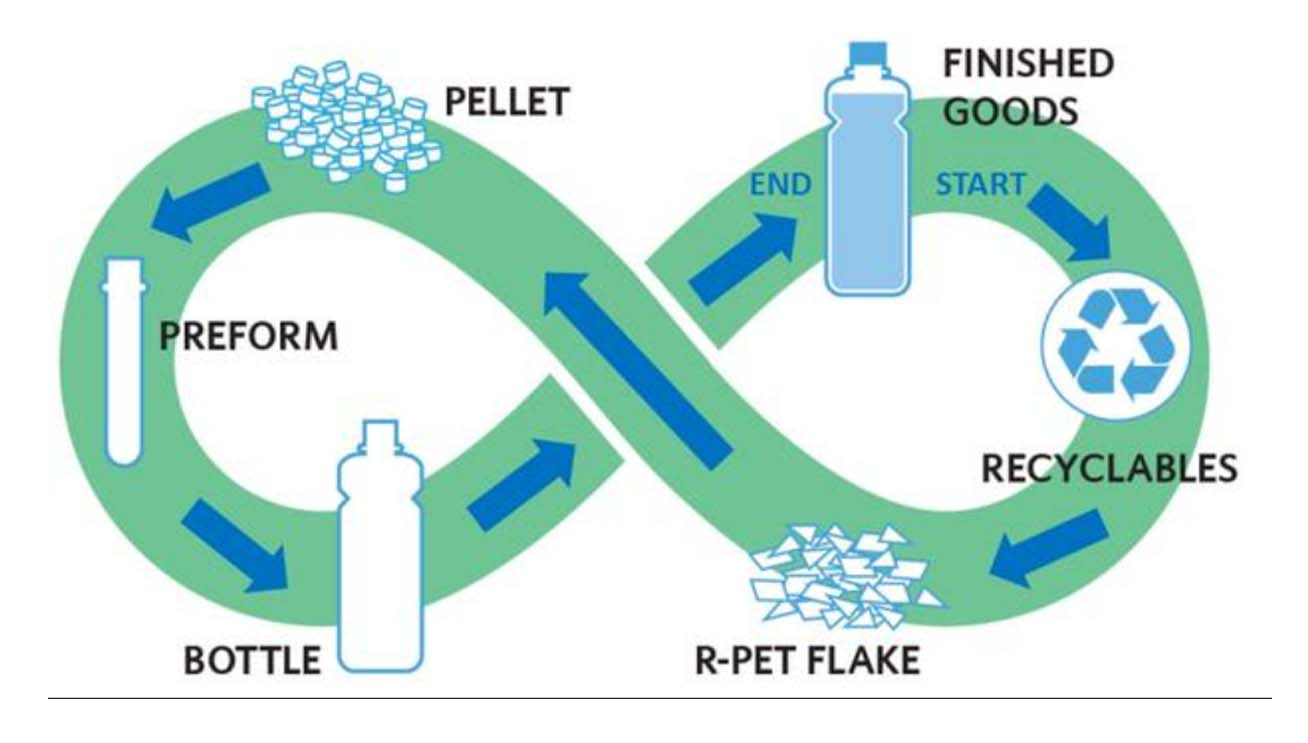
IX. Sustainability: RPET and the Circular Economy
PET is the most widely recycled plastic in the world.
Key advantages:
-
Bottle-to-bottle recycling
-
Cup-to-fiber recycling
-
Low energy consumption
-
Strong demand from beverage companies
-
Global shift toward 30–50% RPET minimums
X. Buyer Checklist: What to Verify When Sourcing PET Packaging
A professional procurement checklist:
-
Food-contact compliance certifications
-
Recycled content percentage (if needed)
-
Clarity consistency (optical QC reports)
-
Impact compression test results
-
Heat resistance data
-
Sealing performance for lids/hinges
-
Traceability of raw PET resin
-
Factory audit capability
-
Shipping and stacking strength test reports
DASHAN’s production system supports all the above with documented QC processes.
FAQ
1. Why is PET widely used in food packaging?
PET offers excellent clarity, strong impact resistance, reliable barrier properties, and wide recyclability, making it suitable for beverages, salads, cold dishes, and retail-ready packaging.
2. Is PET safe for direct food contact?
Yes. PET is internationally recognized as food-safe when produced under FDA and EU 10/2011 standards, with proven chemical stability and low migration levels.
3. Can PET withstand high temperatures?
PET performs best between –70°C and 120°C. It is ideal for cold foods, salads, beverages, and refrigerated items but not suitable for microwaving.
4. How does PET support sustainability?
PET is the world’s most recycled plastic (#1 recycling code). RPET reduces virgin resin demand, cuts carbon emissions, and supports the circular economy.
5. What industries rely most on PET packaging?
Foodservice chains, beverage brands, supermarket delis, fresh produce, bakery items, cold salads, and ready-to-eat meals.
6. What advantages does PET have over PP and PLA?
PET offers superior transparency and barrier performance. PP excels at heat resistance, while PLA is compostable but requires industrial facilities.
7. How does DASHAN ensure PET product quality?
DASHAN follows strict international QC systems, material traceability, and advanced thermoforming processes to ensure clarity, consistency, and global food-contact compliance.
Conclusion
Despite global pressure to reduce single-use plastics, PET remains the world’s most widely used and accepted food-grade packaging material. Its unmatched clarity, recyclability, structural performance, and global regulatory acceptance make it irreplaceable in:
-
Retail food packaging
-
Cold beverages
-
Fruit and salad boxes
-
Tamper-evident containers
-
Deli and bakery applications
With the rise of RPET, improved thermoforming technology, and government-backed recycling incentives, PET is not only here to stay but is growing stronger.
Manufacturers like DASHAN, with global certifications, modern PET facilities, and strong export experience, ensure buyers receive safe, sustainable, high-performance PET packaging aligned with future regulatory trends.
PET is not just a packaging material—
it is the backbone of the future circular food packaging economy.
📚 References
-
PETCORE Europe. PET Market Report. Retrieved from:
https://www.petcore-europe.org/images/2024/PET_report_V5.pdf -
Global Growth Insights. PET Packaging Market Forecast & Growth 2033. Retrieved from:
https://www.globalgrowthinsights.com/market-reports/pet-packaging-market-111394 -
Emergen Research. Recycled PET Market Size, Share & Forecast Report 2024–2034. Retrieved from:
https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/recycled-pet-market -
ScienceDirect. A Systematic Review of PET Circularity Technologies and Management Strategies. Retrieved from:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921344925001594 -
Wikipedia. PET Bottle Recycling. Retrieved from:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PET_bottle_recycling -
Evertis. Circular Economy for PET Food Packaging. Retrieved from:
https://www.evertis.com/circular-economy -
PET vs rPET: What’s the Difference for Buyers?Retrieved from:
PET Vs RPET Cups: Differences, Costs & Buyer Guide
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.