Quick Summary
RPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) is more expensive than PET due to the complexities of the recycling process, limited availability of quality recycled materials, and the need for advanced technologies. While RPET is a more sustainable option, its higher cost reflects these challenges. However, as recycling technologies improve, the price gap may narrow, making RPET more accessible.
Introduction
In the current landscape of packaging, sustainability is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a priority. As the world grapples with the impact of plastic pollution, RPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) is emerging as a key player in reducing the environmental footprint of plastic packaging. However, despite its ecological benefits, RPET comes at a higher price point compared to PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate), its virgin counterpart. This price difference often raises questions among businesses and consumers alike: Why is RPET more expensive than PET?
In this comprehensive blog, we’ll break down the factors contributing to the higher cost of RPET, comparing it to PET, exploring the economic and environmental factors involved, and looking at the future of this sustainable alternative.
1. Understanding PET and RPET
What is PET?
PET, or Polyethylene Terephthalate, is one of the most widely used plastics, particularly in packaging materials such as beverage bottles, food containers, and textiles. PET is derived from petrochemical resources—specifically, terephthalic acid (PTA) and ethylene glycol (EG)—which undergo polymerization to create the plastic polymer. PET is known for its strength, transparency, and recyclability.

What is RPET?
RPET, or Recycled PET, refers to PET plastic that has been repurposed through a recycling process. This plastic can come from post-consumer waste such as used bottles, food packaging, and even discarded textiles. RPET is made by collecting PET waste, cleaning it, and then melting it down to produce new plastic products. The primary environmental benefit of RPET is that it reduces the demand for virgin plastic and helps divert plastic waste from landfills and oceans.
The key difference between PET and RPET lies in their raw material sources. While PET relies entirely on virgin, petroleum-based resources, RPET utilizes post-consumer plastic, making it more sustainable.

2. The Production Process of PET vs RPET
How PET is Produced
The production of PET is a straightforward process that involves extracting petroleum-based raw materials. These materials undergo a polymerization process, where the chemicals are combined under heat and pressure to form PET resin. Once the resin is created, it is molded into the final product, whether that’s plastic bottles, trays, or fibers. The process is energy-intensive but relatively efficient, especially with the advanced production technologies in place.
The Recycling Process of RPET
Producing RPET is more complex. While PET can be mass-produced relatively easily from raw materials, RPET production depends on the availability of recycled plastic. The process begins with the collection and sorting of used PET items, followed by cleaning to remove contaminants like labels, food residue, and other materials. Once cleaned, the plastic is shredded into flakes, which are then melted and reformed into new products.
Recycling PET into RPET introduces several challenges:
-
Quality Control: Used PET materials can be contaminated, which means they must be meticulously cleaned and sorted.
-
Degradation: PET’s quality degrades with each recycling cycle, making it necessary to use advanced technologies to maintain the quality of RPET.
-
Energy Consumption: The energy required for recycling RPET, particularly in cleaning and processing, is higher than the production of virgin PET, which contributes to the overall cost.
3. Factors Contributing to the Higher Cost of RPET
Supply Chain Challenges
The RPET supply chain faces significant challenges compared to PET. Since RPET relies on recycled plastic, the availability of high-quality recycled PET is less predictable than that of virgin PET. While PET can be manufactured on a large scale from raw materials, the supply of recycled materials depends on collection systems, consumer participation, and regional recycling infrastructure.
The quality of the recycled PET can also vary significantly. Contaminants such as labels, food residues, and non-PET plastics can affect the material’s quality, making it necessary to perform extensive cleaning and sorting. These additional steps drive up the cost of RPET production.
Availability of Recycled Materials
Unlike PET, which can be consistently produced from raw materials, RPET is limited by the availability of recyclable plastic. In many parts of the world, recycling rates are still relatively low, meaning that companies often struggle to source enough high-quality RPET to meet demand. This scarcity can drive up the price of RPET, especially when there’s an increased demand for sustainable packaging materials.
Technological Advancements and Costs
Recycling PET into RPET is not a simple task. The process requires sophisticated sorting, cleaning, and decontamination technology to ensure that the recycled plastic meets the necessary standards for quality. These technologies come with high upfront costs, and their maintenance can be expensive. Additionally, because RPET is often recycled from lower-quality materials, the production process may require additional steps to improve its strength and durability, further adding to the cost.
Government Regulations and Incentives
Government regulations can also impact the cost of RPET. In many countries, there are recycling targets and incentives for using recycled materials, which can make RPET an attractive option for businesses. However, the infrastructure needed to collect, sort, and recycle PET is still lacking in many regions, which can increase the overall cost of obtaining RPET.

4. The Environmental Impact of RPET vs PET
Environmental Benefits of RPET
One of the key selling points of RPET is its positive environmental impact. By using post-consumer plastic to create new products, RPET helps reduce the overall plastic waste that ends up in landfills and oceans. Additionally, it reduces the need for petroleum-based raw materials, which are non-renewable and contribute to environmental degradation.
The production of RPET generally requires less energy than the production of virgin PET, which leads to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. For example, producing RPET from recycled plastic can save up to 60% of the energy compared to manufacturing new PET from raw materials. This makes RPET a more eco-friendly option, despite its higher upfront cost.
Reducing Carbon Footprint with RPET
Using RPET instead of virgin PET also reduces the carbon footprint of products. This is particularly important for industries looking to meet their sustainability goals. Since RPET has a smaller environmental footprint over its lifecycle, it is seen as an essential material for companies aiming to minimize their impact on the planet.
Lifecycle Analysis of PET vs RPET
Lifecycle analysis (LCA) studies show that RPET outperforms PET in terms of environmental sustainability. RPET has a significantly lower carbon footprint and uses fewer natural resources compared to virgin PET. These benefits are amplified when RPET is recycled multiple times, promoting a circular economy in packaging and other industries.
5. Market Demand and Consumer Preferences
Rising Demand for Sustainable Packaging
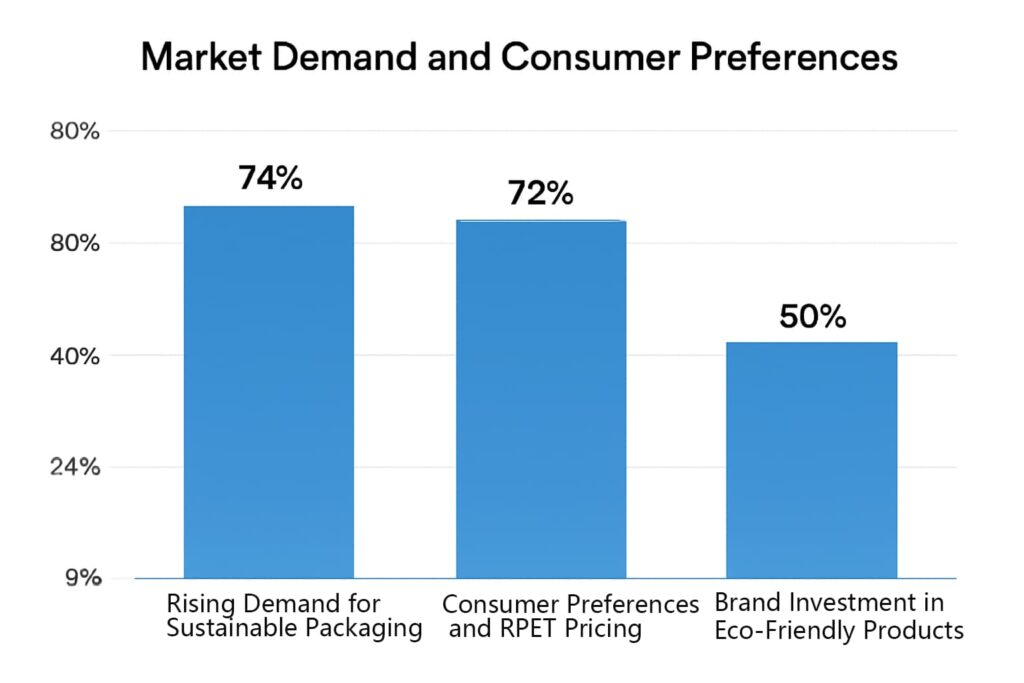
The demand for sustainable packaging solutions has seen a significant rise in recent years. A 2023 study by the Global Data Consumer Survey found that 74% of consumers are more likely to purchase products with eco-friendly packaging. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they increasingly prefer products packaged in materials that are recyclable, biodegradable, or made from recycled materials. This shift towards sustainability is particularly pronounced in younger generations, with 80% of Millennials and Gen Z respondents prioritizing sustainable packaging in their purchasing decisions. RPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) aligns well with these consumer preferences, offering brands an opportunity to position themselves as environmentally responsible.
Consumer Preferences and RPET Pricing
Despite its higher production cost, many consumers are willing to pay a premium for products packaged in RPET. According to Nielsen’s 2022 Global Sustainability Report, 73% of consumers say they are willing to pay more for products with sustainable packaging. This growing preference for eco-friendly products has prompted many brands to invest in RPET as part of their sustainability strategy. However, the production cost of RPET is typically 15-30% higher than standard PET due to the additional steps required to process and recycle the material. These increased costs are often passed on to the consumer, especially in markets where sustainability is a high priority.
Brand Investment in Eco-Friendly Products
Leading brands are heavily investing in eco-friendly packaging to meet the rising demand from consumers who value sustainability. A report by Statista in 2023 revealed that over 50% of major consumer goods companies had increased their investment in sustainable packaging over the past two years. Many companies are adopting RPET as a way to align with their environmental goals and distinguish themselves from competitors. While the initial cost may be higher, these investments are seen as essential for fostering long-term brand loyalty and enhancing corporate reputation. As of 2022, 67% of brands reported that sustainability initiatives positively impacted their brand’s reputation and consumer trust.
6. The Future of RPET
Technological Innovations in RPET Production
The future of RPET is promising. Advances in recycling technology are expected to lower the costs associated with RPET production. Innovations like chemical recycling and improvements in sorting and cleaning technologies could make it easier and more affordable to produce high-quality RPET. These advancements are expected to drive down the price gap between RPET and PET in the coming years.
Price Trends in the RPET Market
The price of RPET is expected to become more competitive as demand grows and technological advancements make the recycling process more efficient. Governments around the world are also pushing for higher recycling rates, which could result in a more stable supply of RPET and lower costs over time.
RPET and the Circular Economy
RPET plays a crucial role in the circular economy, where materials are continuously reused and recycled. As the demand for sustainable packaging grows, RPET is expected to become more widespread and cost-effective, leading to a more sustainable future.
FAQ
-
What is RPET?
RPET stands for Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate. It is a type of plastic made from recycled PET plastic products, such as bottles and food containers. -
Why is RPET more expensive than PET?
RPET is more expensive due to the complex recycling process, the need for advanced technology, and the limited availability of high-quality recycled plastic. -
Is RPET more sustainable than PET?
Yes, RPET is more sustainable because it reduces the need for virgin plastic, lowers energy consumption, and helps reduce plastic waste. -
Can RPET be recycled multiple times?
Yes, RPET can be recycled multiple times, but the quality of the material degrades with each cycle, which is why advanced recycling technologies are needed. -
Is RPET safe for food packaging?
Yes, RPET is safe for food packaging, and many products made from RPET are FDA-approved for food use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the higher cost of RPET compared to PET is primarily due to the complexities of recycling, supply chain challenges, and the need for advanced technologies. However, despite its higher price, RPET offers significant environmental benefits, including reduced plastic waste, lower carbon emissions, and a smaller overall environmental footprint. As the demand for sustainable packaging continues to rise and recycling technologies improve, RPET is poised to become an even more cost-effective and sustainable option for businesses and consumers alike.
References
-
Lifecycle Analysis of Recycled PET. Environmental Protection Agency.
URL: https://www.epa.gov/smm/sustainable-management-materials-lifecycle-analysis -
Global Plastic Recycling Market Analysis. Grand View Research, 2021.
URL: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/plastic-recycling-market -
RPET: An Overview of Benefits and Challenges. Recycling Today, 2022.
URL: https://www.recyclingtoday.com/article/rpet-benefits-and-challenges/ -
Sustainable Packaging: Trends and Innovations. Packaging Digest, 2021.
URL: https://www.packagingdigest.com/sustainable-packaging
Copyright Statement© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this contentwithout written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information andto upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.