Quick Summary
CPET (Crystalline Polyethylene Terephthalate) airline meal trays are engineered to endure both freezing temperatures as low as –40°C and oven heating up to 200–220°C. Their semi-crystalline molecular structure, formed through controlled thermoforming, grants exceptional thermal stability, impact resistance, and dimensional integrity. These trays are designed for automated filling lines, airline galley ovens, and long-term frozen storage, making them the industry standard for aviation catering, frozen ready meals, and institutional foodservice. CPET ensures food safety, reheating efficiency, and consistent performance across extreme temperature cycles.
Introduction
Airline catering is one of the most demanding sectors in global foodservice packaging. Meals prepared in large industrial kitchens must be frozen, transported long distances, reheated in galley ovens thousands of feet above the ground, and finally served safely to passengers. At the heart of this tightly coordinated system lies a material that makes it all possible: CPET (Crystalline Polyethylene Terephthalate).
CPET trays are widely used by airlines, railway catering, institutional foodservice, frozen meal producers, and large-scale meal distribution centers. Their popularity is not accidental—CPET provides a rare combination of thermal stability, durability, food safety, and operational efficiency. One of the most remarkable properties of CPET is its ability to withstand extreme temperature ranges: from –40°C for deep freezing to 220°C for high-heat oven operations.
This article explores why CPET performs so exceptionally well. We dig deep into its material science, crystallization behavior, manufacturing technologies, performance advantages, regulatory compliance, sustainability profile, and real-world applications. The goal is to provide a comprehensive technical reference that helps procurement teams, packaging developers, food manufacturers, and airline catering managers understand exactly what makes CPET trays uniquely reliable.
1. What Is CPET? Understanding the Material Behind the Performance

CPET stands for Crystalline Polyethylene Terephthalate, a form of PET that has been intentionally modified to achieve a semi-crystalline structure. PET is normally used in transparent rigid packaging such as water bottles, salad boxes, and bakery containers. However, traditional PET cannot handle high oven temperatures because its structure is mostly amorphous.
1.1 Amorphous PET (A-PET)
-
Mostly transparent
-
Lower heat resistance (around 60–70°C)
-
Suitable for cold foods and ambient packaging
1.2 Crystalline PET (C-PET or CPET)
-
Opaque due to crystalline regions
-
Heat resistance up to 200–220°C
-
Retains impact strength at freezing temperatures down to –40°C
-
Excellent dimensional stability
CPET’s crystalline structure is the key to its superior temperature performance.
2. The Science Behind Thermal Resistance: Why CPET Performs in Extremes
2.1 Crystallinity: The Foundation of Heat Resistance
The crystalline regions in CPET act like a network of tightly packed molecular chains. These act as a “thermal skeleton” that keeps the tray from deforming when exposed to high heat.
-
Glass transition temperature (Tg): ~75–80°C
-
Melting temperature (Tm): ~245–255°C
-
Crystallinity level: 20–35% (depending on processing)
Because of this structure, CPET doesn’t soften at oven temperatures like polypropylene (PP) or polystyrene (PS).
How Crystallinity Is Achieved
During thermoforming, the sheet is heated and cooled in a controlled pattern that encourages PET molecules to form ordered structures. This process includes:
-
Preheating the sheet
-
Forming the tray shape
-
Rapid cooling at controlled rates
The final result is a tray with crystalline regions that resist melting and maintain dimensional stability even in extreme heat.
2.2 Why CPET Can Be Frozen Without Becoming Brittle
Most plastics become brittle at freezing temperatures because molecular mobility decreases. However, CPET’s crystalline structure distributes stress evenly, allowing the material to retain impact strength even at –40°C.
This makes CPET ideal for:
-
airline frozen entrées
-
frozen ready meals
-
meal-prep programs
-
institutional catering
-
emergency food supply chains
Even after weeks or months in the freezer, a CPET tray remains sturdy and crack-resistant.
2.3 Dual-Oven Usability: Conventional & Microwave
CPET is one of the very few plastics that can safely be used in:
-
gas ovens
-
electric ovens
-
steam ovens
-
microwave ovens
It can withstand:
-
direct heat
-
dry heat
-
moist heat
-
rapid temperature changes
Even thermal shocks—such as moving a tray directly from freezer to a 180°C oven—are tolerated, thanks to CPET’s crystalline stability and controlled flexibility.
3. The CPET Manufacturing Process: How the Material’s Properties Are Engineered
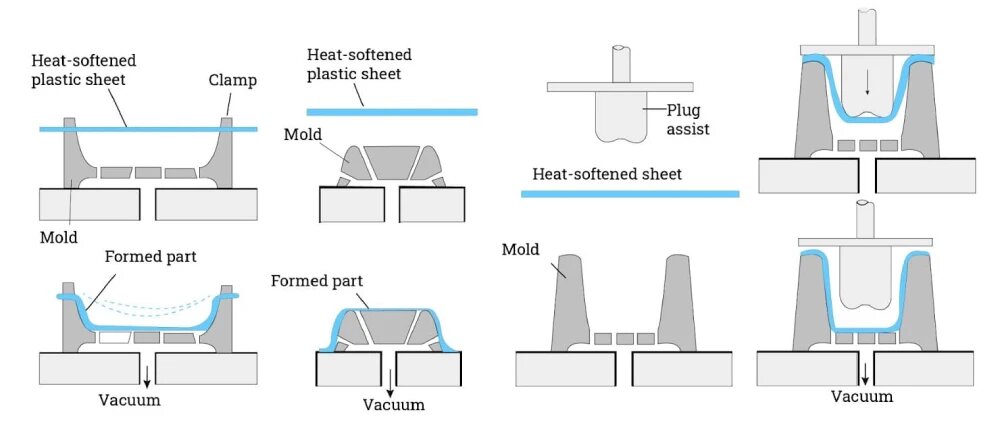
To understand CPET’s reliability, it is important to understand the steps of manufacturing.
3.1 Raw Material Preparation
The base material is PET resin, often blended with:
-
nucleating agents
-
colorants (usually black, white, or natural)
-
impact modifiers
These additives help control crystallization speed and mechanical performance.
3.2 Sheet Extrusion
PET pellets are melted and extruded into flat sheets. The sheet thickness is critical to performance:
-
400–800 microns for airline trays
-
600–1000 microns for frozen meal trays
Precision in this stage ensures uniform heating during thermoforming.
3.3 Thermoforming: The Crystallization Stage
This is the most crucial step.
Key actions during thermoforming:
-
Sheet is heated to ~200°C
-
Material is stretched into the mold
-
Controlled cooling solidifies the crystalline structure
The speed and temperature of cooling determine:
-
crystallinity level
-
rigidity
-
heat resistance
-
resistance to deformation
3.4 Edge Strength & Warp Control
CPET trays used in aviation must remain flat and aligned during automated filling and sealing. Therefore, manufacturers reinforce:
-
tray rims
-
corners
-
sidewalls
This ensures:
-
proper sealing with CPET or PET lids
-
no leakage during reheating
-
compatibility with airline galley equipment
4. Why CPET Is the Preferred Material in Aviation Catering
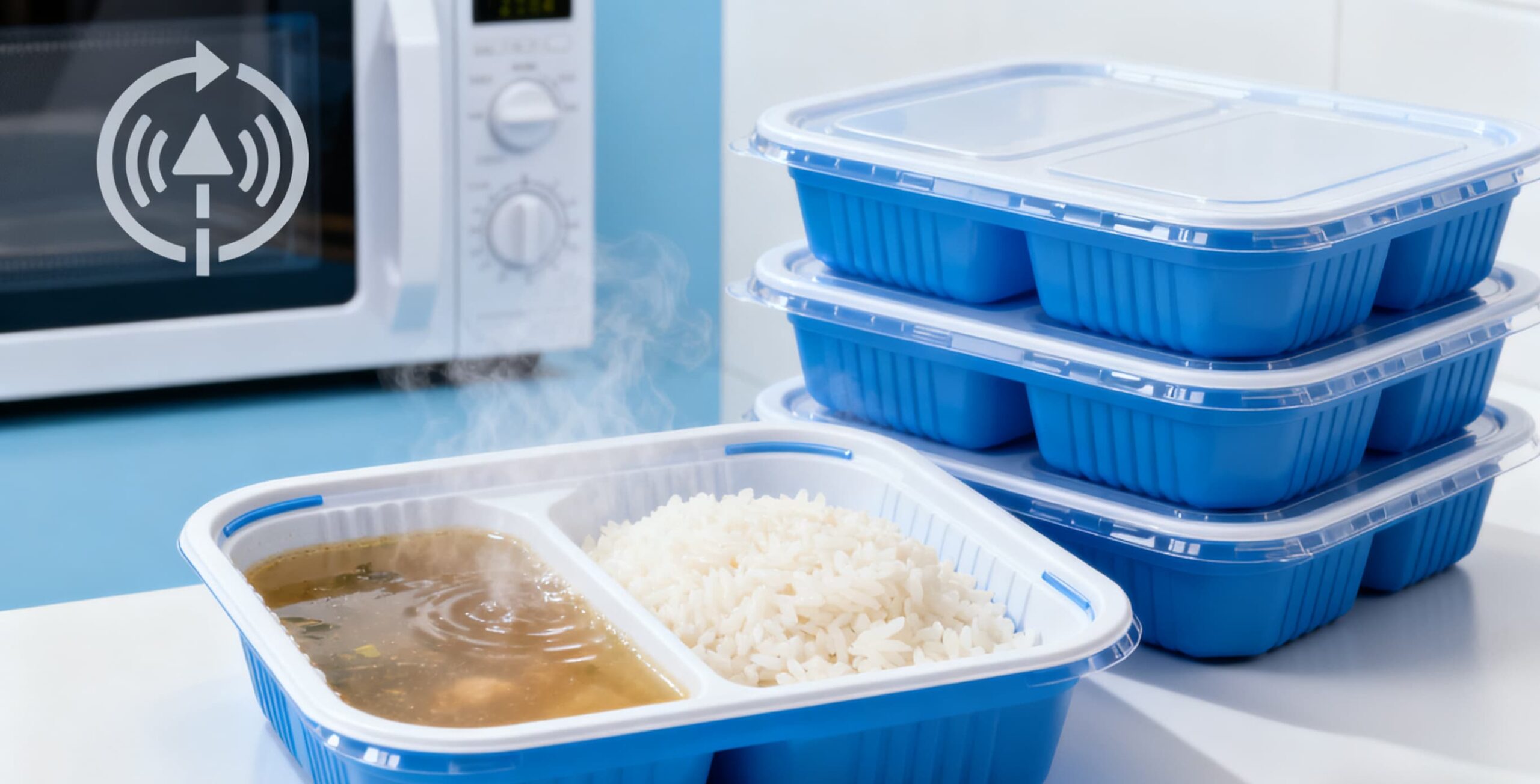

4.1 High Temperature Safety
Airline meals are typically reheated between 160–200°C. CPET can easily tolerate this without:
-
warping
-
melting
-
releasing odors
-
degrading
Galley ovens operate under high airflow and humidity, yet CPET remains stable.
4.2 Compatibility with Freezing Storage
Airline catering cycles often involve:
-
blast freezing at –35°C
-
frozen storage at –18°C
-
reheating in oven at 180–200°C
Most plastics cannot survive this temperature shock, but CPET is specifically engineered for these transitions.
4.3 Dimensional Stability for Automated Operations
CPET trays are compatible with:
-
automated filling machines
-
sealing machines
-
storage racks
-
standardized aircraft ovens
-
hand-held passenger service trays
This standardization is crucial in aviation, where meal components must fit perfectly.
4.4 Food Safety & Compliance
CPET is approved for food contact by:
-
FDA
-
EFSA
-
China GB standards
-
International airline catering standards
It does not release harmful substances under high heat.
5. Performance Comparison: CPET vs Other Materials
| Material | Max Heat Resistance | Freezing Performance | Oven Safe? | Microwave Safe? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPET | 200–220°C | Excellent to –40°C | Yes | Yes | Best all-round performance |
| PP (Polypropylene) | 120–130°C | Good | Microwave only | Yes | Not suitable for airline ovens |
| Aluminum | 250°C+ | Excellent | Yes | No | Heavy; not microwave-safe |
| Paper Pulp + Lining | 100–120°C | Poor to fair | Limited | Yes | Can deform with moisture |
| PS | 70–80°C | Poor | No | No | Brittle; not heat-resistant |
CPET is the only material that performs strongly across all extremes.
6. Applications Beyond Airlines

While CPET is famous for airline meals, its uses extend across many industries.
6.1 Frozen Meal Manufacturing
CPET is a favorite for:
-
ready-to-eat meals
-
lasagna trays
-
microwave dinners
-
hospital meal programs
6.2 Railway Catering
Railways require durable trays that can withstand reheating and movement—CPET fits perfectly.
6.3 Institutional Foodservice
-
schools
-
hospitals
-
military catering
-
offshore operations
6.4 Meal Prep & Delivery Services
The rising meal-kit industry values CPET for its reheating convenience and leak-proof performance.
7. Sustainability Considerations

7.1 Recyclability
CPET belongs to the PET family, meaning it is technically recyclable where infrastructure exists.
7.2 Carbon Footprint
CPET generally has:
-
lower emissions than aluminum
-
better energy efficiency in ovens
-
long storage life, reducing food waste
7.3 Circular Economy Inclusion
Many facilities remanufacture CPET scrap into:
-
new CPET sheets
-
PET fibers
-
industrial materials
8. Challenges and Limitations
Although CPET is highly capable, it has constraints.
8.1 Higher Cost Compared to PP
The specialized production process increases costs.
8.2 Opaque Appearance
CPET trays are usually black or white and cannot be clear.
8.3 Recycling Differences by Region
While recyclable, infrastructure varies across countries.
9.Why Choose DASHAN?

Choosing a reliable supplier is essential when sourcing CPET trays for aviation or large-scale meal production. DASHAN stands out as a trusted manufacturer with years of experience in thermoforming technology, strict quality control, and compliance with global food-contact standards such as FDA, EU 10/2011, and ISO certifications. The company operates modern production facilities and has supplied CPET trays to clients across Europe, the Middle East, and Asia, ensuring stable quality and timely delivery. With advanced equipment, consistent material sourcing, and strong export capability, DASHAN provides airlines, caterers, and food manufacturers with safe, high-performance CPET solutions designed for both extreme heat and freezing applications.
🔹FAQ
1. Why can CPET trays withstand both freezing and oven heating?
CPET’s semi-crystalline structure provides high thermal stability and impact resistance. Its crystals act like a rigid framework, preventing deformation in high heat and brittleness in freezing conditions.
2. What temperature range can CPET trays handle?
CPET trays typically withstand –40°C to +200°C (and up to +220°C depending on formulation), making them suitable for both deep freezing and airline galley ovens.
3. Are CPET trays safe for microwaves and conventional ovens?
Yes. Unlike many plastics, CPET is safe for microwave ovens, steam ovens, and traditional ovens, without melting or releasing harmful substances.
4. Why are CPET trays preferred in airlines?
They maintain structural integrity through freezing–reheating cycles, work with automated sealing equipment, fit standard galley ovens, and meet global food safety regulations.
5. Is CPET recyclable?
CPET belongs to the PET resin family and is technically recyclable. Actual recyclability depends on local recycling infrastructure and sorting capabilities.
6. How are CPET trays manufactured?
They are produced through extrusion + thermoforming, where controlled heating and cooling create a semi-crystalline structure responsible for the material’s high heat resistance.
7. Can CPET trays be used for meals other than airline catering?
Yes. They are widely used in ready meals, frozen foods, hospital meals, railway catering, and meal-prep applications.
Conclusion
CPET airline trays are engineering marvels designed to withstand some of the most extreme temperature environments in the foodservice world. Their crystallized structure allows them to maintain rigidity at 200°C in ovens while staying tough and impact-resistant at –40°C in deep-freeze conditions. This combination of thermal performance, safety, durability, and compatibility with automated airline operations makes CPET the gold standard material for in-flight catering.
From a scientific perspective, CPET’s success comes from its semi-crystalline molecular structure, precise manufacturing controls, and balanced mechanical properties. From a practical perspective, it solves real-world challenges related to food safety, transportation, handling, storage, and reheating.
As airlines and food producers continue to push for efficiency and safety, CPET remains one of the few materials capable of meeting all requirements—making it indispensable in global catering and frozen food production.
References
-
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) – Food Contact Materials
https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/food-contact-materials -
U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) – Food Contact Substances
https://www.fda.gov/food/food-ingredients-packaging/food-contact-substances-fcs -
PlasticsEurope – PET Material Information
https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/pet/ -
IATA – Catering Quality and Safety Guidelines
https://www.iata.org/en/programs/catering/ -
PETRA – PET Resin Technical Data
https://www.petresin.org/news_and_reports.asp
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.





