Introduction
Polypropylene (PP) has emerged as one of the most commonly used materials in the packaging industry, known for its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. As consumers and businesses continue to prioritize sustainability and functionality, PP has proven to be a reliable option across various sectors, from food packaging to medical supplies. This article delves into the key benefits of using PP for packaging, highlighting its physical properties, environmental impact, and commercial advantages, with a focus on its growing adoption in the packaging market.
1. What is Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer produced through the polymerization of propylene monomers. It is a versatile and affordable material, used extensively for packaging, especially in products requiring flexibility, lightweight designs, and cost-efficient manufacturing processes. PP can be molded into rigid containers, flexible films, and a variety of other forms to suit different applications.
1.1 Chemical Structure and Properties
PP’s molecular structure consists of long hydrocarbon chains, which provide it with several distinct characteristics:
-
Crystalline Structure: This gives PP its high strength and rigidity while maintaining a relatively low density.
-
Thermal Resistance: PP has a high melting point compared to other plastics, making it ideal for products exposed to heat.
-
Resistance to Chemicals: PP does not react easily with many acids, bases, or solvents, which makes it suitable for chemical-resistant packaging.
These properties make PP a highly durable and reliable material for packaging.

2. Key Advantages of Using PP for Packaging
2.1 Durability and Strength
PP offers an optimal balance of strength and flexibility, ensuring that packaged products remain intact throughout their lifecycle. Its ability to resist deformation under stress and strain makes it an ideal choice for heavy-duty packaging. Whether it’s packaging bulk food items or electronics, PP maintains its integrity in demanding environments.
-
Impact Resistance: Unlike other materials like PET, PP has superior impact resistance, which reduces the risk of damage during transportation or storage.
-
Tensile Strength: PP maintains excellent tensile strength even under high pressure, reducing the likelihood of packaging failure.
This makes PP especially useful for packaging products that require protection from external damage, such as fragile foods or medical devices.
2.2 Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most attractive aspects of PP is its affordability. The material is relatively inexpensive compared to alternatives like CPET, PLA, and PET, allowing businesses to save significantly on production costs while still providing high-quality packaging. Moreover, PP’s lightweight nature reduces shipping and storage costs, contributing to overall cost savings.
2.3 Lightweight and Space-Efficient
The lightweight property of PP offers multiple advantages:
-
Reduced Shipping Costs: The lightweight nature of PP helps lower transportation expenses by reducing the weight of packaged products.
-
Space Efficiency: PP’s strength-to-weight ratio allows for space-efficient packaging designs that can help businesses save on storage costs. This is especially important in industries such as foodservice and retail, where shelf space is limited.
2.4 Chemical and Moisture Resistance
PP’s ability to resist chemical corrosion and moisture makes it highly suitable for packaging goods that are exposed to various environmental conditions.
-
Chemical Resistance: PP is impervious to many substances like oils, acids, and bases, making it a go-to choice for food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
-
Moisture Resistance: PP prevents moisture from seeping into packaged products, which is crucial for products like snacks, frozen foods, and fresh produce that require protection from humidity.
2.5 Versatility in Design and Customization
PP can be easily molded into a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and styles. This makes it an extremely flexible material that can be used in numerous packaging formats, such as:
-
Rigid containers: For ready-to-eat meals, frozen foods, and deli items.
-
Flexible films: For snacks, candy bars, and consumer goods.
-
Lids, closures, and seals: Often used to enhance product security and convenience.
This design flexibility allows for innovative packaging solutions that can meet specific branding, functional, and aesthetic requirements.

3. PP in Food Packaging
PP’s contribution to the food packaging sector is substantial, offering numerous advantages in preserving the quality of food products. Its durability, resistance to chemicals, and heat tolerance make it a popular choice in the food industry.
3.1 Food Safety Standards
PP is recognized as a safe material for food contact by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EFSA. It meets strict food safety regulations, ensuring that food remains uncontaminated during storage, handling, and transportation.
-
Non-Toxicity: PP is non-toxic, ensuring that no harmful chemicals leach into the food, even when exposed to high temperatures.
-
Bacterial Resistance: Its resistance to bacterial growth makes PP a hygienic option for packaging perishable foods such as dairy products and meats.
3.2 Preservation of Freshness
PP packaging helps preserve the freshness and quality of food items by acting as a barrier to moisture, oxygen, and light. This is especially critical for perishable goods, such as:
-
Fresh fruits and vegetables
-
Deli meats and cheeses
-
Frozen meals
By protecting food from external contaminants and providing a longer shelf life, PP helps minimize food waste and maintain quality.
3.3 Microwave and Freezer Safe
PP is microwave safe, allowing consumers to reheat food in the packaging without worry. Additionally, PP’s freezer resistance ensures that it remains stable and intact when storing food at low temperatures, making it ideal for frozen meal packaging.

4. Environmental Impact of PP Packaging
As sustainability becomes a core focus for industries worldwide, PP is often praised for its environmentally friendly attributes. While not biodegradable, PP is recyclable, offering a pathway to reduce plastic waste.
4.1 Recyclability and Waste Reduction
PP is one of the most commonly recycled plastics, with many facilities equipped to handle its disposal. It can be reprocessed into new products, such as:
-
Recycled containers
-
Textile fibers for carpets or clothing
-
Industrial parts
By recycling PP, businesses can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable packaging cycle.
4.2 Lower Environmental Impact Compared to Other Plastics
PP has a lower environmental impact in terms of energy consumption during production when compared to PET and PVC. Additionally, PP is less harmful to the environment during disposal compared to materials that release harmful chemicals when burned or discarded.
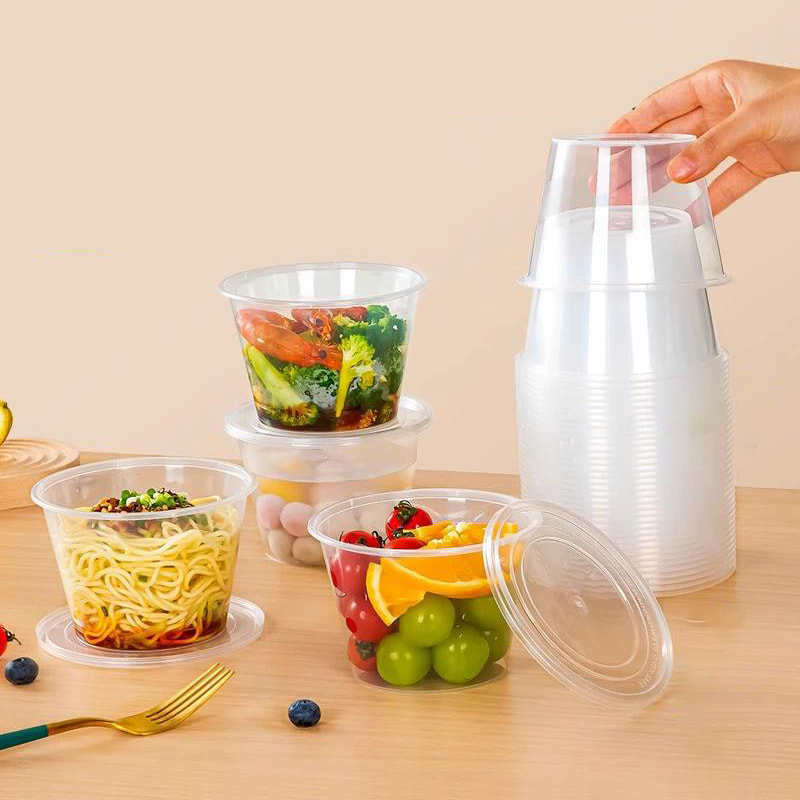

5. PP in Medical and Pharmaceutical Packaging
PP is also widely used in medical packaging due to its high sterilization capabilities and protective qualities.
5.1 Sterilization and Safety
PP is highly resistant to chemicals and can withstand autoclaving or steam sterilization, which is essential for medical products like surgical instruments, medical devices, and pharmaceutical containers.
5.2 Protective Barrier for Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, PP is often used to package items such as pills, tablets, and liquids due to its moisture-resistant properties and ability to protect sensitive contents from environmental factors like light and oxygen.

6. FAQs about PP Packaging
Q1: Is PP biodegradable?
PP is not inherently biodegradable; however, it is recyclable, which makes it more environmentally friendly than non-recyclable plastics.
Q2: Can PP be used for hot food packaging?
Yes, PP is heat-resistant and can be used for packaging hot food, such as microwavable meals, without the risk of melting or compromising the quality of the food.
Q3: Is PP safe for food packaging?
Yes, PP is recognized as safe for food contact by regulatory authorities like the FDA and EFSA, ensuring that it poses no threat to food quality or consumer health.
Q4: How does PP compare to PET in food packaging?
While PET is often preferred for beverages and transparent packaging, PP is more cost-effective, heat-resistant, and versatile for a wider range of packaging, particularly in rigid containers and food wraps.
7. Conclusion
Polypropylene (PP) is a superior material for packaging, offering numerous advantages ranging from durability and cost-effectiveness to recyclability and food safety. Its diverse range of applications across various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, positions it as one of the most versatile and reliable packaging solutions available today. As sustainability becomes an increasing priority, PP continues to evolve, meeting modern environmental challenges while supporting global packaging needs.
References
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.