Quick Summary:
Turkey’s recent decision to allow recycled plastics (rPET) for food packaging marks a significant step toward sustainable packaging solutions globally. This move aligns with the growing trend of using recycled materials in food packaging to reduce plastic waste and carbon emissions. In this article, we compare the three major materials used in food packaging—PET, PLA, and rPET—analyzing their recycling rates, environmental impact, and market popularity. PET remains the most widely used material, while rPET is gaining traction due to its eco-friendly benefits. PLA, though biodegradable, is less widely adopted due to its limitations in temperature resistance and composting requirements. As the demand for sustainable packaging grows, the adoption of recycled and biodegradable materials will continue to rise.
Introduction: A Step Forward in Sustainable Packaging – Turkey’s Policy on Recycled Plastics
In a groundbreaking move, Turkey has recently approved the use of recycled plastics for food contact materials, specifically rPET (recycled polyethylene terephthalate). This new policy from Turkey’s Turkish Food Codex opens the door for greater adoption of recycled plastics in the food packaging sector, as long as these materials meet stringent safety and quality standards.
This decision is significant as it aligns with the global push towards sustainability and circular economies, especially in the face of growing plastic waste and environmental concerns. Recycled plastics, like rPET, offer an eco-friendly solution by reducing the need for virgin plastic production, which in turn lowers carbon emissions and conserves valuable resources.
As more countries adopt similar policies, the food packaging industry is facing a major shift towards sustainable materials. This development raises an important question: Which materials are best for food packaging—PET, PLA, or rPET—and what are the preferences among consumers and manufacturers?
In this blog, we will delve into the global recycling rates, examine the popularity of PET, PLA, and rPET in food packaging, and analyze the key characteristics of each material. By using data and insights from the packaging industry, we will explore which material is leading the market and why.

Section 1: The Global Recycling Landscape and the Rise of rPET
1.1 The Global Recycling Rate Crisis
Despite significant strides in recycling efforts, the global recycling rate for plastics remains alarmingly low. According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, only about 9% of plastics are successfully recycled. While some materials, like PET, have a higher recycling rate, others like PLA face challenges due to their biodegradability and the need for specific composting conditions.
| Region | Recycling Rate |
|---|---|
| Europe | 32% |
| North America | 25% |
| Asia | 5% |
| Rest of World | 6% |
This stark contrast highlights the global recycling challenges we face and the urgent need for innovative solutions. The decision to allow rPET in food contact materials is part of a broader global trend towards making better use of post-consumer waste. Countries like Turkey are leading the way in encouraging the use of recycled plastics to reduce landfill waste, curb pollution, and meet sustainability targets.

1.2 The Role of rPET in the Circular Economy
Recycling plastics, particularly PET, is a key component of the circular economy. rPET is produced by reprocessing used PET products, such as bottles and containers, into new food-safe packaging. This not only reduces plastic waste but also conserves raw materials and energy that would otherwise be used in the production of virgin plastic.
With Turkey’s new approval for rPET in food packaging, more companies will likely follow suit, using recycled materials that meet food safety standards. This marks an exciting shift towards sustainable packaging solutions that can support a greener future.
Section 2: PET, PLA, and rPET – Characteristics and Market Trends
2.1 PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
PET is one of the most commonly used materials for food packaging due to its strength, durability, and versatility. It is widely used in beverage bottles, food containers, and even in flexible films.
Key Properties of PET:
-
Highly Recyclable: PET is one of the most recycled plastics in the world, making it an attractive option for eco-conscious brands and consumers.
-
Durability: PET is strong, lightweight, and resistant to impact and heat.
-
Clarity: PET is transparent, making it ideal for showcasing food products and beverages.
Global Usage in Food Packaging:
-
Beverage Packaging: PET is the primary material for bottled beverages, including water, soft drinks, and juices.
-
Packaging Films: PET is used in the packaging of snacks, confectionery, and other food products that require a high degree of transparency.
| Material | Market Share | Key Uses |
|---|---|---|
| PET | 45% | Bottles, Films |
| PLA | 10% | Cups, Containers |
| rPET | 15% | Recycled Bottles, Trays |

2.2 PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is a biodegradable plastic made from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane. It is often used in foodservice packaging, including takeaway containers, cups, and trays, particularly for cold foods and beverages.
Key Properties of PLA:
-
Biodegradable: PLA is compostable in industrial composting facilities, making it a popular choice for environmentally-conscious consumers.
-
Sustainability: PLA is made from renewable resources, which contributes to a lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based plastics.
-
Temperature Sensitivity: PLA is not suitable for hot foods or beverages because it softens at higher temperatures.
Global Usage in Food Packaging:
-
Cold Food & Beverages: PLA is commonly used for ice cream tubs, cold drinks, and salads.
-
Takeaway Packaging: PLA containers are used widely in the foodservice industry for takeout boxes and salad bowls.

2.3 rPET (Recycled PET)
rPET is made from post-consumer recycled PET, offering a sustainable alternative to virgin PET. It retains most of the desirable properties of PET while reducing the environmental impact associated with plastic production.
Key Properties of rPET:
-
Recycled Material: rPET helps close the loop in the plastic lifecycle, making it an important material for a circular economy.
-
Durability: rPET maintains the same strength, clarity, and performance as virgin PET, making it a suitable material for food packaging.
-
Food Safety: rPET is safe for food contact, provided it meets strict regulatory standards.
Global Usage in Food Packaging:
-
Beverages: rPET is increasingly used in beverage packaging, especially for water and carbonated drinks.
-
Food Trays: rPET is used in the production of trays for fresh produce, ready-to-eat meals, and other food products.

Section 3: Material Comparison – PET, PLA, and rPET
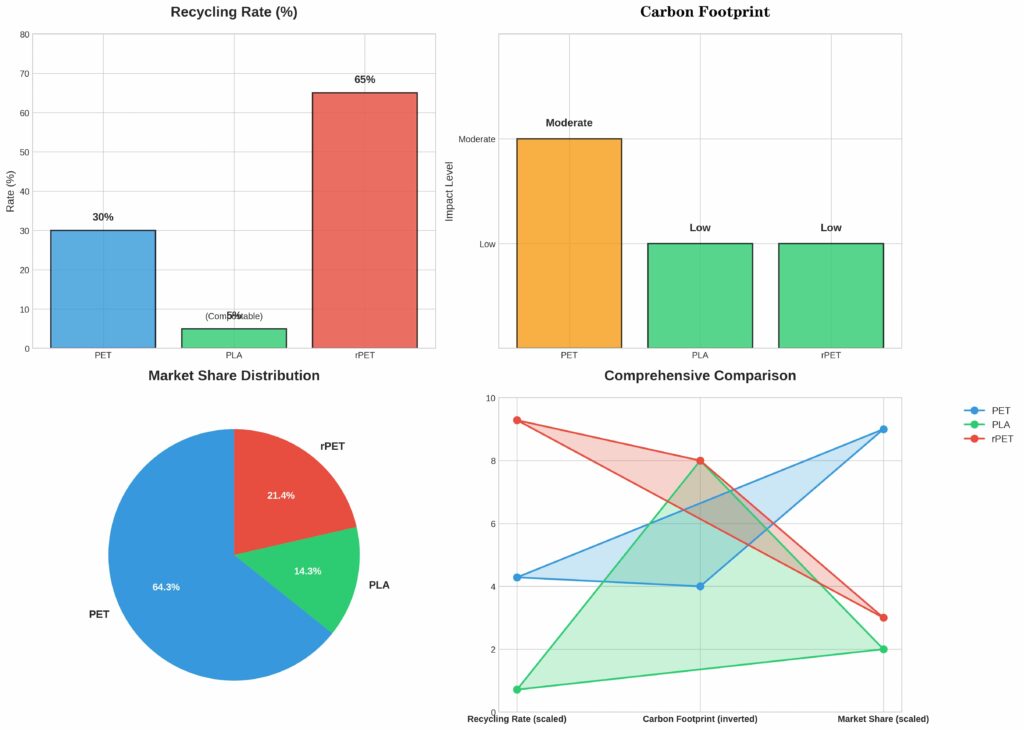
This section provides a comparative analysis of PET, PLA, and rPET based on their sustainability, market demand, and environmental impact.
| Material | Recycling Rate | Carbon Footprint | Market Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 30% | Moderate | 45% |
| PLA | Low (Compostable) | Low | 10% |
| rPET | 60-70% | Low | 15% |
3.1 Sustainability
-
PET is highly recyclable, but the process of recycling virgin PET into new products is energy-intensive.
-
PLA is a biodegradable material made from renewable resources, making it a more sustainable option for certain applications.
-
rPET is highly sustainable because it is made from recycled materials, thus reducing the need for virgin plastic production.
3.2 Consumer Preference and Market Trends
-
PET remains the most popular material in the food packaging market, particularly in beverages and packaged snacks. It has a larger market share due to its strength, recyclability, and versatility.
-
PLA has a smaller market share but is gaining popularity in eco-conscious markets, particularly for cold beverages and takeaway packaging.
-
rPET is increasingly popular as consumers and brands become more aware of sustainability. It is particularly favored by brands aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and environmental impact.
Section 4: The Most Popular Food Packaging Material – Which One Takes the Lead?
Based on current market trends, PET continues to dominate the food packaging industry due to its durability, cost-effectiveness, and widespread recyclability. However, rPET is rapidly gaining ground, particularly in the beverage industry, as companies strive to meet sustainability targets. PLA, while an excellent choice for certain cold food applications, still faces limitations in terms of heat resistance and widespread recycling infrastructure.
In terms of food packaging, PET is still the most widely used material. However, with more countries, including Turkey, adopting policies that promote rPET and sustainable packaging, it is likely that rPET will continue to gain market share, especially as consumers demand more eco-friendly options.
Conclusion: The Future of Food Packaging Materials
The global shift toward recycled plastics and sustainable materials like rPET is gaining momentum. With countries like Turkey leading the way in approving recycled plastics for food packaging, more regions will likely adopt similar policies, further encouraging the use of sustainable materials. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, manufacturers will need to prioritize eco-friendly solutions that reduce plastic waste and conserve natural resources.
DaShan, as a leading provider of sustainable food packaging solutions, is well-positioned to meet these growing demands. By embracing rPET, PLA, and other eco-friendly materials, we can contribute to a more sustainable future while meeting the needs of the food packaging industry.

FAQ Section
-
What is the difference between PET and rPET?
-
PET is virgin plastic, while rPET is recycled PET, reducing the need for new plastic production and offering environmental benefits.
-
-
Is PLA compostable?
-
Yes, PLA is biodegradable and compostable under industrial composting conditions.
-
-
Can rPET be used for hot food packaging?
-
Yes, rPET can be used for hot food packaging as long as it meets food safety standards.
-
-
Which material is best for eco-friendly food packaging?
-
rPET is considered one of the best eco-friendly options as it is made from recycled materials, reducing plastic waste and the need for virgin plastic production.
-
References
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. (2020). The New Plastics Economy: Rethinking the future of plastics. Retrieved from https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org
- World Economic Forum. (2018). The New Plastics Economy: Rethinking the future of plastics and catalysing action. Retrieved from https://www.weforum.org
- European Commission. (2018). A European Strategy for Plastics in a Circular Economy. European Union. Retrieved from https://ec.europa.eu
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.