Introduction: The Importance of Sustainable Packaging
Packaging plays a crucial role in the modern world, providing protection, convenience, and branding for products. However, the environmental impact of packaging has become a growing concern in recent years. Sustainable packaging has emerged as a solution to mitigate the harmful effects of traditional packaging materials, such as plastics, which contribute significantly to pollution and resource depletion.
Sustainable packaging refers to materials that have minimal impact on the environment throughout their lifecycle. This includes the use of recyclable, biodegradable, or renewable materials, as well as designing packaging to reduce waste, increase reusability, and lower carbon emissions.
As consumer awareness about environmental issues increases, there is a growing demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions. Governments, brands, and manufacturers are under pressure to develop and adopt sustainable packaging alternatives. This shift is driven by several factors, including the increasing volume of waste, regulatory changes, and consumer preferences for environmentally responsible products.
In this article, we will explore the challenges and opportunities surrounding sustainable packaging, examine how companies are adapting to these changes, and discuss the future of packaging in a sustainable world.

Challenges Facing the Widespread Adoption of Eco-Friendly Packaging
While sustainable packaging offers significant environmental benefits, its widespread adoption faces several challenges. These barriers are primarily related to cost, technological limitations, consumer behavior, and supply chain constraints.
1. Cost Challenges
One of the most significant obstacles to the adoption of sustainable packaging is the cost. Sustainable materials, such as bioplastics, biodegradable plastics, and recycled materials, often come at a premium compared to traditional packaging materials like petroleum-based plastics. The high production costs associated with these materials are passed onto manufacturers, which ultimately results in higher prices for consumers.
-
Material Costs: The cost of raw materials for sustainable packaging is often higher due to the complex processes involved in sourcing and manufacturing eco-friendly materials. For instance, biodegradable plastics made from renewable sources such as cornstarch or sugarcane are more expensive than conventional plastic.
-
Production Costs: Sustainable packaging may require specialized production processes, which can be less efficient and more costly. This includes costs for equipment, labor, and energy used to create these packaging solutions.
-
Scale Limitations: Many eco-friendly materials are not yet produced at scale, making them more expensive to obtain. As demand for sustainable packaging grows, economies of scale will likely drive down prices, but until then, the cost barrier remains.
-
Consumer Price Sensitivity: Many consumers are unwilling to pay a premium for environmentally friendly packaging, especially when the benefits are not immediately apparent. This is particularly true in price-sensitive markets where cost is a significant consideration for purchasing decisions.
2. Technological Challenges
The technological challenges associated with sustainable packaging are primarily related to the material properties of eco-friendly options and the infrastructure required to support them.
-
Lack of Infrastructure for Recycling: In many regions, the infrastructure to process and recycle eco-friendly materials is insufficient or nonexistent. For example, biodegradable plastics may not break down properly in landfill environments if they are not processed in specific composting facilities.
-
Material Limitations: While some eco-friendly materials offer environmental benefits, they may not meet the performance standards required for certain products. For example, some biodegradable materials may not provide the necessary barrier properties for food packaging, leading to spoilage and waste.
-
Inconsistent Standards: There is currently no universal standard for sustainable packaging. Different regions and organizations may have varying definitions of what constitutes “eco-friendly” or “biodegradable,” leading to confusion in the market. Consumers and manufacturers alike may find it challenging to navigate these inconsistencies.
3. Consumer Behavior and Awareness
Despite increasing awareness of environmental issues, many consumers still prioritize convenience and affordability over sustainability. This poses a challenge for brands trying to shift towards sustainable packaging.
-
Awareness Gap: Many consumers are not fully aware of the environmental impact of their packaging choices. Even when they are aware, they may not understand the full lifecycle of packaging materials, such as the energy used in production or the challenges associated with recycling.
-
Convenience vs. Sustainability: Consumers often choose products based on convenience. For example, single-use plastics remain popular because they are lightweight, inexpensive, and readily available. Sustainable alternatives, such as reusable containers or compostable packaging, may not offer the same level of convenience, which can deter consumers from making environmentally conscious choices.
-
Misconceptions about Biodegradable and Recyclable Materials: Many consumers mistakenly believe that all “green” packaging is biodegradable or recyclable when, in reality, this is not always the case. Some biodegradable plastics may only break down under specific conditions, and many materials are not easily recyclable in existing systems.
4. Supply Chain and Logistics
The supply chain for sustainable packaging can be more complex than traditional packaging systems. This complexity often leads to higher costs and logistical challenges.
-
Supply Chain Complexities: Sourcing sustainable materials can be more difficult and expensive, especially if they are produced in limited quantities. Companies may struggle to find reliable suppliers for eco-friendly materials, and transportation costs can increase if materials need to be sourced from distant locations.
-
Storage and Handling Issues: Some sustainable materials are less durable and more sensitive to temperature and humidity than traditional materials. This can create challenges in storage, transportation, and shelf life, leading to increased costs and potential spoilage.
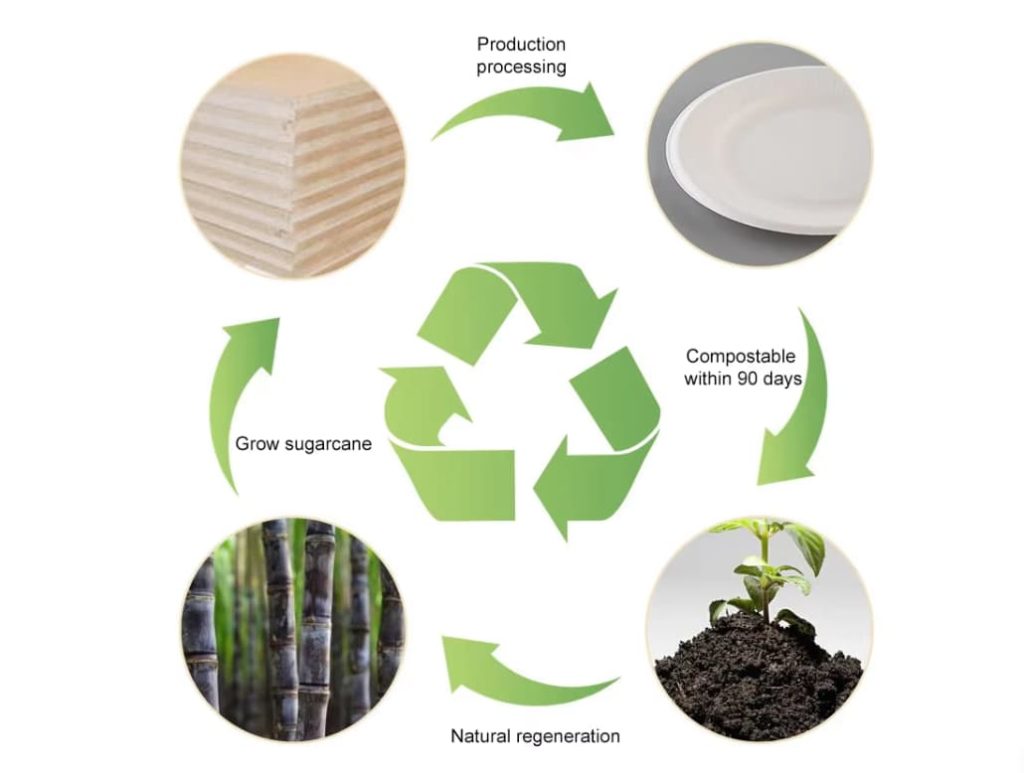

Opportunities in Eco-Friendly Packaging
While there are significant challenges to adopting sustainable packaging, there are also many opportunities for growth and innovation. These opportunities arise from regulatory changes, consumer demand, technological advancements, and the potential for business growth.
1. Regulatory Pressures and Opportunities
Governments around the world are implementing stricter regulations on packaging waste, particularly single-use plastics. These regulations present an opportunity for companies to adopt sustainable packaging solutions and stay ahead of regulatory requirements.
-
Government Policies: Many countries have introduced laws aimed at reducing plastic waste and encouraging the use of sustainable packaging. For example, the European Union’s Plastics Strategy calls for a significant reduction in single-use plastics and encourages the use of recyclable and biodegradable materials.
-
Tax Incentives and Subsidies: Governments may provide tax incentives, grants, or subsidies to companies that adopt sustainable packaging practices. This helps offset some of the costs associated with switching to eco-friendly packaging.
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Companies that adopt sustainable packaging practices can improve their CSR efforts and demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship. This can help enhance their brand image and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
2. Consumer Demand for Sustainable Products
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is increasing demand for products with sustainable packaging.
-
Eco-Conscious Consumers: A growing number of consumers prefer products that use eco-friendly packaging. This trend is particularly strong in industries like food and beverage, beauty, and consumer goods, where packaging plays a significant role in brand perception.
-
Brand Differentiation: Companies that adopt sustainable packaging can differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace. Consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for products that align with their values, including environmental sustainability.
-
Case Studies: Several major companies have successfully integrated sustainable packaging into their products. For example, Coca-Cola has committed to using 50% recycled content in its plastic bottles by 2030, while Unilever has set a goal to make all of its plastic packaging recyclable, reusable, or compostable by 2025.
3. Innovation in Materials and Technology
Innovation in materials and packaging technologies is opening up new possibilities for sustainable packaging.
-
Breakthroughs in Biodegradable Materials: Advances in bioplastics, such as PLA (polylactic acid), PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates), and other plant-based plastics, offer promising alternatives to traditional plastic packaging. These materials are biodegradable and compostable, reducing their environmental impact.
-
Recyclable and Reusable Materials: RPET (recycled polyethylene terephthalate) and other recycled materials are becoming more popular in packaging. These materials can be recycled multiple times, reducing the need for virgin plastic and minimizing waste.
-
Technological Advancements in Packaging Machinery: New packaging technologies allow for more efficient use of materials and better performance of eco-friendly packaging. This includes innovations in sealing, labeling, and production processes that improve sustainability.
4. Business Opportunities and Market Growth
The demand for sustainable packaging is creating new business opportunities in the packaging industry. Companies that innovate and invest in sustainable packaging solutions are well-positioned to grow in the coming years.
-
Investment in Green Packaging Companies: The growing demand for eco-friendly packaging has led to a surge in investment in companies that specialize in sustainable packaging solutions. This includes companies that produce biodegradable materials, develop new recycling technologies, and offer packaging design services.
-
Product Customization and Branding: Packaging is a powerful tool for brand differentiation. Companies can use eco-friendly packaging to convey their sustainability values and appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.

Solutions to Overcome the Barriers to Eco-Friendly Packaging
To overcome the challenges associated with sustainable packaging, companies, governments, and consumers must work together to implement effective solutions.
1. Cost Reduction Strategies
-
Economies of Scale: As demand for sustainable packaging increases, production scales up, leading to cost reductions. Larger production volumes allow manufacturers to spread the costs of R&D, sourcing, and production across more units, making eco-friendly packaging more affordable.
-
Technological Innovation: Continued advancements in material science and manufacturing technologies will help reduce the costs of sustainable packaging. Companies investing in R&D can develop cheaper alternatives that perform just as well as traditional packaging.
-
Collaborative Efforts: Partnerships between packaging manufacturers, brands, and governments can help reduce the costs associated with sustainable packaging development. Collaborative efforts can lead to shared resources, better economies of scale, and more efficient production methods.
2. Technological Advancements
-
Improved Recycling Technology: Investment in better recycling infrastructure and technology is essential to making sustainable packaging more widely accepted. This includes developing more efficient systems for sorting and processing biodegradable and recyclable materials.
-
Material Innovation: Ongoing research into alternative materials that mimic the properties of traditional packaging while being more sustainable will help overcome many of the technological limitations associated with eco-friendly packaging.
3. Consumer Education and Awareness
-
Educational Campaigns: Governments, NGOs, and companies can help raise awareness about the environmental impact of packaging and the benefits of choosing eco-friendly options. Educational campaigns can also address common misconceptions about biodegradable and recyclable materials.
-
Transparency in Labeling: Clear and accurate labeling on products and packaging can help consumers make more informed decisions. Transparency in labeling will also help clarify which materials are truly sustainable and which are not.
4. Supply Chain and Logistics Solutions
-
Sustainable Supply Chain Practices: Companies can work with suppliers to source raw materials sustainably, improve production efficiencies, and reduce waste throughout their supply chains.
-
Partnerships with Recycling Organizations: Brands can collaborate with recycling companies and implement take-back programs to increase the recyclability of packaging materials.
Conclusion: The Future of Sustainable Packaging
Sustainable packaging is no longer a niche trend but a critical aspect of modern business operations. As the global demand for eco-friendly packaging continues to grow, companies must overcome the challenges associated with cost, technology, consumer behavior, and supply chains. However, the opportunities presented by sustainable packaging—ranging from regulatory compliance to increased consumer loyalty—are immense.
By embracing innovation, educating consumers, and collaborating across industries, we can overcome the barriers to sustainable packaging and create a more sustainable future for packaging and the planet.

FAQ
-
What is sustainable packaging?
Sustainable packaging refers to materials that have a minimal impact on the environment throughout their lifecycle. This includes using recyclable, biodegradable, or renewable resources. -
Why is eco-friendly packaging important?
Eco-friendly packaging helps reduce environmental waste, carbon footprint, and pollution. It supports the global move towards sustainability and helps companies comply with environmental regulations. -
What are the main challenges in adopting sustainable packaging?
The key challenges include high production costs, limited availability of materials, technological limitations, and consumer habits that prioritize convenience over sustainability. -
How can companies overcome the costs of sustainable packaging?
Companies can reduce costs by investing in innovative technologies, collaborating with packaging suppliers, optimizing production processes, and focusing on long-term cost savings through eco-friendly practices. -
What are some examples of successful eco-friendly packaging?
Examples include biodegradable PLA packaging, paper-based materials for food products, and reusable packaging solutions. Companies like Patagonia, Coca-Cola, and Unilever have successfully implemented these solutions. -
Is sustainable packaging more expensive than traditional packaging?
In most cases, sustainable packaging is initially more expensive due to the cost of research, development, and sourcing of eco-friendly materials. However, in the long term, it can lead to cost savings due to lower waste management costs and improved brand image. -
How does sustainable packaging affect consumer behavior?
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they prefer brands that offer eco-friendly packaging. This shift in consumer behavior can help drive sales and improve brand loyalty. -
Can all packaging materials be made sustainable?
While many materials, like plastic, can be made more sustainable, not all packaging materials are easy to recycle or biodegradable. Ongoing research is essential to develop materials that meet sustainability goals. -
What role do governments play in promoting sustainable packaging?
Governments can promote sustainable packaging by enacting policies that encourage recycling, reduce waste, and provide incentives for companies that adopt eco-friendly materials and practices.
References
-
Smith, J. (2023). Sustainable Packaging in the Modern World. Journal of Environmental Studies, 18(4), 234-248.
-
Green, A., & Lee, D. (2022). The Future of Packaging: Trends in Sustainability. Eco-Packaging Solutions, 12(1), 56-72.
-
Thompson, R. (2021). Challenges in the Recycling of Eco-Friendly Materials. International Packaging Journal, 15(3), 145-160.
-
Patel, K., & Johnson, E. (2022). Packaging Innovations for Sustainability. Packaging Tech Review, 8(2), 112-128.
-
United Nations Environment Programme (2022). The Role of Packaging in Global Waste Management. Retrieved from www.unep.org.
-
Green Packaging Initiative. (2021). Eco-friendly Packaging Trends and Consumer Behavior. Global Packaging Report, 9(2), 90-103.
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.