Quick Summary
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) plastic cups are among the most trusted packaging options for the global foodservice and beverage industries. Their strength, clarity, and recyclability make them ideal for iced drinks, smoothies, milk teas, and ready-to-drink products. This comprehensive guide explores how PET cups are made, how to select the right type for your business, and how they support global sustainability goals.
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of modern foodservice, packaging plays a critical role in shaping the consumer experience. For cafes, beverage brands, and quick-service restaurants, the right disposable cup is not merely a container — it’s an extension of brand identity, product protection, and environmental responsibility.
Among available materials, PET plastic cups stand out as a reliable and visually appealing option. They combine crystal clarity, excellent physical performance, and compatibility with global recycling systems. From the bustling streets of Tokyo to European supermarkets and American drive-thrus, PET cups have become synonymous with quality beverage presentation.
According to Packaging Europe 2024, global consumption of PET cups has risen by 28% over the last five years, primarily due to consumer preference for clear, safe, and recyclable packaging.
1. What Makes PET Plastic Unique

PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is a thermoplastic polymer in the polyester family. It is composed of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, forming a highly symmetrical molecular structure. This symmetry gives PET exceptional physical and chemical properties that outperform many alternative materials like PP, PS, or PLA.
1.1 Core Physical and Mechanical Properties
-
High Impact Strength: PET cups can withstand impacts 3–5 times greater than traditional plastic films.
-
Thermal Resistance: They remain stable from -70°C to 120°C, tolerating both refrigerated and mildly heated applications.
-
Barrier Protection: Excellent resistance to oxygen, CO₂, and moisture maintains beverage freshness and carbonation.
-
Transparency and Gloss: A naturally clear polymer with a light transmittance of over 90%, ideal for showcasing beverages.
-
Chemical Resistance: Withstands oils, mild acids, and alcohol without deformation.
-
Dimensional Stability: Retains shape under pressure, preventing lid leakage or warping.
1.2 Hygiene and Safety
PET is inherently non-toxic and odorless. It meets FDA (U.S.), LFGB (Germany), and EU Regulation No. 10/2011 food-contact requirements, making it one of the safest plastics in direct food applications. Its surface does not promote bacterial growth, a vital feature for single-use beverage packaging.
2. Common Causes of PET Cup Discoloration and Quality Defects
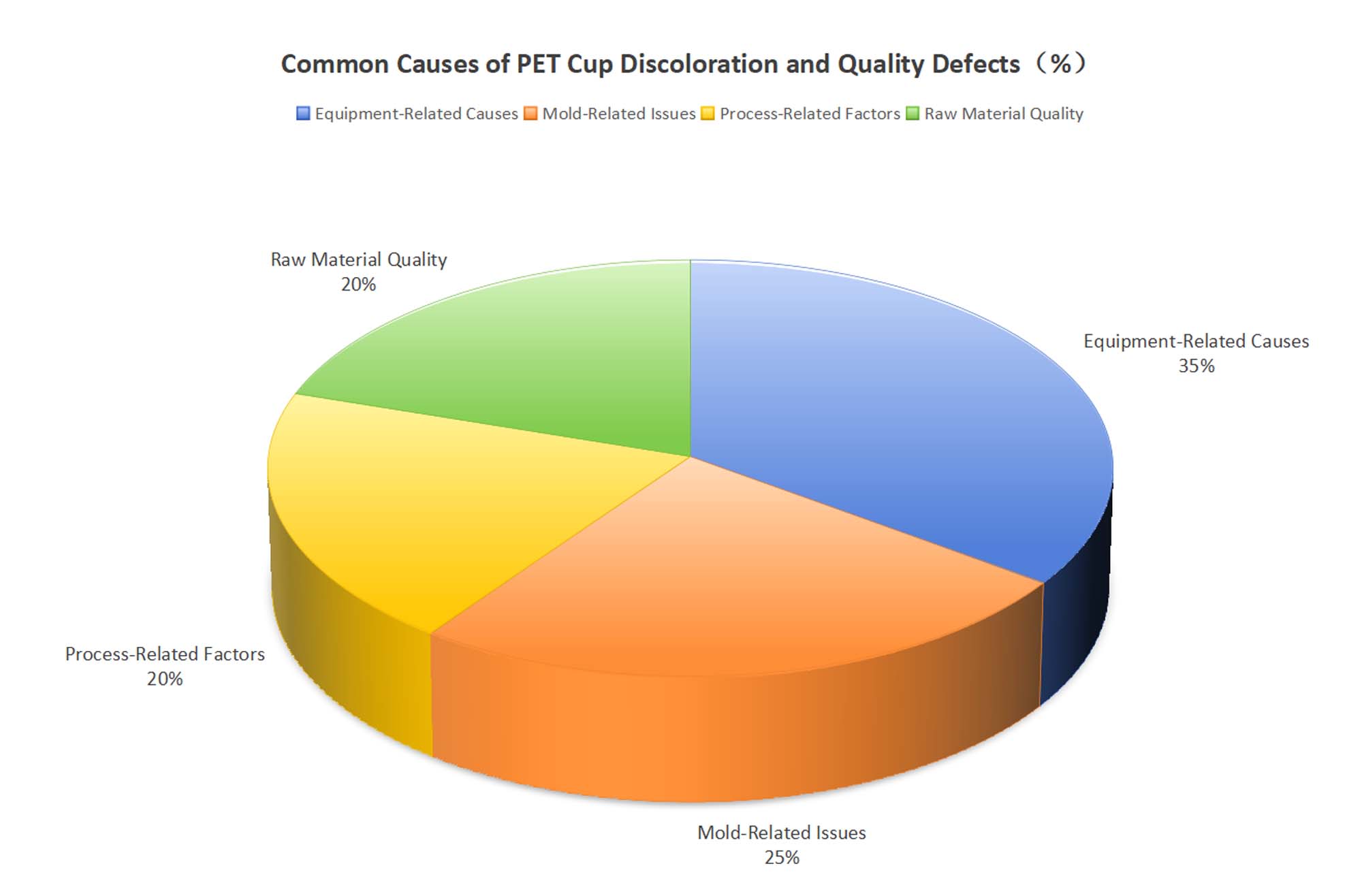
Despite its excellent clarity, improper production or handling can lead to yellowing, haziness, or warping. Recognizing these issues helps buyers assess supplier quality.
2.1 Equipment-Related Causes
-
Contamination in barrels or feeders leads to degraded resin.
-
Malfunctioning thermocouples or heating zones cause overheating.
-
Metal particles inside screws or cylinders create friction-induced burn marks.
2.2 Mold-Related Issues
-
Poor ventilation traps hot air, causing oxidation.
-
Small gates or nozzles increase shear rate and discolor resin.
-
Overuse of release agents contaminates the polymer surface.
2.3 Process-Related Factors
-
Excessive screw rotation or back pressure raises melt temperature.
-
Improper cooling times can cause uneven shrinkage or opacity.
2.4 Raw Material Quality
-
Moisture in PET resin promotes hydrolysis during melting, breaking molecular chains.
-
Poor-quality additives or masterbatches decompose under heat.
Expert Tip — Dr. Hiroshi Tanaka, Tokyo Institute of Packaging Engineering:
3. How PET Plastic Cups Are Made: The Thermoforming Process
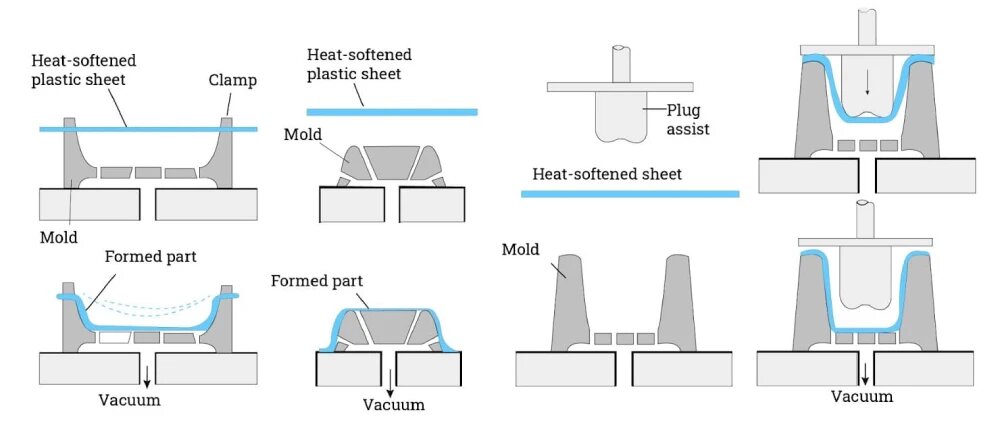
While injection molding is widely used for rigid plastic components, thermoforming dominates PET cup manufacturing due to its cost-efficiency, flexibility, and scalability.
3.1 Step-by-Step Process
-
Extrusion: PET resin pellets are melted and extruded into thin sheets.
-
Sheet Heating: The PET sheet passes through infrared heaters until it reaches ~110–120°C.
-
Forming: Heated sheets are stretched over cup molds using vacuum and air pressure.
-
Cooling: The formed cups are cooled rapidly to lock in clarity and rigidity.
-
Trimming: A precision die cuts each cup to its final rim diameter.
-
Stacking and Packaging: Cups are stacked, quality-checked, and packaged for export.
3.2 Advantages of Thermoforming
-
Consistent wall thickness and shape precision.
-
Faster cycle times than injection molding.
-
Lower tooling cost for multiple cup sizes.
-
Supports recycled PET (rPET) blending.
3.3 Evolving Manufacturing Technology
Recent advancements include multi-layer thermoforming, allowing integration of functional barriers (like UV-blocking or anti-fog layers). This improves performance while maintaining recyclability.
4. Choosing the Right PET Cup for Your Business
Selecting the ideal PET cup involves matching material, design, and function to your specific market needs.
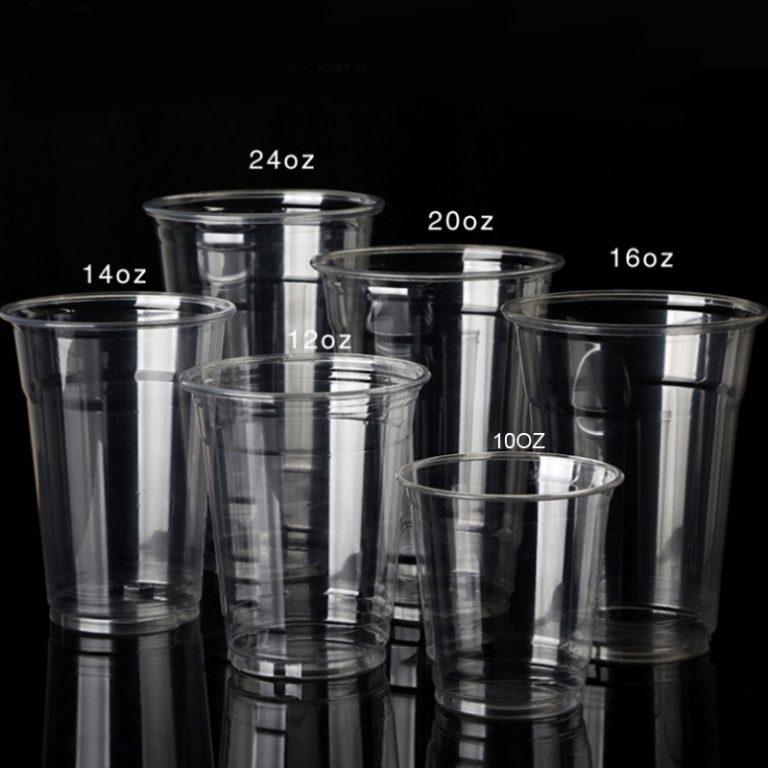

4.1 Key Selection Criteria
-
Volume & Dimensions: Commonly 12oz–24oz; ensure fit with cup holders and sealing lids.
-
Wall Thickness: Thicker walls improve rigidity but increase material usage.
-
Lid Compatibility: Choose secure-fitting flat or dome lids (for whipped cream or toppings).
-
Brand Customization: Offset or UV printing for logos; embossing for premium branding.
-
Stackability: Efficient stacking saves logistics costs.
-
Temperature Use: Designed for cold or ambient liquids (avoid >70°C).
4.2 Expert Recommendation
— Dr. Maria Cohen, Senior Materials Scientist, University of Leeds
5. International Quality and Safety Standards
Reputable PET cup suppliers must comply with international safety and quality protocols to ensure traceability and food safety.
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| FDA 21 CFR 177.1630 | Defines PET for food contact in the U.S. |
| EU Regulation No. 10/2011 | Establishes migration limits for plastic materials. |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality management certification for consistency. |
| BRCGS Packaging Standard | Ensures global food packaging hygiene compliance. |
| SGS / Intertek Testing | Confirms migration, odor, and heavy metal safety. |
DASHAN’s Practice:
Every PET cup batch is tested for haze, tensile strength, heat distortion, and migration. Records are archived for traceability, ensuring compliance with major international buyers.
6. Best Practices for Using PET Plastic Cups

6.1 Handling and Storage
-
Store in dry, shaded areas away from UV exposure.
-
Avoid stacking under heavy weight to prevent deformation.
-
Do not expose to heat above 50°C before use.
6.2 Beverage Filling Guidelines
-
Fill only with cold or ambient drinks (e.g., iced tea, smoothies, beer).
-
Avoid direct contact with boiling liquids.
-
Use matching lids and straws for leak-proof performance.
6.3 Recycling and Disposal
Encourage recycling by printing “Please Recycle – PET #1” on cup bases. PET cups can be reprocessed into polyester fibers, new packaging, or rPET sheets — closing the loop.
7. Sustainability and the Future of PET Cups
PET’s recyclability makes it a cornerstone of sustainable packaging. Global initiatives like the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s New Plastics Economy support its circular potential.
7.1 rPET (Recycled PET) Integration
Many brands now use up to 100% rPET to cut carbon emissions.
DASHAN sources certified rPET pellets for thermoforming, ensuring food-grade purity.
7.2 Lightweighting and Carbon Reduction
Modern thermoforming enables thinner yet stronger walls, reducing material use by 10–20% without compromising strength.
7.3 Emerging Bio-PET Innovations
Bio-based PET derived from renewable feedstocks like corn sugar and bio-paraxylene offers similar performance with lower carbon impact.
Case Example – DASHAN Sustainability Initiative:
DASHAN targets carbon-neutral manufacturing by 2030, investing in closed-loop recycling systems and renewable energy use across its PET production lines.
8. Common Problems and Troubleshooting
| Problem | Likely Cause | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Yellowing | Overheating or resin degradation | Lower heating temperature; dry resin properly |
| Cracking | Thin wall or improper stacking | Increase gauge; adjust mold pressure |
| Warping | Poor cooling or uneven heating | Optimize forming temperature |
| Sealing failure | Lid mismatch | Use certified compatible lids |
Expert Insight:
— Prof. Daniel Kim, Korean Institute of Polymer Technology
9. Market Trends and Industry Outlook
According to Grand View Research 2024, the global PET cup market is projected to exceed USD 6.2 billion by 2030, driven by rising demand in cold beverage sectors and sustainability-conscious consumers.
9.1 Regional Insights
-
Asia-Pacific: Fastest-growing due to rising café culture in China, Japan, and Southeast Asia.
-
Europe: Strong regulations push for rPET use.
-
North America: Growth in take-out beverages and branded packaging.
9.2 Competitive Advantage of PET
-
Lower carbon footprint than multi-material composites.
-
Existing recycling infrastructure in over 100 countries.
-
Lightweight for reduced shipping emissions.
Industry Outlook:
The PET market is expected to evolve toward 100% recycled circular systems, with digital traceability (QR-coded materials) ensuring transparency in every stage.
10. DASHAN: Your Trusted Partner in Sustainable PET Cup Manufacturing
PET plastic cups combine high clarity, mechanical strength, and recyclability—making them one of the most balanced and trusted packaging solutions in the global beverage industry. For businesses, proper selection and handling not only enhance product presentation and quality but also strengthen sustainability goals and corporate environmental responsibility.
DASHAN, a professional food packaging manufacturer, brings years of thermoforming expertise, state-of-the-art production facilities, and a rigorous quality control system to every PET product. The company specializes in developing safe, durable, and eco-friendly PET cups that meet international food-grade standards such as FDA, EU, and LFGB.
For OEM and ODM custom PET cup projects, DASHAN provides end-to-end solutions—from design and mold development to thermoforming, printing, branding, and global export logistics. Partnering with leading beverage chains, supermarkets, and packaging distributors across 50+ countries, DASHAN ensures that every cup not only delivers performance but also reflects your brand’s sustainability vision.
— Dr. Laura Mitchell, Senior Sustainability Advisor, Global Packaging Forum
🟦 FAQ
1. What are PET plastic cups made of?
PET cups are made from polyethylene terephthalate, a strong, lightweight, and recyclable plastic known for its clarity and excellent barrier properties. It’s widely used for food-grade packaging due to its safety and performance.
2. Are PET plastic cups safe for hot and cold beverages?
Yes. PET cups can safely handle temperatures between -70°C and 120°C, maintaining their clarity and strength without warping. However, they are not recommended for boiling liquids or microwave use.
3. How does thermoforming affect PET cup quality?
Thermoforming allows PET sheets to be shaped precisely, producing cups with consistent wall thickness and structural stability. It improves visual clarity and minimizes material waste, ensuring both performance and aesthetics.
4. Why do PET cups sometimes turn yellow or discolored?
Discoloration can result from high processing temperatures, contamination, or moisture in raw materials. Proper temperature control, clean equipment, and dry resin help maintain color and transparency during production.
5. How can businesses ensure the quality of PET cups?
Choose suppliers certified by standards such as ISO 9001, FDA, and EU Food Contact Regulations. Reliable manufacturers conduct optical clarity tests, impact resistance checks, and ensure raw material traceability.
6. What environmental advantages do PET cups offer?
PET is fully recyclable and compatible with global recycling systems. When collected and processed correctly, PET cups can be turned into new packaging or textile fibers, supporting a circular economy.
7. How should PET cups be stored and handled?
Store in a cool, dry, and UV-protected environment. Avoid exposure to high temperatures or direct sunlight, which can cause slight deformation or surface dullness over time.
8. What is the difference between PET, PP, and PLA cups?
PET offers superior clarity and impact strength; PP is more heat-resistant; PLA is compostable but less temperature-stable. For visual presentation and recyclability, PET remains the preferred global choice.
9. How does DASHAN ensure PET cup quality and sustainability?
DASHAN follows strict international quality control and environmental management systems, ensuring each PET cup meets global food safety, durability, and recyclability standards.
Conclusion
PET plastic cups combine clarity, strength, and recyclability, making them a trusted choice for modern foodservice packaging. With proper selection, manufacturing control, and sustainable sourcing, businesses can ensure safety, performance, and environmental responsibility—all in one cup.
References
-
Packaging Europe. Global PET Packaging Market Report 2024.
-
Grand View Research. Disposable Drinkware Industry Forecast, 2024–2030.
-
U.S. Food & Drug Administration. CFR 21 Section 177.1630 – Polyethylene Terephthalate.
-
European Commission. Regulation (EU) No. 10/2011 on Plastic Food Contact Materials.
-
Journal of Polymer Engineering. Advances in PET Thermoforming for Food Packaging, 2023.
-
Ellen MacArthur Foundation. New Plastics Economy Report 2024.
-
University of Leeds, School of Materials Science. Comparative Analysis of PET and Bio-PET, 2023.
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.





