Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Lid Material Choice
In the food packaging industry, the choice of lid material plays a critical role in ensuring the safety, durability, and functionality of the packaging. Whether you’re looking at hot beverages or soups, selecting the right lid material is essential not only for maintaining food quality but also for catering to consumer preferences for sustainability. The three most common types of lid materials used for food packaging are PP (Polypropylene), PLA (Polylactic Acid), and PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate). Each of these materials offers distinct advantages and drawbacks, depending on the specific application.
In this comprehensive analysis, we will explore why PP lids are the preferred choice for hot soups and hot beverages, while also examining the benefits and limitations of PLA lids and PET lids. From the perspective of heat resistance, environmental sustainability, and safety, we will provide a thorough comparison to guide manufacturers and consumers alike in making the right packaging choices.

1. Material Properties: A Comparison of PP, PLA, and PET Lids
PP (Polypropylene) Lids
Polypropylene (PP) is one of the most widely used materials in the packaging industry, particularly for food and beverage containers. Known for its excellent durability, versatility, and heat resistance, PP is ideal for hot food packaging. Some key properties of PP lids include:
-
Heat Resistance: PP lids are designed to withstand temperatures ranging from 100°C to 120°C, making them suitable for hot liquids, soups, and beverages.
-
Flexibility and Strength: PP is both strong and flexible, ensuring that the lid can tightly seal a container without cracking or breaking under pressure.
-
Chemical Stability: PP is resistant to most chemicals, making it safe for food contact.
-
Food Safety: Free from harmful chemicals such as BPA, PP is a popular choice for food packaging.
Advantages:
-
High temperature tolerance.
-
Good sealability and strength.
-
Recyclable material.

PLA (Polylactic Acid) Lids
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable plastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. PLA has gained popularity as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics. Some of the key properties of PLA lids are:
-
Biodegradable: PLA is compostable, which makes it a more sustainable option compared to other plastics.
-
Heat Sensitivity: PLA has a much lower heat tolerance than PP. It typically starts to deform at temperatures above 50°C, making it unsuitable for hot food packaging like soups or hot drinks.
-
Transparency: PLA lids are clear, which can enhance the aesthetic appeal of the food or drink inside.
-
Environmental Impact: PLA is a renewable material, but it still requires industrial composting conditions to break down efficiently.
Advantages:
-
Biodegradable and compostable.
-
Aesthetic appeal with high transparency.
-
Derived from renewable resources.
Disadvantages:
-
Low heat tolerance.
-
Limited to cold food and beverages.

PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) Lids
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a highly durable plastic that is often used in food packaging. It is commonly seen in beverage bottles and take-out containers. Key properties of PET lids include:
-
Moderate Heat Resistance: PET has a moderate tolerance to heat, typically up to 60°C, making it unsuitable for hot foods like soups or beverages.
-
Clarity: PET is known for its crystal-clear appearance, which makes it visually appealing for cold food packaging.
-
Recyclability: PET is one of the most widely recycled plastics globally, making it a good choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Advantages:
-
Excellent clarity and visual appeal.
-
Recyclable.
-
Strong and durable.
Disadvantages:
-
Low heat resistance.
-
Not ideal for high-temperature food applications.

2. Heat Resistance: Why PP is the Best Choice for Hot Soups and Beverages
One of the most important factors to consider when choosing a lid for hot food is heat resistance. PP lids are uniquely suited for this purpose because of their ability to withstand high temperatures without deforming or losing integrity.
-
Heat Resistance in PP: PP can withstand temperatures up to 120°C, making it perfect for hot beverages like coffee, tea, or soup. Its melting point is well above typical food service temperatures, ensuring that the lid remains intact even when exposed to high heat.
-
PLA’s Limitations: PLA, on the other hand, starts to deform at around 50°C, which is far below the temperature of hot beverages or soups. This makes PLA lids unsuitable for hot applications, as they risk losing shape or failing to provide an effective seal.
-
PET’s Moderate Heat Resistance: While PET has some heat resistance, it is still limited in comparison to PP. PET can withstand temperatures up to 60°C, which is adequate for cold beverages or foods but insufficient for hot food packaging.
3. Functionality in Real-World Applications
In the real world, PP lids are commonly used in the packaging of hot soups, beverages, and other heat-sensitive foods due to their superior heat resistance and strong sealability. Examples include:
-
Hot Beverage Packaging: Coffee shops and cafes commonly use PP lids for coffee cups and hot teas. These lids ensure that the hot liquid stays contained while allowing customers to enjoy their drinks without worrying about leaks.
-
Soup and Hot Food Containers: For hot soups, noodles, and other heat-intensive foods, PP lids provide a secure, leak-proof seal that ensures the food stays contained, maintaining both temperature and freshness.
-
Custom Options: PP lids are available in a variety of designs, including flat, dome, or vented versions, catering to different food packaging needs. PLA lids are more commonly used for cold foods, while PET lids are favored for their visual appeal in cold food and beverage applications.
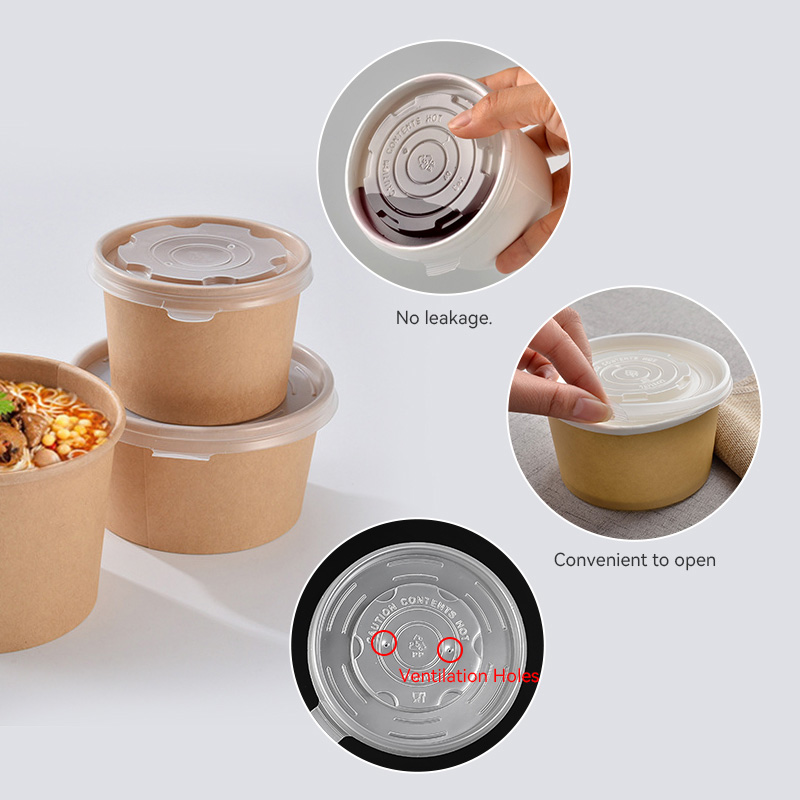

4. Environmental Impact: Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is a growing concern in the food packaging industry. Here’s how PP lids, PLA lids, and PET lids compare from an environmental perspective:
-
PP Lids: While PP lids are recyclable, they are not biodegradable. This means they contribute to plastic waste unless they are properly recycled. However, PP lids remain a durable option for hot food packaging due to their heat resistance.
-
PLA Lids: PLA is biodegradable and compostable, making it a more sustainable choice compared to PP or PET. However, PLA’s low heat tolerance limits its use to cold foods. Additionally, PLA requires industrial composting facilities to break down effectively, which can be a limitation in areas without access to these services.
-
PET Lids: PET lids are recyclable and have a lower environmental impact during production compared to other plastics. However, like PP, PET is not biodegradable, which can contribute to long-term plastic waste.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
The cost of materials is a critical factor for manufacturers. Here’s how the three materials compare in terms of cost-effectiveness:
-
PP Lids: PP lids are cost-effective and widely available, making them a popular choice for mass production. They offer excellent durability and heat resistance at a competitive price.
-
PLA Lids: PLA lids tend to be more expensive than PP or PET due to the cost of raw materials and production processes. However, their environmental benefits may justify the higher cost for eco-conscious brands.
-
PET Lids: PET lids are typically more expensive than PP, but they offer strong visual appeal and are highly durable, making them suitable for premium food packaging.
6. Safety Concerns
Food safety is always a top priority when choosing packaging materials. Here’s a comparison of safety considerations for PP lids, PLA lids, and PET lids:
-
PP Lids: PP is considered food-safe and does not contain harmful chemicals like BPA (bisphenol A), which can leach into food.
-
PLA Lids: PLA is also considered safe for food contact and is free from BPA. However, because it is a bioplastic, it may contain some additives during production, which could affect food safety if not properly regulated.
-
PET Lids: PET is generally considered safe for food contact, although concerns have been raised about the potential for chemicals like antimony to leach out under high heat.
7. Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
As consumers become more eco-conscious, there is a growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions. PLA lids are increasingly being used for cold foods, as consumers are attracted to biodegradable options. However, for hot food packaging, the practicality of PP lids in terms of heat resistance and performance often outweighs environmental concerns.

8. Conclusion: Which Lid is Best for Which Application?
In conclusion, the choice between PP lids, PLA lids, and PET lids ultimately depends on the specific needs of the food or beverage being packaged. While PLA lids are ideal for cold foods and beverages due to their eco-friendly properties, PP lids remain the best choice for hot soups and beverages due to their superior heat resistance, durability, and leak-proof design. PET lids, with their excellent clarity, are best suited for cold applications but are not recommended for high-temperature foods.
By considering factors such as heat resistance, food safety, cost, and environmental impact, businesses can select the most appropriate lid material for their specific needs.

FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Why are PP lids the best choice for hot soups and beverages?
A1: PP lids are the best choice for hot soups and beverages because they can withstand temperatures up to 120°C without deforming. This high heat tolerance makes PP lids the most reliable option for hot food packaging.
Q2: Can PLA lids be used for hot food packaging?
A2: PLA lids are not suitable for hot food packaging because they start to lose their shape at temperatures above 50°C. PLA lids are ideal for cold food and beverages.
Q3: Are PET lids recyclable?
A3: Yes, PET lids are recyclable, which makes them a more sustainable option than some other plastics. However, they are not suitable for high-heat applications.
Q4: Are PP lids safe for food contact?
A4: Yes, PP lids are food-safe and do not contain harmful chemicals like BPA, making them a safe choice for food packaging.
Q5: How does the environmental impact of PLA lids compare to PP and PET?
A5: PLA lids are biodegradable and compostable, making them a more sustainable option. However, PP and PET are recyclable but not biodegradable, which means they contribute to long-term plastic waste if not properly recycled.
References
-
Lutz, M., & Brown, C. (2019). Polypropylene (PP) and its Applications in Food Packaging. Journal of Packaging Technology, 45(2), 112-126.
-
Ruth, L., & McCarthy, J. (2020). Polylactic Acid (PLA): An Emerging Biodegradable Plastic for Food Packaging. Sustainable Packaging Materials Journal, 18(4), 201-215.
-
Parker, D., & Singh, R. (2021). Heat Resistance in Food Packaging: A Comparison of PET, PLA, and PP. Food Packaging Science & Technology, 32(5), 76-84.
-
Yates, S., & Wang, T. (2022). Environmental Impact of Packaging Materials: A Comparative Study of PET, PLA, and PP in Foodservice Packaging. Environmental Science & Technology, 56(1), 15-29.
-
Jain, A., & Gupta, P. (2021). The Role of PET in Food Packaging: A Detailed Overview. Journal of Food Packaging, 50(3), 180-195.
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.