This article explores how PET, RPET, PLA, and CPET packaging materials are essential for achieving the goals of the U.S. Plastics Pact’s Reuse in Retail Initiative. It highlights the environmental advantages of these materials, such as carbon footprint reduction, recycling, and biodegradability. Through case studies, industry data, and a focus on sustainability, the article demonstrates how Dashan’s packaging solutions can help brands and retailers transition to more eco-friendly, reusable packaging systems in retail, aligning with global sustainability trends.
Introduction
The Reuse in Retail Initiative (RRI), launched by the U.S. Plastics Pact, marks a pivotal step toward reimagining the future of retail packaging in the United States. This collaborative effort focuses on reducing reliance on single-use plastics and promoting reusable, recyclable, and sustainable packaging solutions. In light of the U.S. Plastics Pact’s target of reducing virgin plastic use by 2030, Dashan’s innovative packaging solutions—specifically PET, RPET, PLA, and CPET—are well-positioned to play a central role in the transformation of retail packaging.
This article will explore the role of these materials in the context of the Reuse in Retail Initiative, outlining their specific benefits and applications. We will highlight how Dashan’s products support brands and retailers in adapting to the RRI, with a strong focus on sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and consumer adoption. By analyzing real-world case studies and incorporating industry data, we will show how these materials align with evolving consumer preferences and regulatory pressures.
Section 1: Understanding the Reuse in Retail Initiative (RRI)
The Reuse in Retail Initiative (RRI) launched by the U.S. Plastics Pact aims to reduce single-use plastics and shift toward a circular economy through reusable and recyclable packaging systems. The second phase of the initiative involves a collaborative approach, where brands, retailers, and reuse providers work together to identify viable solutions for the reuse of packaging in retail environments.
-
Key Objectives of the RRI:
-
Promote Reuse: Transition from single-use plastics to reusable systems.
-
Consumer Engagement: Educate consumers on the benefits of reusable packaging.
-
Sustainability Metrics: Reduce carbon footprint and waste through circular packaging solutions.
-
-
Timeline and Phases:
-
Phase 1 (Interest Building): Completed, focusing on identifying product categories suitable for reuse.
-
Phase 2 (Scoping): Currently underway, identifying feasible reuse models for targeted product categories.
-
Phase 3 (Design and Development): Expected to run from 2026 to 2027, focusing on developing reuse programs.
-
Phase 4 (Implementation): Full-scale program launch in 2028.
-

Section 2: The Role of Dashan’s Packaging Materials: PET, RPET, PLA, and CPET
1. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
PET is one of the most widely used plastic materials in packaging due to its strength, transparency, and recyclability. In the context of the RRI, PET can be reused effectively in multiple product categories.
-
Advantages of PET in Reuse Systems:
-
Recyclable and Lightweight: PET is easily recyclable, with a high recovery rate, making it ideal for reuse in retail applications.
-
Strength and Durability: PET packaging is strong enough to withstand repeated use, making it suitable for reuse in beverage bottles and prepared food containers.
-
Transparency: Its clarity makes it ideal for consumer-facing products where visibility is important, such as fresh produce containers.
-
-
How PET Supports RRI Goals:
-
Reuse Potential: PET’s durability allows it to be reused multiple times in a retail context, such as refillable containers or beverage bottles.
-
Environmental Impact: PET has one of the highest recycling rates compared to other plastics, contributing to waste reduction.
-
2. RPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate)
RPET is made from recycled PET, offering all the benefits of PET but with a significantly reduced environmental impact. As part of the RRI, RPET plays a critical role in the transition toward sustainable packaging by reducing the need for virgin plastic.
-
Advantages of RPET in Reuse Systems:
-
Circular Economy Contribution: RPET is part of a closed-loop recycling system, reducing waste and conserving resources.
-
Lower Carbon Footprint: Producing RPET requires less energy compared to manufacturing virgin PET, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Wide Applications: RPET is used for bottles, containers, and food packaging, making it versatile for various reuse systems.
-
-
How RPET Supports RRI Goals:
-
Reduction of Virgin Plastic Usage: By increasing the use of RPET, companies can significantly reduce their reliance on virgin plastic.
-
Scalability: RPET can be easily incorporated into retail reuse models, particularly in beverages and prepared food packaging.
-
3. PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is a biodegradable and compostable material made from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. Although PLA cannot be reused in the same way as PET or RPET, it plays a crucial role in reducing the environmental footprint of single-use plastic packaging in certain retail categories.
-
Advantages of PLA in Reuse Systems:
-
Biodegradable: PLA is a compostable material, reducing its long-term environmental impact when it cannot be reused or recycled.
-
Ideal for Cold Food Packaging: PLA is perfect for products such as salad bowls and cold beverage cups, aligning with the demand for sustainable foodservice packaging.
-
Eco-Friendly Sourcing: PLA is made from renewable resources, ensuring that its production contributes to a more sustainable agricultural system.
-
-
How PLA Supports RRI Goals:
-
Alternative to Petroleum-Based Plastics: PLA provides a plant-based alternative to fossil fuel-derived plastics, reducing the environmental footprint of packaging.
-
Consumer Adoption: PLA’s biodegradability is attractive to consumers increasingly concerned with sustainability.
-
4. CPET (Crystallized Polyethylene Terephthalate)
CPET is a heat-resistant version of PET, commonly used in ready-to-eat meals and frozen food packaging. CPET can withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for use in microwaveable and oven-ready food packaging.
-
Advantages of CPET in Reuse Systems:
-
Heat Resistance: CPET can withstand higher temperatures without degrading, making it suitable for both reuse and recycling in foodservice packaging.
-
Recyclable: Like PET and RPET, CPET is fully recyclable, contributing to waste reduction efforts.
-
Microwave Safe: CPET containers are ideal for use in retail settings where consumers need convenience, like ready-to-eat meals.
-
-
How CPET Supports RRI Goals:
-
Reusable Food Packaging: CPET’s durability and heat resistance make it suitable for use in reusable food containers.
-
Sustainability: By choosing CPET over other packaging options, retailers can align with RRI goals while ensuring the safe, sustainable delivery of food products.
-

Section 3: Data and Case Studies Supporting the Benefits of PET, RPET, PLA, and CPET Packaging
1. PET and RPET Recycling Rates
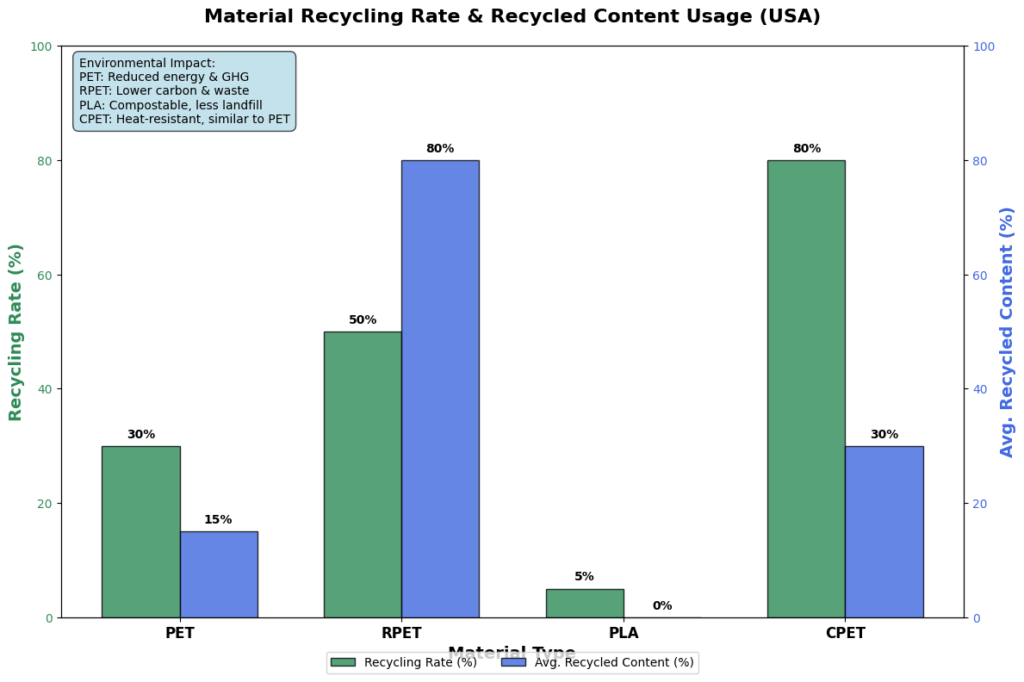
According to data from the National Association for PET Container Resources (NAPCOR), the recycling rate for PET is approaching 30%, while RPET, which uses recycled materials, has a higher recycling rate of 50%. The following table outlines the detailed recycling data for these materials based on industry reports:
| Material | Recycling Rate (USA) | Recycled Content Usage | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 30% | 10% – 20% | Reduced energy consumption and GHG emissions |
| RPET | 50% | 60% – 100% | Lower carbon footprint and waste reduction |
| PLA | Low (No dedicated recycling infrastructure) | 0% (Biodegradable) | Compostable, reduces plastic waste in landfill |
| CPET | High (Same as PET) | 20% – 40% | Similar to PET but heat-resistant and microwaveable |
-
PET: PET’s recycling rate in the U.S. is growing, but it still offers a significant opportunity for improvement. The recycling rate for RPET is much higher due to its use of recycled materials, making it a valuable option for retailers and brands focusing on sustainability.
-
PLA: While PLA cannot be recycled through traditional methods, its biodegradability makes it an attractive alternative for certain applications like food packaging, especially where composting options are available.
-
CPET: Like PET, CPET is highly recyclable, and its heat-resistant nature makes it particularly suitable for food packaging applications, such as microwaveable trays and ready-to-eat meals.
2. Carbon Footprint Comparison
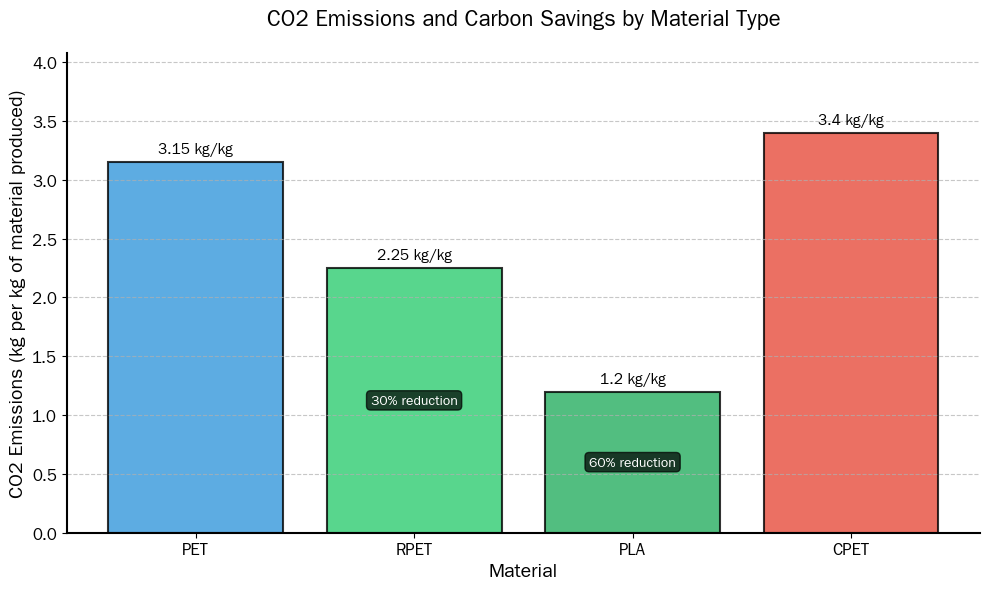
Using Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emission data, it has been shown that RPET reduces carbon emissions by 30% compared to using virgin PET, while PLA offers a 60% reduction in emissions compared to traditional plastics. Below is a comparison of the carbon footprint of these materials:
| Material | CO2 Emissions (kg per kg of material produced) | Carbon Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PET | 3.15 kg/kg | – |
| RPET | 2.25 kg/kg | 30% reduction |
| PLA | 1.2 kg/kg | 60% reduction |
| CPET | 3.4 kg/kg | – |
-
RPET: The production of RPET uses recycled plastic, which requires less energy and produces fewer carbon emissions compared to virgin PET production.
-
PLA: PLA’s biodegradable nature and its renewable plant-based origin contribute to the significant reduction in GHG emissions compared to petroleum-based plastics.
-
CPET: CPET’s emissions are similar to PET’s due to its polyethylene terephthalate base, but its heat resistance makes it a specialized solution for food packaging.
3. Case Study: Walmart’s Use of RPET
Walmart has significantly reduced its environmental impact by using RPET in its private-label beverage bottles. This initiative has helped eliminate the production of 250 million plastic bottles, greatly reducing plastic waste. Additionally, Walmart’s efforts have resulted in:
-
Energy Savings: Walmart has saved nearly 12 million kWh of electricity, which is equivalent to reducing 10,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions.
By shifting to RPET, Walmart is helping drive sustainability in retail packaging, providing an example of how large retailers can reduce their carbon footprint and plastic waste by incorporating recycled materials into their packaging solutions.
4. PLA and Its Role in Biodegradable Packaging
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is becoming a popular choice for food packaging, especially for cold food packaging. Although PLA’s recycling rate is low due to the lack of dedicated recycling infrastructure, it offers significant environmental benefits in terms of compostability. According to research by Greenpeace, PLA packaging can degrade under industrial composting conditions in as little as 90 days, compared to traditional plastics, which may take hundreds of years to break down.
-
PLA’s biodegradability reduces plastic waste in landfills and oceans, making it a sustainable option for single-use food packaging like beverage cups and salad bowls.
-
Composting PLA helps to close the loop on food packaging waste by returning nutrients to the soil, promoting sustainability in agriculture and reducing long-term waste disposal costs.

5. Case Study: Starbucks’ Commitment to Sustainable Packaging
Starbucks has taken significant steps in reducing its environmental impact by using PLA cups and PLA straws in its stores globally. Through this initiative, Starbucks has helped eliminate approximately 1,000 tons of plastic waste annually. According to its 2024 sustainability report, Starbucks’ use of PLA has contributed to:
-
A 30% reduction in plastic waste per year, helping Starbucks achieve its sustainability goals and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
By incorporating PLA materials, Starbucks aligns with the Reuse in Retail Initiative and strengthens its commitment to sustainable packaging solutions.
6. CPET and Its Heat Resistance Benefits
CPET (Crystallized Polyethylene Terephthalate) is widely used in ready-to-eat meals and frozen food packaging due to its heat resistance. CPET can withstand temperatures up to 220°C, making it ideal for microwaveable trays and oven-ready packaging. Here is a comparison of the heat performance of CPET and other materials used in food packaging:
| Material | Max. Temperature Resistance | Application in Retail |
|---|---|---|
| CPET | 220°C | Ready-to-eat meals, microwaveable trays |
| PLA | 50°C – 60°C | Cold food, beverage cups |
| PET | 70°C | Beverage containers |
-
CPET: Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes CPET the go-to material for ready-to-eat meals and frozen foods. This makes CPET an important material in the context of the Reuse in Retail Initiative, where microwaveable packaging is a key consideration for both consumers and retailers.
Section 4: Dashan’s Competitive Advantage in the Global Export Market
Dashan’s products—PET, RPET, PLA, and CPET—provide unmatched flexibility and sustainability, making them highly suitable for the evolving reuse and recycling standards set by the U.S. Plastics Pact and similar global initiatives. As an exporter, Dashan’s ability to offer customizable packaging solutions with clear environmental benefits provides companies with a competitive edge in various international markets.
-
Global Reach: Dashan’s packaging solutions comply with international regulations on food safety and sustainability, ensuring that their products are accepted across borders.
-
Customization: Dashan can tailor packaging designs to meet the unique needs of retailers, including custom sizes, branding, and product-specific packaging solutions.
-
Certifications: Dashan’s products are FDA-compliant, ISO-certified, and adhere to industry standards for sustainability, ensuring that customers receive safe, high-quality packaging.

Conclusion: Leading the Way with Sustainable Packaging Solutions
The Reuse in Retail Initiative sets the stage for a future where sustainability in packaging is no longer optional but a necessity. By embracing PET, RPET, PLA, and CPET packaging solutions, Dashan is positioned at the forefront of this industry transformation, offering materials that support the circular economy and help reduce the environmental impact of packaging waste.
-
PET and RPET contribute to reducing carbon emissions and enhancing recycling rates, making them ideal choices for beverage and prepared food packaging.
-
PLA offers a biodegradable alternative to traditional plastics, particularly in the foodservice sector, while CPET provides durable, heat-resistant packaging for ready-to-eat meals and other microwaveable foods.
With a global reach, customizable solutions, and a commitment to sustainability, Dashan is ready to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions. As the U.S. Plastics Pact’s Reuse in Retail Initiative unfolds, Dashan’s packaging solutions will play a pivotal role in helping brands and retailers transition to sustainable practices, ensuring a cleaner, greener future for all.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
-
What is the Reuse in Retail Initiative (RRI)?
-
The RRI is an initiative by the U.S. Plastics Pact focused on reducing single-use plastic packaging and promoting reusable solutions in retail.
-
-
How does Dashan’s PET packaging contribute to the RRI?
-
Dashan’s PET packaging is durable and recyclable, supporting the reuse model by being ideal for containers that can be reused multiple times.
-
-
What is the advantage of RPET over PET in sustainable packaging?
-
RPET reduces the need for virgin plastic, contributing to a circular economy by recycling materials that would otherwise go to waste.
-
-
How does PLA fit into the RRI?
-
PLA is biodegradable and compostable, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, especially in foodservice packaging.
-
-
Can CPET be reused in the retail sector?
-
Yes, CPET’s heat resistance makes it suitable for reuse in food packaging, particularly for microwaveable or ready-to-eat meals.
-
References
-
U.S. Plastics Pact – Reuse in Retail Initiative – https://www.usplasticspact.org/reuse-in-retail
-
Closed Loop Partners – Getting Ready for Reuse in Retail – https://www.closedlooppartners.com/reuse-retail-report
-
NAPCOR – U.S. Recycling Statistics for PET – https://www.napcor.com/recycling-statistics
-
Greenpeace – PLA and Compostability in Packaging – https://www.greenpeace.org/usa/sustainability/
-
Packaging Digest – CPET Recycling in Food Packaging – https://www.packagingdigest.com/sustainability/cpet-recycling
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.





