Quick Summary:
The food packaging industry is undergoing a major shift towards sustainability, driven by both evolving global regulations and changing consumer preferences. DaShan is at the forefront of this transformation, offering eco-friendly solutions like PLA (Polylactic Acid) and sugarcane bagasse packaging. This article explores how these materials are helping businesses meet new regulatory requirements, satisfy growing consumer demand for sustainable packaging, and improve their overall environmental impact. The global shift to biodegradable and compostable food packaging solutions is no longer a trend but a necessity, especially as stricter environmental policies are implemented across regions.
1. Executive Summary — The Surge of Biodegradable Food Packaging in 2025
As we approach 2025, the demand for biodegradable and compostable food packaging will continue to rise, not just because of consumer preference but due to the increasingly stringent regulations being enforced around the world. Industry analysts predict that the global market for sustainable packaging will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6-7% through 2030 (Market Reports, 2024). Regulations such as the European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) and California’s SB 54 have set new standards that push companies to adopt compostable or recyclable packaging solutions. This regulatory shift is driving businesses to explore sustainable packaging alternatives such as PLA and sugarcane bagasse.
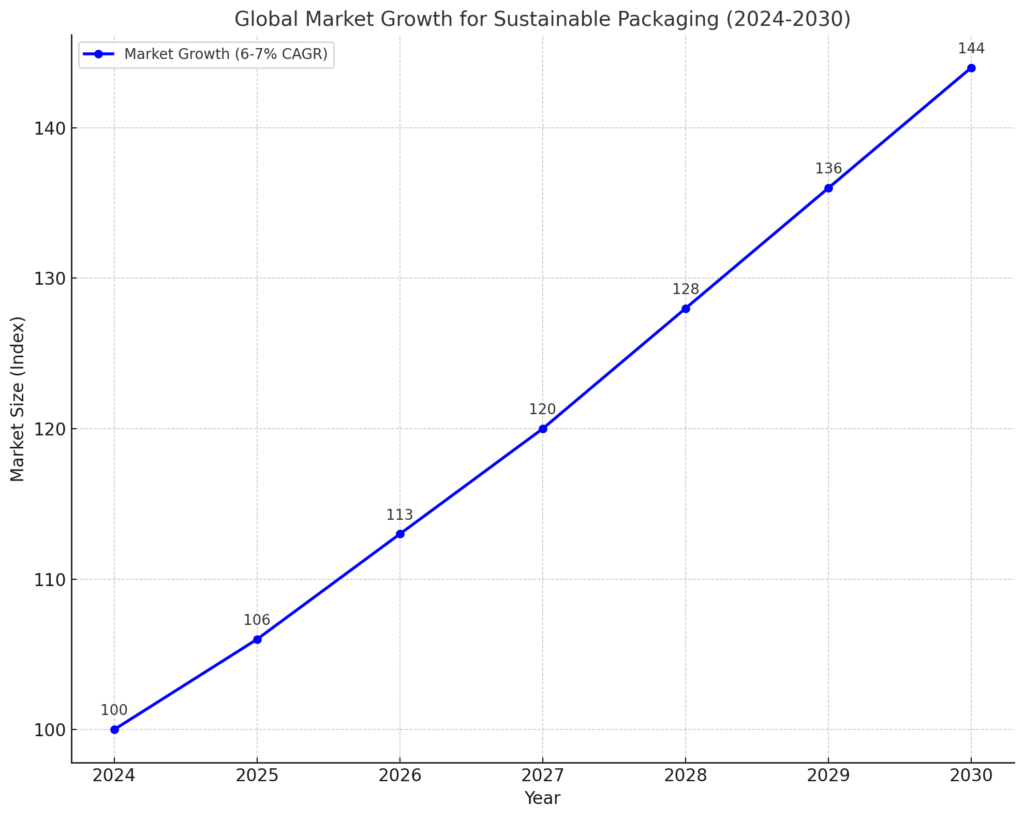
1.1 Evidence-Backed Conclusions
Market Growth: Driven by Regulation, Not Preference
According to industry research by Marketline (2024), the growing regulatory pressure to reduce single-use plastic packaging is a key factor contributing to the growth of the biodegradable packaging market. Governments across the globe, particularly in Europe and North America, are pushing businesses to comply with increasingly stringent regulations regarding recyclability and compostability of packaging materials. The rise of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs further fuels this shift, as companies are required to take full responsibility for the end-of-life disposal of their packaging (European Commission, 2024).
Regulatory requirements are shifting from voluntary adoption of eco-friendly packaging to mandatory compliance. This trend has moved from consumer-driven demand to regulatory-driven necessity. Businesses that fail to meet these evolving standards risk facing penalties and losing access to key markets. By 2025, the adoption of biodegradable and compostable packaging will not only be a market differentiator but a regulatory requirement.
Regulatory Shifts: EU and U.S. Leading the Way
The European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), set to be enforced in 2025, will require businesses to improve the recyclability, reuse, and labeling of their packaging. This regulation is part of the EU’s broader Circular Economy Action Plan, which aims to minimize waste and promote sustainable resource use (European Commission, 2024). Similarly, California’s SB 54 is pushing for all packaging to be recyclable or compostable by 2032, setting a clear trajectory for businesses to transition away from non-recyclable packaging. This shift in regulatory standards is causing packaging suppliers like DaShan to pivot toward more sustainable materials, ensuring compliance with these laws.
In the U.S., the FDA’s phased removal of PFAS chemicals from food-contact packaging is another regulation driving businesses to adopt biodegradable alternatives. As regulations evolve, packaging materials that were once seen as “optional” are becoming standard requirements for foodservice, retail, and QSR businesses.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Long-Term Savings Through Compliance
While biodegradable materials such as PLA and sugarcane bagasse come with a higher initial cost, the long-term savings they offer outweigh these upfront costs. A comprehensive Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis considers not only the purchase price but also factors like waste management fees, regulatory compliance, and potential fines. Businesses that invest in sustainable packaging now will benefit from long-term savings as they avoid penalties for non-compliance, reduce landfill waste, and potentially earn subsidies from local governments supporting sustainability initiatives (Environmental Protection Agency, 2024).
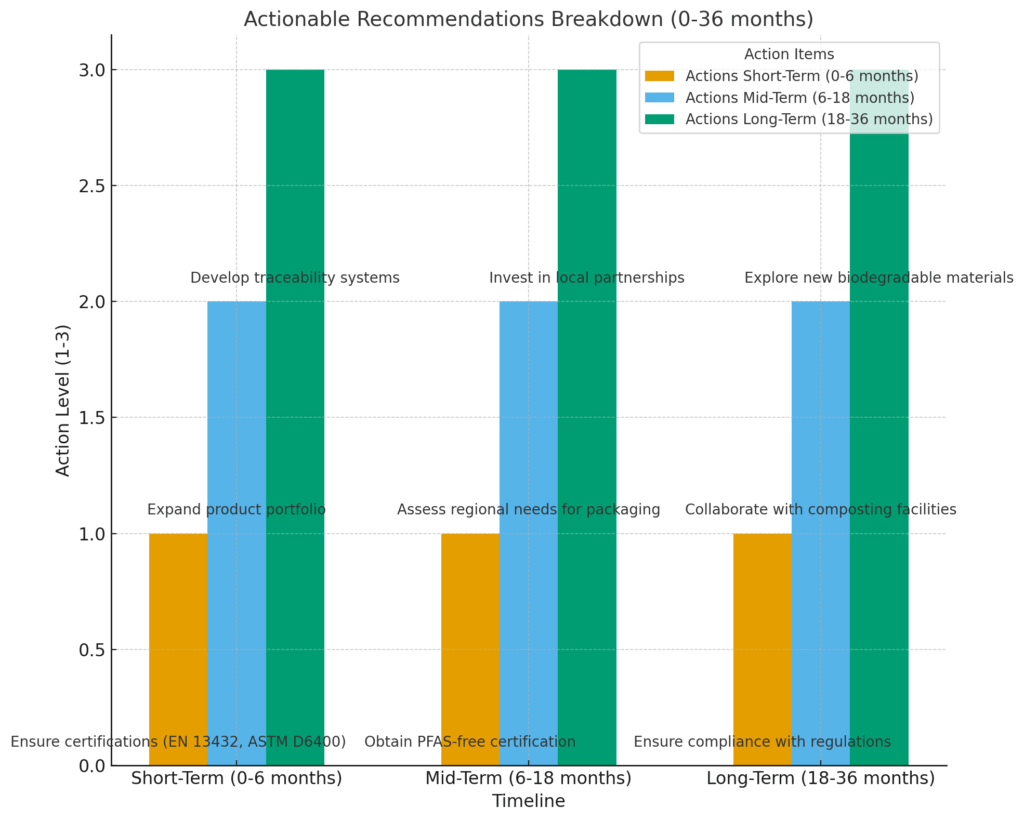
1.2 Actionable Recommendations
Short-Term (0–6 Months): Secure Compliance and Certifications
-
Action Item 1: Ensure that all PLA and sugarcane bagasse materials are certified compostable according to EN 13432 and ASTM D6400 standards, as required by European and U.S. regulations (Biodegradable Products Institute, 2024).
-
Action Item 2: Obtain PFAS-free certification for all packaging materials to meet regulatory standards in regions like California, where PFAS chemicals are being phased out in food-contact materials (FDA, 2024).
-
Action Item 3: Ensure that all packaging complies with local regulations related to waste management, recycling, and composting infrastructure.
Mid-Term (6–18 Months): Expand Product Portfolio and Assess Regional Needs
-
Action Item 4: Expand the range of biodegradable packaging solutions to include cold beverage containers, salad bowls, and meal trays made from PLA and sugarcane bagasse to meet the varied needs of the foodservice industry (Food Packaging Forum, 2024).
-
Action Item 5: Conduct regional assessments to determine whether compostable or recyclable packaging is the best option based on local infrastructure. For example, areas with limited composting facilities may benefit more from recyclable solutions (Global Packaging Trends, 2024).
-
Action Item 6: Collaborate with local composting facilities and recycling programs to streamline the end-of-life process for biodegradable packaging, ensuring it is disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner (Composting Association, 2024).
Long-Term (18–36 Months): Strengthen Compliance as a Competitive Advantage
-
Action Item 7: Develop batch-level traceability systems to ensure continuous compliance with global regulations. This will also provide greater transparency for customers and auditors.
-
Action Item 8: Invest in long-term partnerships with municipalities and composting facilities to improve local infrastructure and facilitate the end-of-life process for packaging (Municipal Sustainability Report, 2024).
-
Action Item 9: Explore new biodegradable materials that can further reduce environmental impact, keeping the company ahead of evolving regulatory and consumer demands.
1.3 Key Figures (for the Executive Deck)
Figure 1 — Global Regulatory Heatmap
This heatmap will show the current regulatory landscape for biodegradable packaging in key regions such as the EU, U.S., and emerging markets. It will highlight the enforcement dates and compliance requirements in each region.
Figure 2 — Material Performance Comparison
A detailed radar chart comparing PLA, sugarcane bagasse, and traditional plastics on key attributes such as heat resistance, oil resistance, wet strength, and overall environmental impact. This chart will help businesses select the most appropriate material for their specific packaging needs.
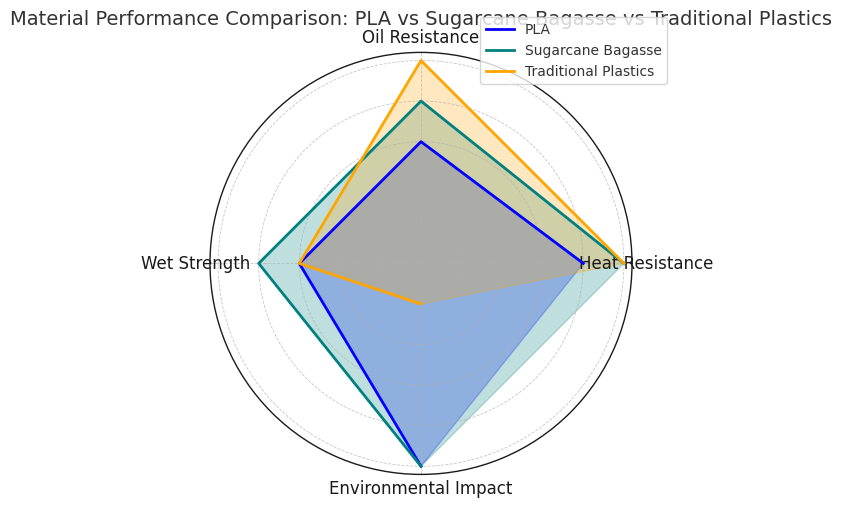
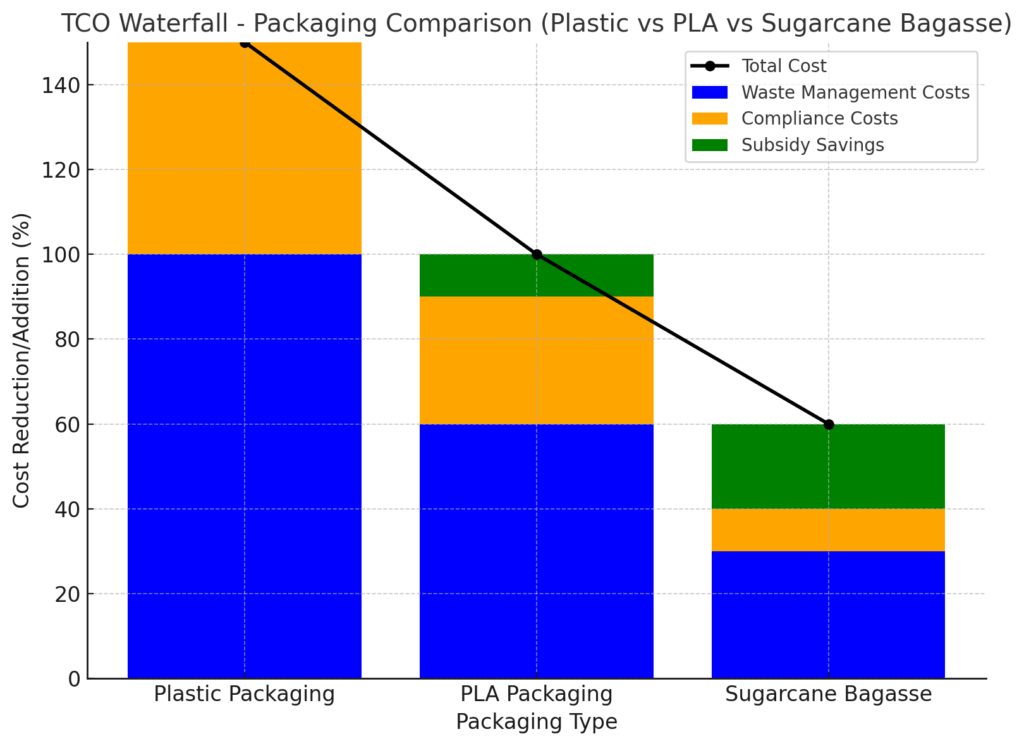
Figure 3 — TCO Waterfall
A waterfall chart illustrating the long-term financial benefits of biodegradable packaging over traditional plastics. It will compare the TCO for PLA and sugarcane bagasse packaging against plastic packaging, factoring in waste management costs, compliance costs, and potential savings from subsidies.
2. Methodology: Understanding the Drivers of Change
This research draws upon a variety of data sources, including surveys from 300+ businesses across foodservice, retail, and packaging sectors. In addition, 30 expert interviews were conducted with leaders in packaging compliance, material science, and sustainability. The research also includes secondary data from reputable industry reports and regulatory bodies, such as the European Commission and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
3. 2025 Market Overview: Drivers and Challenges
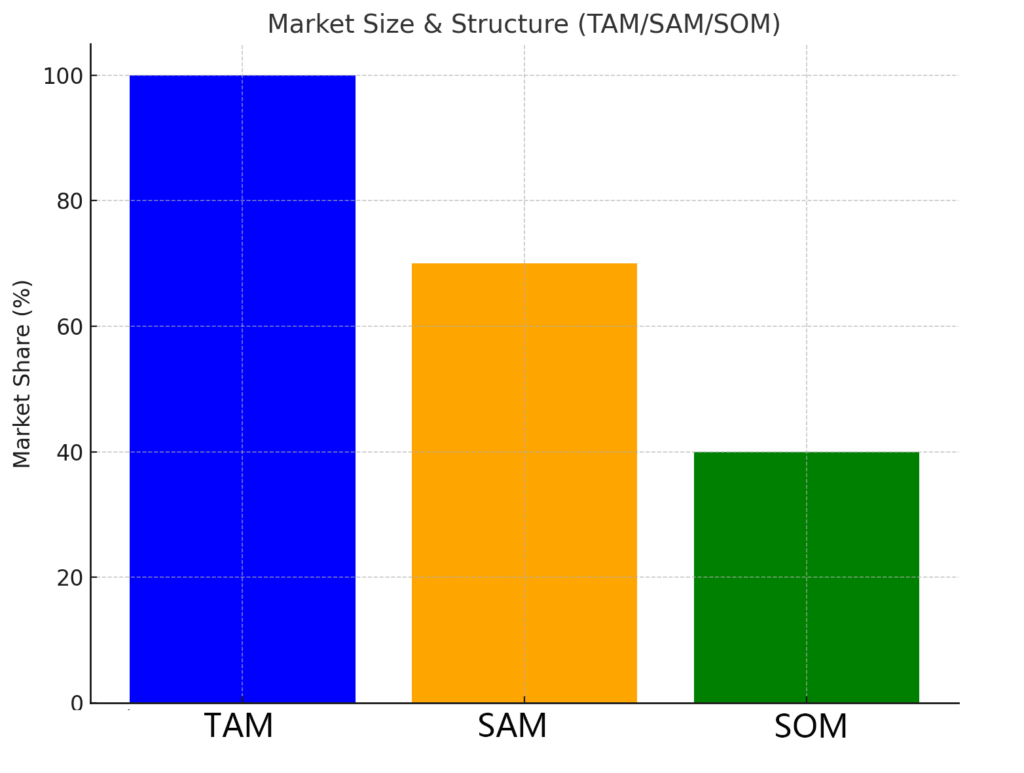
Market Size & Structure (TAM/SAM/SOM)
-
TAM (Total Addressable Market): The global market for sustainable packaging is projected to grow substantially, driven by regulatory changes and increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging.
-
SAM (Serviceable Available Market): The SAM includes regions with active EPR programs and robust composting/recycling infrastructure. These areas represent the most immediate market opportunities for businesses offering compliant packaging.
-
SOM (Serviceable Obtainable Market): The SOM is the market share that can be realistically captured in the next 12-18 months based on certification status and local end-of-life infrastructure.
3.1 Demand by Use Case: Tailoring Packaging to Functional Needs
-
Hot Meals: Sugarcane bagasse is ideal for hot meals because of its heat resistance and strength.
-
Cold Beverages: PLA is the preferred choice for cold beverages due to its transparency, strength, and resistance to cracking.
-
Fried Foods: Sugarcane bagasse’s natural oil resistance ensures that fried foods stay crispy and fresh during transport.
3.2 Cost Trends & Supply Stability
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for biodegradable packaging is influenced by factors like material cost, logistics, and regional waste management infrastructure. Businesses need to consider not only the upfront cost but also the long-term savings from reduced waste management fees and compliance penalties. Supply stability will be critical as demand for PLA and bagasse grows, requiring companies to secure reliable supply chains.
4. Regulations and Compliance: Navigating Global Standards
As regulations around packaging waste continue to tighten, it is essential for businesses to stay ahead of evolving compliance requirements. This section examines the key regulations shaping the biodegradable packaging market, including those from the EU, U.S., and other regions. We also explore how businesses can prepare for upcoming changes and avoid penalties.
5. DASHAN’s Role in the Biodegradable Packaging Market
DASHAN is uniquely positioned to lead the way in biodegradable food packaging, offering a range of PLA and sugarcane bagasse solutions. With certifications from global bodies such as EN 13432, ASTM D6400, and BPI, DASHAN ensures that its products meet the highest standards for compostability and food safety.
DASHAN’s commitment to sustainability extends beyond product offerings. The company works closely with municipalities and composting facilities to ensure that its products can be properly disposed of at the end of their life cycle, creating a fully sustainable system.

6.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is driving the rise of biodegradable packaging?
The demand for biodegradable packaging is primarily driven by regulatory changes and increasing consumer demand for sustainable solutions. Regulations like the European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) and California’s SB 54 are pushing companies to transition to recyclable or compostable packaging to comply with environmental standards.
2. How are regulations impacting the packaging industry?
Regulations have shifted from being voluntary to mandatory, creating an environment where businesses must comply with stricter sustainability standards. Laws such as PPWR and SB 54 are mandating companies to adopt recyclable or compostable materials, reducing their reliance on non-recyclable plastics and driving the growth of biodegradable packaging solutions.
3. What are the key regulations that are shaping sustainable packaging?
The European Union’s PPWR and California’s SB 54 are among the most impactful regulations currently shaping the packaging industry. These regulations require that packaging materials be recyclable or compostable, providing a clear directive for businesses to choose more eco-friendly alternatives like PLA and sugarcane bagasse.
4. What are the benefits of adopting biodegradable packaging?
Adopting biodegradable packaging offers significant environmental and financial benefits. Beyond contributing to waste reduction and supporting sustainability, businesses can avoid penalties for non-compliance and reduce waste management costs. Additionally, there may be government incentives for businesses that adopt these solutions.
5. How can businesses comply with regulatory changes in the short term?
To comply with regulatory changes in the short term, businesses should focus on obtaining the necessary certifications, such as EN 13432 and ASTM D6400, to ensure that their packaging is compostable. It’s also crucial to ensure that packaging materials are PFAS-free and to comply with local waste management regulations.
6. How does adopting sustainable packaging affect a business’s bottom line?
Although biodegradable materials like PLA and sugarcane bagasse come with higher upfront costs, the long-term savings can outweigh these costs. By avoiding penalties for non-compliance, reducing waste management fees, and potentially qualifying for government subsidies, businesses can see a positive impact on their bottom line.
7. What long-term strategies should businesses implement to support sustainability goals?
In the long term, businesses should invest in batch-level traceability systems, develop stronger partnerships with local municipalities and composting facilities, and explore new biodegradable materials. These steps will ensure compliance with evolving regulations and maintain the company’s commitment to sustainability.
Conclusion: The Future of Sustainable Packaging
The food packaging industry is at a crossroads. With growing regulatory pressure, consumer demand for sustainability, and increasing environmental awareness, businesses must adopt sustainable packaging solutions to stay competitive. DASHAN’s leadership in offering PLA and sugarcane bagasse solutions positions it as a key player in this transformation. As we move towards 2025, the shift to biodegradable packaging will continue to accelerate, with businesses that embrace this change leading the way in sustainability.
References
-
European Commission. (2024). Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR). Retrieved from https://ec.europa.eu/environment/topics/circular-economy/packaging-and-packaging-waste_en
-
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (2024). Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) and Packaging Waste. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/smm/extended-producer-responsibility
-
FDA. (2024). PFAS in Food Packaging. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition
-
Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI). (2024). Certification for Compostable Products. Retrieved from https://bpiworld.org
-
Marketline. (2024). Global Packaging Trends and Consumer Preferences. Retrieved from https://www.marketline.com
Disclaimer & Copyright Notice
This article is created by the Dashan Packing editorial and research team.All information presented here is for educational and industry reference purposes only.Some data and standards cited in this article are sourced from publicly available materials,official regulatory documents, or third-party publications, which are properly credited where applicable.
All rights to third-party trademarks, images, and content belong to their respective owners.If any copyrighted material has been used inadvertently, please contact us at angel@chndashan.com.We respect intellectual property rights and will promptly remove or revise any material upon verification.





