Quick Summary
The European Union’s sustainability policies—including the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), Single-Use Plastics Directive, and EU Food-Contact Material standards—are reshaping the packaging landscape. Polypropylene (PP) has emerged as a compliant, recyclable, and economically viable solution for foodservice packaging. Due to its high heat resistance, chemical stability, clarity options, and mono-material recyclability, PP products such as cups, trays, plates, clamshell boxes, and takeaway food containers are increasingly favored in the EU market. These regulations create new opportunities for manufacturers like DASHAN, whose PP product lines align with EU environmental and safety requirements.
Introduction
Across the European Union, environmental legislation has transformed the food-packaging industry more dramatically than at any time in the last 30 years. Regulations such as the Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD) and the emerging Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) are forcing brands, foodservice operators, airlines, supermarkets, and packaging suppliers to rethink the materials they rely on.
However—contrary to common misconceptions—Polypropylene (PP) is not being banned or phased out in the EU. Instead, it is increasingly valued for its recyclability, material efficiency, safety, and compatibility with the EU’s circular-economy model.
This article provides a detailed policy analysis, market data, and technical insights into why PP remains a preferred packaging material in Europe. It also demonstrates how DASHAN’s extensive PP product portfolio—including PP cups, trays, plates, clamshell boxes, takeaway containers, compartment containers, and PP lids—perfectly fits current and upcoming EU requirements.
With nearly 20 years of manufacturing experience and active participation in major exhibitions across Dubai, Russia, Malaysia, and Thailand, DASHAN has built strong expertise in supplying globally compliant PP packaging. This article reflects that real-world experience, supported by industry data and authoritative references.
1. Understanding the EU Policy Framework: PP Is Not Restricted
1.1 The Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD): What It Really Targets
The SUPD aims to reduce plastic litter by banning or restricting:
-
EPS foam containers
-
Oxo-degradable plastics
-
Plastic cutlery and plates (mostly PS, not PP)
-
Plastic straws and stirrers
-
Certain beverage container components
Importantly, PP is not banned under SUPD.
PP food packaging—including PP trays, microwaveable PP containers, PP cups, and PP lids—remains fully legal and widely used across Europe.
The European Commission classifies PP as:
-
Recyclable
-
Compatible with existing waste streams
-
Suitable for food-contact materials
SUPD aims to eliminate unrecyclable plastics, not recyclable, mono-material PP.
1.2 PPWR (Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation)
Expected to fully take effect by 2030, PPWR focuses on:
-
Increasing recycling efficiency
-
Reducing unnecessary packaging
-
Standardizing labeling
-
Improving design for recyclability
This regulation strongly favors mono-material packaging, which PP excels at.
Why PP fits PPWR requirements:
-
PP is mono-material, enabling high sorting purity
-
Low carbon footprint due to lightweight properties
-
High heat resistance enabling reuse and durability
-
Extensive recycling systems across the EU
PP’s mechanical recyclability (and the growing demand for rPP) makes it a central material for Europe’s circular-economy transition.
2. Market Data: PP Remains One of Europe’s Most Important Polymers
2.1 EU Polymer Demand by Material (2023)
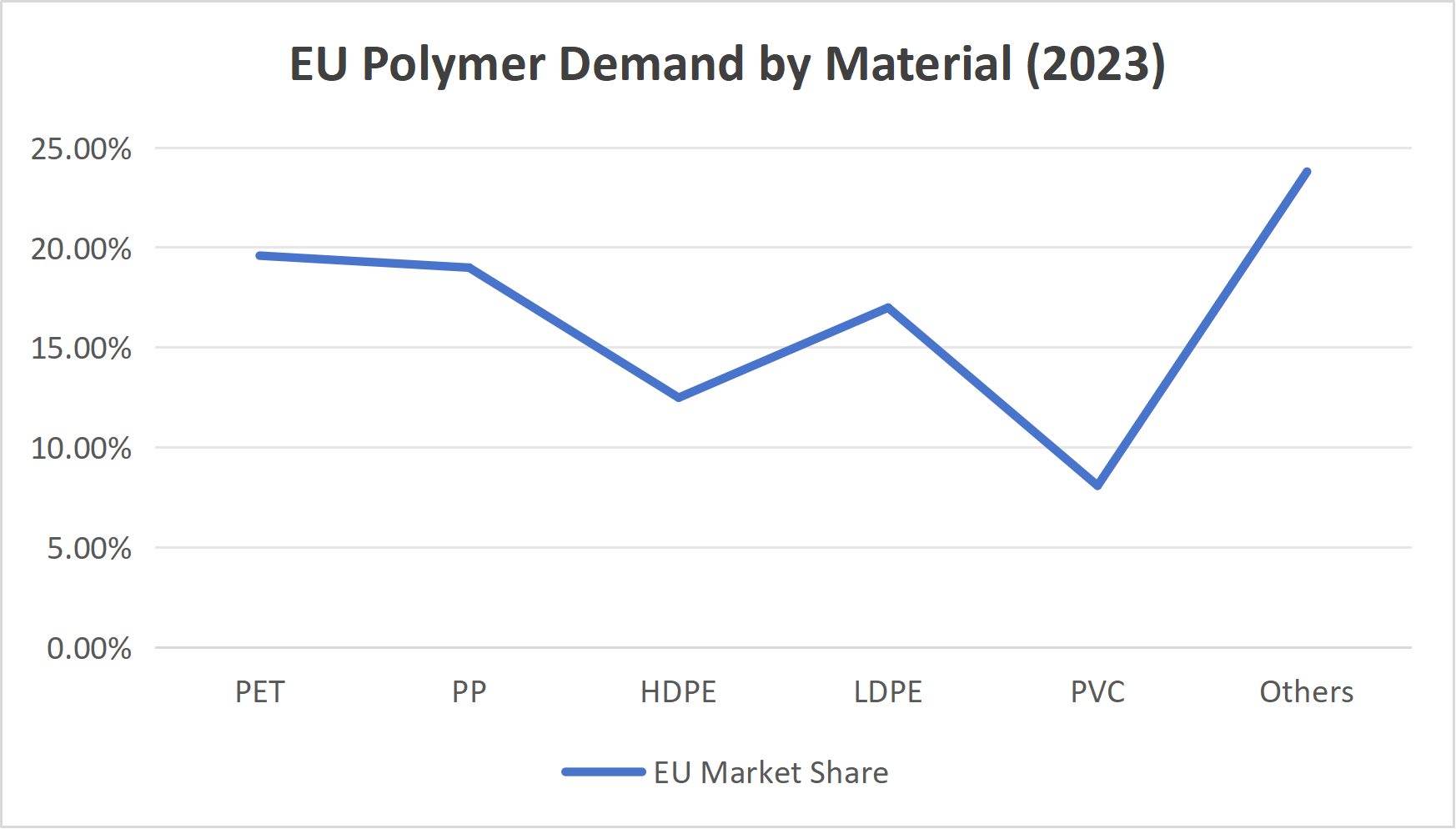
📌 PP is the second most demanded polymer in Europe, nearly equal to PET.
This demonstrates strong structural demand driven by:
-
Food packaging
-
Medical applications
-
Automotive parts
-
Household goods
PP remains a critical material for European industries.
2.2 EU Recycling Rates for PP (2018–2022)
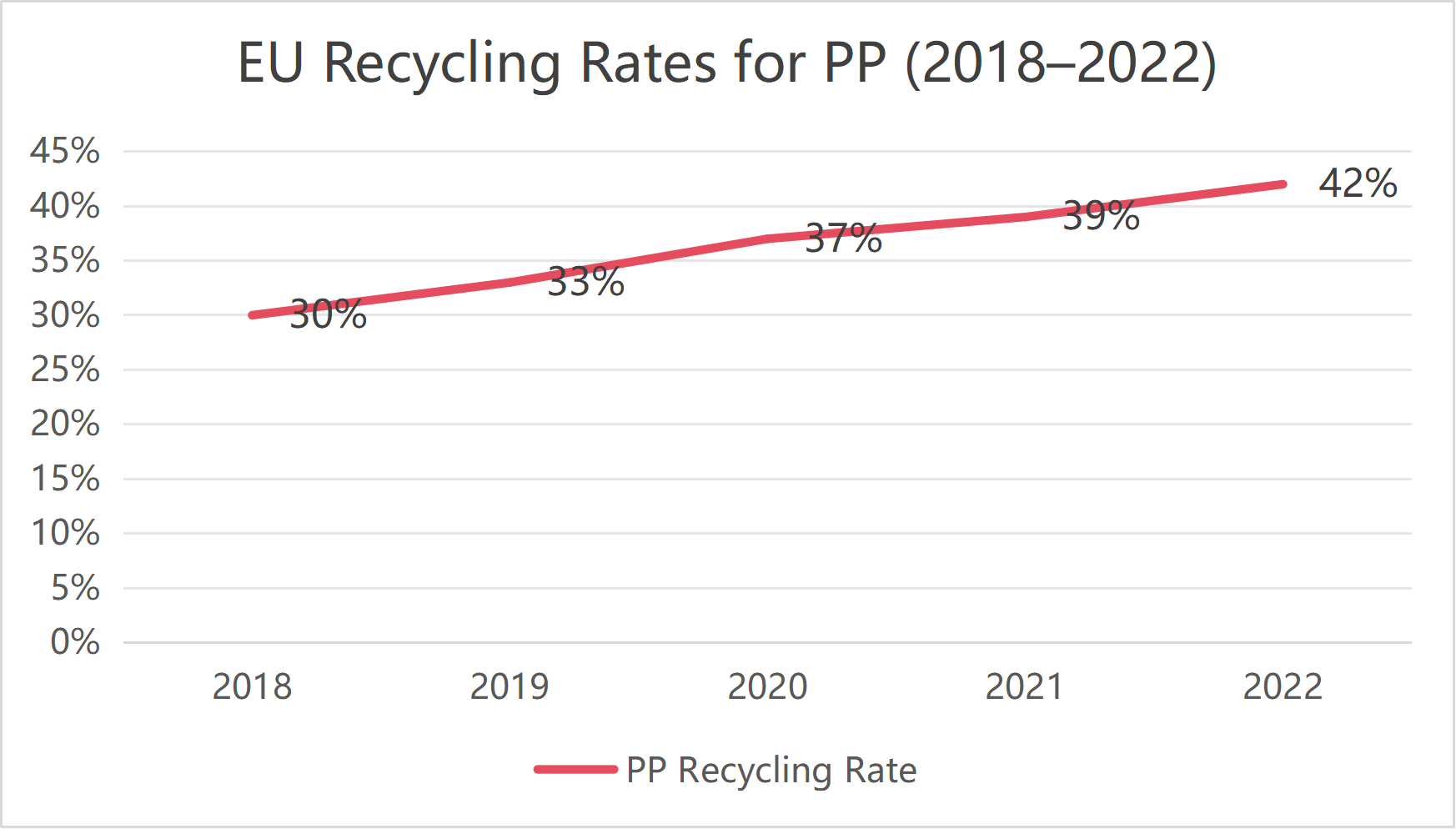
This steady rise reflects:
-
Enhanced recycling infrastructure
-
Higher collection rates
-
EU investments in mechanical recycling systems
By 2030, PP recycling rates are expected to exceed 50%, making it one of the fastest-improving materials in Europe.
2.3 PP Production in Europe
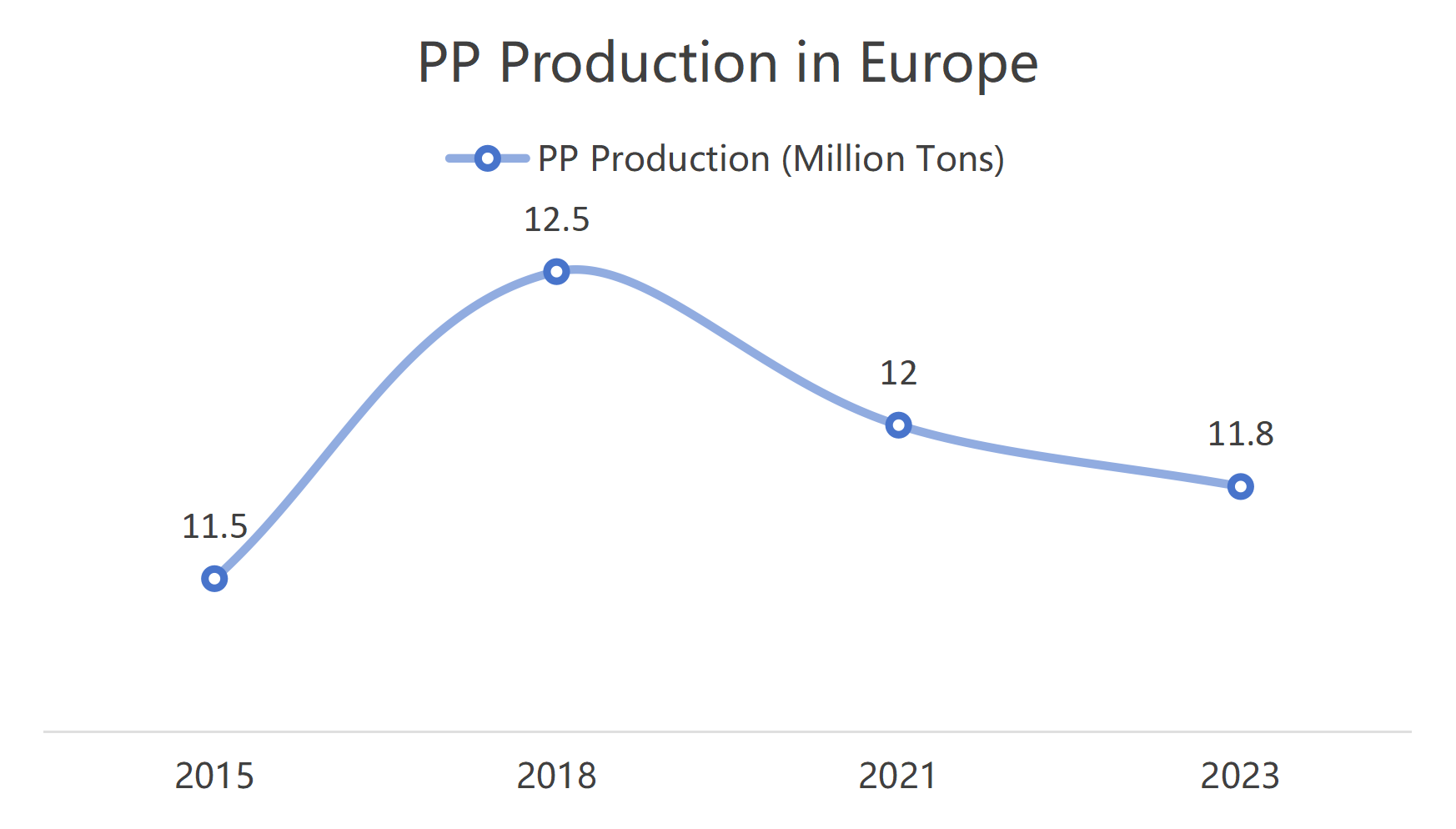
Despite policy pressures, PP demand remains stable due to its recyclability and cost-effectiveness.
3. Why the EU Still Strongly Supports PP
Europe’s sustainability agenda is not anti-plastic; it is anti-waste. PP aligns particularly well with EU policy targets.
3.1 Excellent Recyclability
PP is easier to recycle than mixed-material packaging due to:
-
Mono-material design
-
Ease of sorting
-
Lower contamination levels
Sorting lines in Germany, France, Spain, and the Netherlands consistently achieve 90–95% purity for PP streams.
3.2 Lightweight Composition → Reduced Carbon Footprint
Compared with PET, PP requires:
-
Less energy to produce
-
Less energy to transport
-
Less overall material weight
PP is one of the lowest-impact plastics per kg of packaged food.
3.3 Heat Resistance & Microwave Safety
PP remains stable under:
-
High temperatures
-
Microwave reheating
-
Hot-fill applications
This makes PP ideal for:
-
Microwaveable takeaway meals
-
Convenience foods
-
Airline catering
-
Meal delivery services
3.4 Proven Food-Contact Safety
PP is approved under:
-
EU 10/2011 for food contact
-
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)
-
US FDA
-
German BfR standards
It does not release hazardous chemicals under normal conditions.
4. PP vs PET vs PLA in the EU Market
PP is the most balanced, most versatile, and most compliant material under EU regulations.
5. DASHAN’s PP Product Line: Designed for EU Compliance & Market Demand
DASHAN’s portfolio aligns precisely with the EU’s shift toward recyclable, mono-material packaging.
5.1 PP Cups

-
Highly transparent options
-
Suitable for cold drinks, smoothies, fruit cups
-
Recyclable in standard PP streams
-
Compatible with PP or PET dome lids
EU Demand: Growing in convenience retail & beverage chains
5.2 PP Trays

Used widely for:
-
Ready-to-eat meals
-
Hot-food sections
-
Airline catering
-
Meal-prep brands
Featuring:
-
Microwave-safe design
-
Strong heat resistance
-
Lightweight structure
5.3 PP Plates

A sustainable alternative to PS plates:
-
Not banned under SUPD
-
Reusable
-
Lightweight
-
Strong rigidity
EU Demand: Catering, events, food courts
5.4 PP Clamshell Boxes

Ideal for:
-
Bakery items
-
Pastries
-
Produce
-
Takeaway meals
Benefits:
-
Clear or semi-clear visibility
-
Recyclable
-
Durable hinges
-
Grease and moisture resistance
5.5 PP Takeaway Food Containers
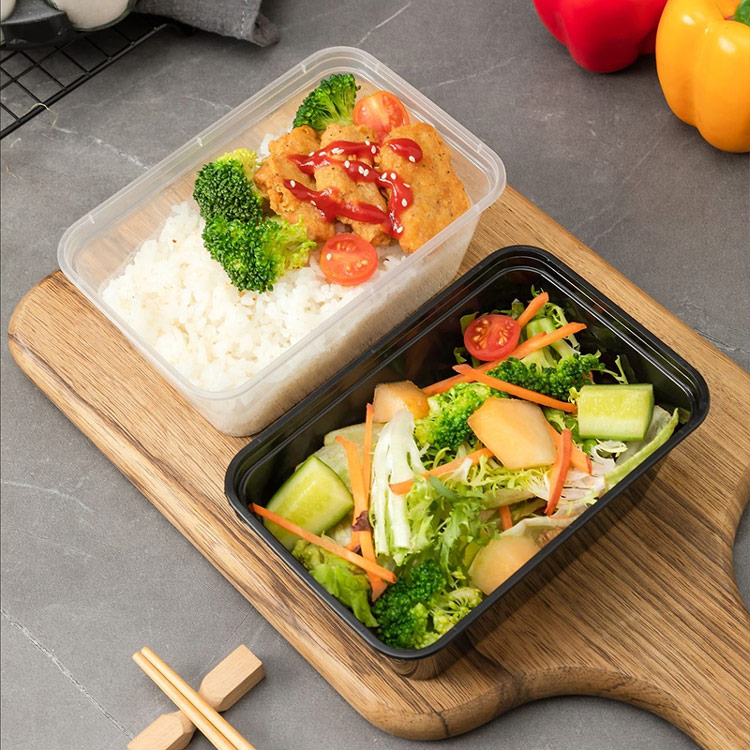

A high-growth category in Europe.
Perfect for:
-
Lunch boxes
-
Meal delivery
-
Restaurant takeout
-
Microwave reheating
EU buyers value:
-
Leak-resistant lids
-
Temperature versatility
-
Mono-material recyclability
5.6 PP Compartment Containers
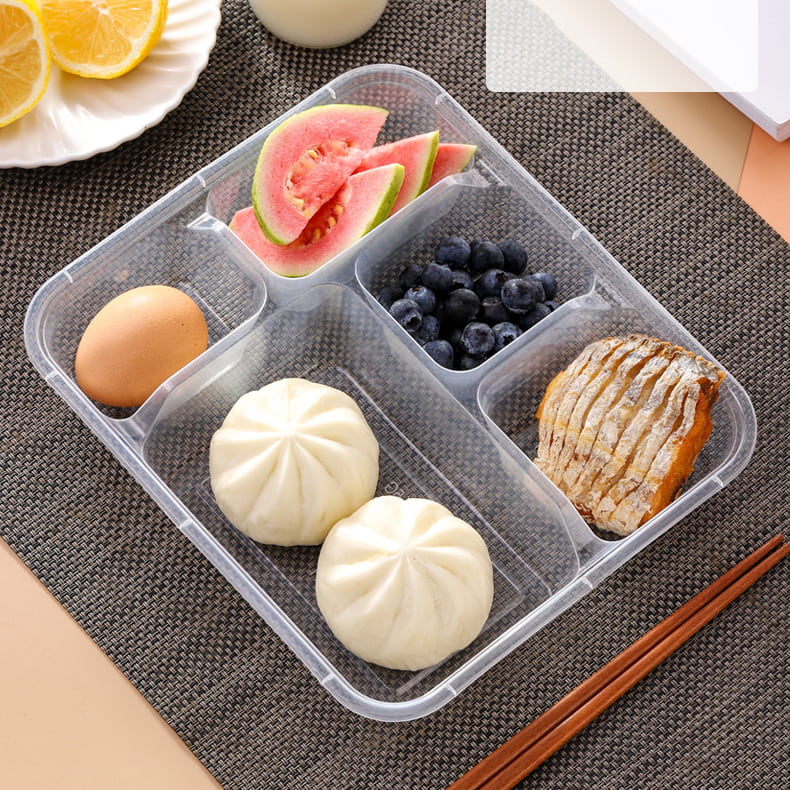

A preferred product for meal-prep programs:
-
2, 3, or 5 compartments
-
Perfect for portion control
-
Microwaveable
-
Airline & institutional catering
PP compartment trays offer better sustainability performance than PET multilayer trays.
5.7 PP Lids
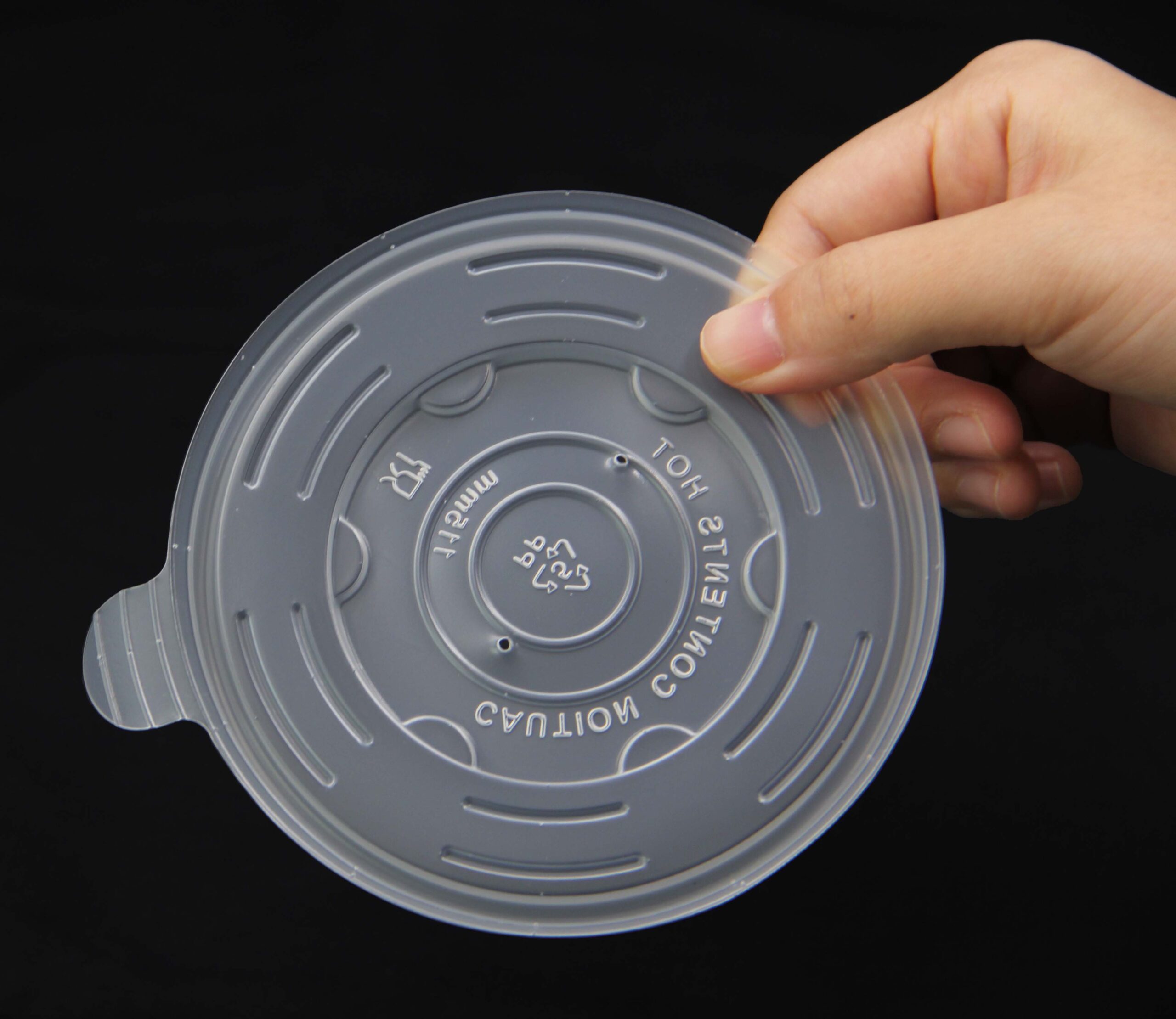

Compatible with:
-
PP bowls
-
PP trays
-
Bagasse bowls
-
PET containers
Benefits:
-
Secure sealing
-
Anti-fog options
-
Fully recyclable
This product category is essential for DTC meal brands and supermarket delis.
6. EU Market Opportunities for PP Packaging
6.1 Decline of PS & Multilayer Plastics
Policies are pushing companies to move away from:
-
Polystyrene (limited recyclability)
-
PET/PE laminated structures
-
Multilayer barrier trays
PP benefits directly from this shift.
6.2 Growth in Meal Delivery & Ready Meals
Europe’s ready-meal market grows 6–8% annually.
PP is the preferred material because:
-
It tolerates reheating
-
It maintains food quality
-
It is easy for consumers to recycle
6.3 Airlines & Travel Catering
Airlines require:
-
Lightweight
-
Cost-effective
-
High-temperature-resistant materials
PP airline trays and PP hot-meal containers remain the industry standard.
6.4 PP + Recycling Technology Advancements
New investments in:
-
Near-infrared (NIR) sorting
-
Chemical recycling
-
Food-grade rPP
will substantially raise PP recycling rates by 2030.
7. Why European Importers Choose DASHAN

✔ 20 years of manufacturing experience
✔ Participation in major international exhibitions
(Dubai, Russia, Malaysia, Thailand)
✔ Stable production capacity supporting large retail chains
✔ Expertise in PP formulations & food-contact compliance
✔ Customization for EU market standards
✔ Full product line covering all PP foodservice sectors
DASHAN is positioned as a trusted long-term partner for European distributors, wholesalers, supermarket groups, airline caterers, and foodservice brands.
FAQ
1. Why is polypropylene (PP) favored under EU packaging policies?
- Because PP is a recyclable mono-material that aligns with PPWR circular economy targets and can achieve the 2030 recyclability requirements more easily than multi-layer plastics.
2. Is PP allowed for food-contact applications in the EU?
- Yes. PP fully complies with EU Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 and (EU) No 10/2011 for food-contact plastics when manufactured under proper migration limits.
3. Does PP help companies meet EU circular economy goals?
- Yes. PP is easier to sort and recycle due to established recycling streams, supporting the EU’s 55% plastic recycling target by 2030.
4. Is PP considered environmentally friendly in the EU regulatory framework?
- While it is not biodegradable, PP is considered a “preferred recyclable plastic” because single-material PP packaging meets PPWR recyclability benchmarks.
5. Can PP replace banned single-use plastics under the EU SUP Directive?
- Yes. PP is not among the restricted materials under SUPD when used for food packaging, making it a common replacement for polystyrene (PS) and PVC.
6. What PP products are commonly accepted in EU markets?
- PP cups, trays, plates, clamshell boxes, takeaway containers, compartment food containers, and PP lids—all widely used for foodservice and retail.
7. What advantages does PP offer compared with PET or PLA?
- PP offers higher heat resistance, microwave safety, lower density, and excellent chemical stability—making it ideal for hot foods and takeaway meals.
8. How does DASHAN fit into the EU PP packaging market?
- DASHAN provides PP cups, trays, plates, clamshell boxes, lids, and multi-compartment containers manufactured to EU food-contact and sustainability standards.
Conclusion
EU sustainability policies do not restrict polypropylene; instead, the EU views PP as a key recyclable material aligned with its circular-economy goals. With strong recyclability, excellent heat resistance, food safety approval, and stable cost, PP is expected to remain central to Europe’s food-packaging system throughout the next decade.
DASHAN’s PP portfolio—covering PP cups, trays, plates, clamshell boxes, takeaway containers, compartment food containers, and PP lids—offers a comprehensive, regulation-ready solution for brands seeking reliable and compliant packaging in the EU market.
For companies targeting Europe, strategically adopting high-quality PP packaging is not just a regulatory necessity—it is a competitive advantage.
📚 References
-
European Commission – Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR)
https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/waste-and-recycling/packaging-waste_en -
EU Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD)
https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/plastics/single-use-plastics_en -
EU Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on Food-Contact Plastics
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2011/10 -
Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 – Materials in Contact With Food
-
Plastics Europe – Polypropylene Market Report
-
European Recycling Industries’ Confederation – PP Recycling Overview
-
CEFLEX – Designing PP Packaging for Circularity
https://ceflex.eu/ -
Ellen MacArthur Foundation – Recyclable Plastics Framework
https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.





