Quick Summary
Eco-friendly takeout packaging made from cornstarch and bagasse provides a sustainable alternative to single-use plastics. Biodegradable, compostable, and food-safe, these materials reduce environmental impact while supporting consumer and brand responsibility.

Introduction
In the age of convenience, takeout meals have become a staple in our daily lives. Whether it’s grabbing a quick lunch during work or ordering dinner on a cozy night in, food delivery has transformed the way we eat. However, with the rise of convenience comes a surge in waste—particularly single-use plastics, which have devastating environmental impacts.
Plastic containers, cutlery, and bags often end up in landfills, oceans, and rivers, taking hundreds of years to decompose. Even worse, they contribute to microplastic pollution, harming marine life and entering the food chain. The urgency to address this issue has never been greater. Consumers, restaurants, and foodservice providers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly alternatives that reduce waste while maintaining convenience.
Among the most promising solutions are cornstarch-based and bagasse-based packaging. These biodegradable materials offer a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics without compromising durability or functionality. This article explores why switching to these eco-friendly takeout solutions is essential, how they work, and what benefits they bring to both the environment and businesses.
The Environmental Problem with Traditional Takeout Packaging
Plastic has been the go-to material for takeout containers for decades. Lightweight, cheap, and sturdy, it seems like a perfect solution. Yet, the environmental cost is immense.
-
Persistence in the environment: Conventional plastics can take 400–500 years to break down. During this time, they fragment into microplastics that infiltrate soil, water, and food chains.
-
Wildlife hazards: Marine animals often mistake plastic for food, leading to ingestion, injury, or death. Birds, fish, and turtles are particularly at risk.
-
Carbon footprint: Producing plastic involves fossil fuels and releases greenhouse gases, further exacerbating climate change.
With the global takeout market booming, millions of plastic containers are discarded every day. Switching to biodegradable alternatives like cornstarch and bagasse can drastically reduce this environmental burden.
Cornstarch Packaging: Nature’s Polysaccharide Solution
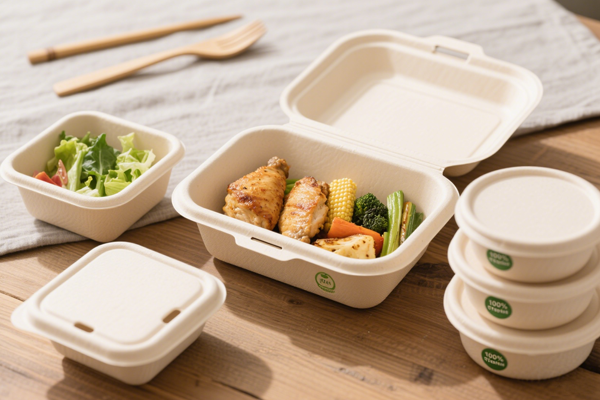

Cornstarch is a natural polymer extracted from corn kernels. Its application in food packaging has grown rapidly due to its biodegradability and versatility.
How Cornstarch Packaging Works
Cornstarch-based containers are typically made by converting starch into a thermoplastic material, which can be molded into plates, bowls, cups, and cutlery. Once exposed to composting conditions or soil, microbes break down the starch into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass—leaving no harmful residue behind.
Advantages of Cornstarch Packaging
-
Biodegradable and Compostable: Unlike conventional plastic, cornstarch packaging decomposes naturally, often within 60–180 days in composting facilities.
-
Safe for Food: Cornstarch is non-toxic and food-safe, suitable for hot or cold dishes.
-
Durable: Modern cornstarch containers are heat-resistant and sturdy enough for takeout meals, soups, and sauces.
-
Eco-Conscious Branding: Restaurants can highlight their sustainable practices by using cornstarch packaging, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Applications
Cornstarch packaging is ideal for:
-
Single-use plates, bowls, and trays
-
Disposable cutlery (spoons, forks, knives)
-
Food delivery boxes
-
Coffee cups and lids (for cold drinks)
Bagasse Packaging: A Sugarcane Byproduct with a Purpose
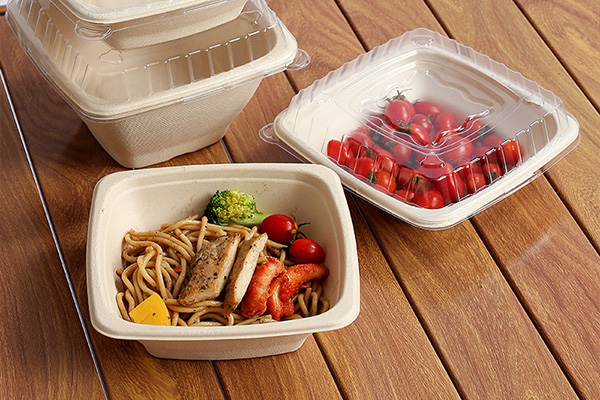

Bagasse is the fibrous residue left after extracting juice from sugarcane. Once considered waste, bagasse has emerged as a versatile material for sustainable packaging.
How Bagasse Packaging Works
Bagasse is processed into pulp, then molded into trays, plates, and clamshell boxes. Like cornstarch, it is fully biodegradable and compostable. Its natural fibers make it exceptionally strong and heat-resistant.
Advantages of Bagasse Packaging
-
High Heat Resistance: Suitable for hot meals and microwaving without deforming.
-
Moisture and Grease Resistant: Ideal for oily or saucy dishes.
-
Compostable and Sustainable: Bagasse decomposes naturally in composting conditions, reducing landfill waste.
-
Eco-Friendly Image: Using bagasse signals commitment to sustainability and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Applications
Bagasse packaging works well for:
-
Takeout containers with compartments
-
Lids and clamshell boxes
-
Dessert cups and trays
-
Plates for casual dining and catering
Benefits of Switching to Cornstarch and Bagasse Packaging
Environmental Impact
Switching from plastic to cornstarch or bagasse packaging can significantly reduce:
-
Plastic waste in landfills
-
Ocean and river pollution
-
Carbon footprint from fossil fuel extraction and processing
Health and Safety
Biodegradable materials are typically non-toxic, free from harmful chemicals such as PFAS, BPA, or PFOA, and safe for food contact.
Consumer Perception
Restaurants and food delivery services using eco-friendly packaging can enhance brand loyalty. A growing number of consumers actively seek businesses that demonstrate environmental responsibility.
Regulatory Compliance
With global policies increasingly targeting single-use plastics, adopting cornstarch and bagasse packaging helps businesses stay ahead of regulations and reduce the risk of penalties.
Challenges and Considerations
While biodegradable packaging has many advantages, there are some considerations:
-
Composting Infrastructure: Biodegradable products require proper composting conditions. Improper disposal may limit environmental benefits.
-
Cost: Cornstarch and bagasse packaging can be slightly more expensive than conventional plastics, though the price gap is narrowing.
-
Consumer Education: Customers may need guidance on how to dispose of packaging properly to ensure it breaks down as intended.
Despite these challenges, the long-term benefits for the planet and business reputation outweigh the drawbacks.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Restaurants Going Green
Many foodservice brands worldwide have embraced cornstarch and bagasse packaging:
-
Fast-casual restaurants in North America and Europe offer 100% biodegradable takeout boxes.
-
Coffee shops use cornstarch cups and bagasse lids to replace traditional plastic options.
-
Catering companies have switched to compartmentalized bagasse trays, reducing single-use plastic consumption by up to 80%.
Consumer Adoption
A survey showed that 72% of consumers are willing to pay a small premium for eco-friendly takeout containers, demonstrating the market potential for biodegradable packaging.
Tips for Restaurants and Consumers
-
Choose Certified Biodegradable Products: Look for products certified compostable according to standards such as ASTM D6400 or EN 13432.
-
Educate Staff and Customers: Place disposal instructions on packaging to encourage correct composting.
-
Integrate Branding: Customize biodegradable packaging with logos or messages to highlight your eco-conscious approach.
-
Evaluate Product Performance: Ensure packaging meets requirements for heat, grease, and durability before full adoption.
FAQ
-
What is cornstarch packaging?
Cornstarch packaging is made from natural starch extracted from corn. It is biodegradable, compostable, and safe for hot or cold food. -
What is bagasse packaging?
Bagasse packaging comes from sugarcane fibers left after juice extraction. It is strong, heat-resistant, and fully compostable. -
Are biodegradable containers as durable as plastic?
Modern cornstarch and bagasse containers are designed for durability, heat resistance, and moisture control, comparable to many single-use plastics. -
Can I microwave or heat food in bagasse containers?
Yes, bagasse containers are typically safe for microwaving and can handle hot, oily, or saucy foods. -
How should I dispose of cornstarch and bagasse products?
Ideally, compost in an industrial or home compost facility. If composting is unavailable, they can be discarded in organic waste bins, though full degradation may take longer. -
Are these materials environmentally safe if they end up in landfills?
They degrade faster than plastic, though composting is optimal. Their environmental footprint is still lower than traditional plastics. -
Do these containers contain chemicals like PFAS, BPA, or PFOA?
No. Cornstarch and bagasse products are free from these harmful chemicals, making them safe for food contact.References
-
“Biodegradable Plastics and Marine Litter” – United Nations Environment Programme
https://www.unep.org/resources/report/biodegradable-plastics-and-marine-litter -
“Cornstarch Packaging Market Overview” – MarketsandMarkets
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/cornstarch-packaging-market-2275809.html -
“Bagasse Packaging for Food Industry” – Food Packaging Forum
https://www.foodpackagingforum.org/food-packaging-health/bagasse-packaging -
“Consumer Attitudes Towards Eco-Friendly Packaging” – Nielsen
https://www.nielsen.com/us/en/insights/report/2021/sustainable-packaging-consumer-trends -
“Industrial Composting and Foodservice Packaging” – ASTM D6400 Standard
https://www.astm.org/d6400-21.html
-