Quick Summary
Bagasse plates are made from natural sugarcane fiber, offering high strength, heat resistance, and food safety for both hot and cold dishes. Tested for global standards, DASHAN’s bagasse products combine eco-friendliness with professional durability and compostability.
Introduction: The Shift Toward Eco-Friendly Tablewar
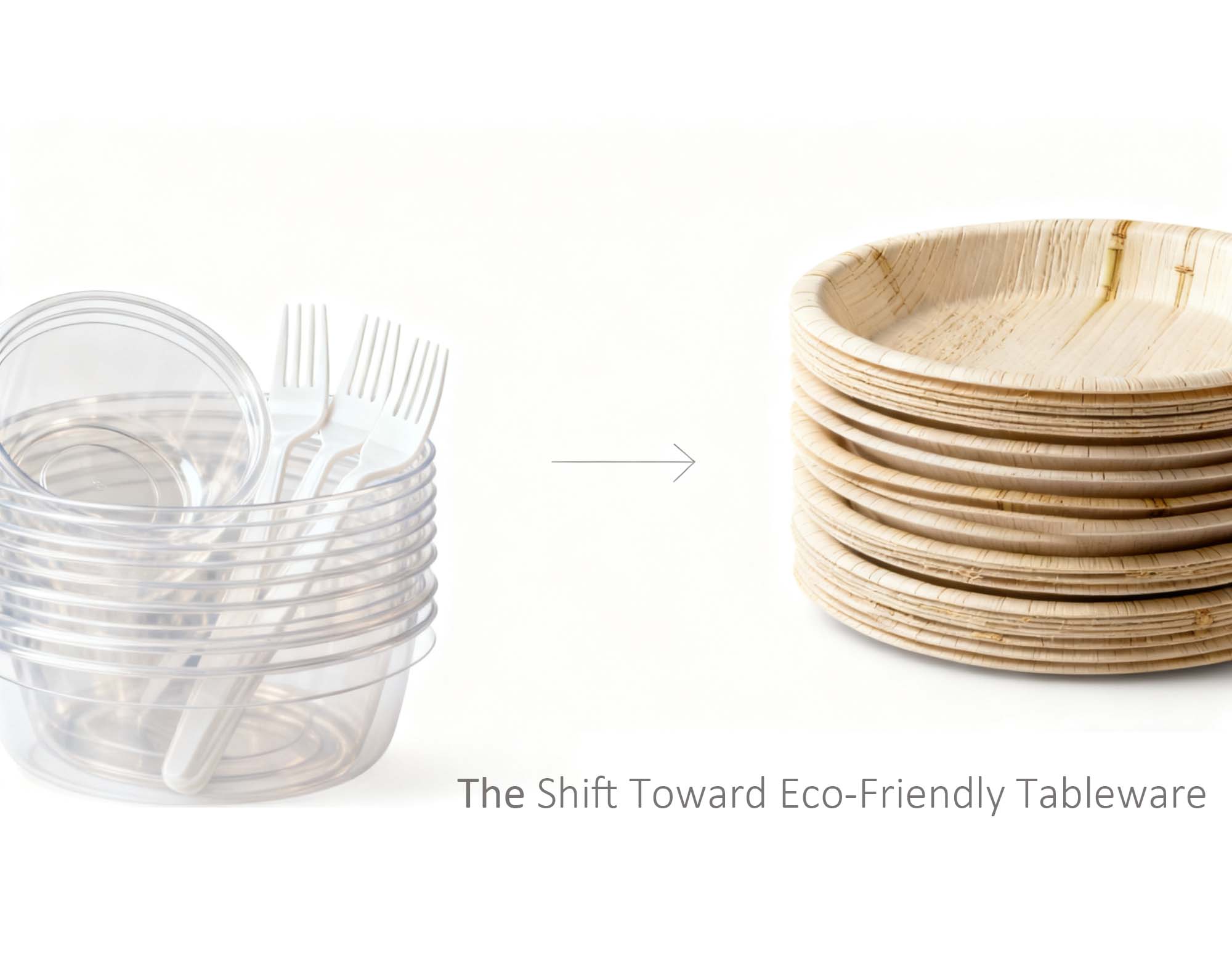

As the global foodservice industry transitions toward sustainable materials, sugarcane bagasse products have emerged as one of the leading alternatives to single-use plastics. Governments worldwide—from the EU and the UK to Canada, Australia, and parts of Asia—have enforced bans or restrictions on disposable plastics.
In this changing landscape, bagasse plates have gained traction for their natural composition, biodegradability, and surprisingly strong performance in real-world food applications.
Yet, a common question remains: How durable and safe are bagasse plates when used with hot or cold foods? This article explores the material science behind bagasse, its thermal and mechanical stability, and how manufacturers like DASHAN ensure consistent safety and reliability through advanced forming and quality systems.
What Is Bagasse? The Natural Fiber Behind the Innovation

Bagasse is the fibrous residue left after sugarcane stalks are crushed to extract juice. Instead of being discarded or burned, it is now upcycled into high-performance tableware and food packaging.
This cellulose-rich material is renewable, compostable, and carbon-neutral, offering a circular alternative to fossil-based plastics.
When pressed under heat and pressure, the fibers bind naturally, forming a dense and sturdy structure—without requiring synthetic binders. The result is a lightweight, strong, and eco-friendly material ideal for disposable food containers.
Key Properties of Bagasse Material
-
100% biodegradable and compostable within 45–90 days
-
Free from BPA, PFAS, and other toxic substances
-
Excellent water and oil resistance
-
Naturally off-white, smooth texture suitable for direct food contact
These features make bagasse an excellent base material for plates, bowls, trays, and clamshells used in restaurants, catering, and retail packaging.
Strength and Durability: More Than Meets the Eye
Bagasse may look delicate due to its plant origin, but its fiber matrix structure gives it surprising mechanical strength.
The long sugarcane fibers interlock under thermo-pressure, resulting in a solid, rigid body with minimal flex. Modern forming techniques have further improved density and impact resistance.
Durability in Real-World Conditions
-
Stacking Strength: Bagasse plates can withstand considerable stacking weight during transport without bending.
-
Impact Resistance: Drop and vibration tests show stability comparable to light plastic trays.
-
Moisture Resistance: When used for wet dishes like curries or salads, properly pressed bagasse plates maintain structural integrity for over 3 hours without leakage.
At DASHAN, products are tested for compression load and flexural resistance to ensure consistent durability across different plate sizes and weights.
Heat Resistance and Cold Tolerance
Handling Hot Foods
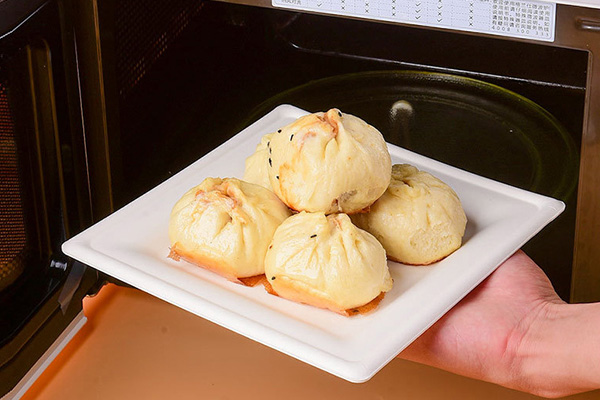

One of bagasse’s major advantages is its ability to withstand high temperatures.
Unlike paper plates that soften or deform, bagasse plates remain stable at temperatures up to 100–120°C (212–248°F). They are safe for serving hot meals, soups, and fried dishes.
Bagasse can also handle microwave reheating (typically up to 3 minutes at 800W) and short-term oven use below 200°C. This makes them suitable for ready-to-eat meals, catering, and takeaway applications.
Cold and Frozen Food Applications
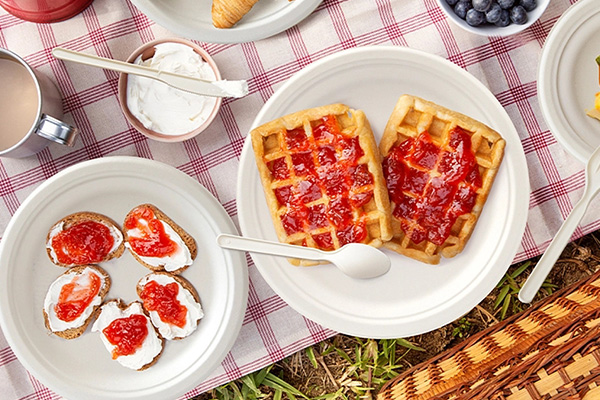

Bagasse products also perform well in low-temperature conditions, capable of resisting deformation or brittleness down to –20°C (–4°F).
This means they can safely hold frozen desserts, salads, and refrigerated foods without condensation damage.
| Temperature Range | Performance | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| –20°C to 0°C | No cracking or deformation | Ice cream, fruit salad |
| 0°C to 100°C | Stable structure | Hot meals, soups |
| 100°C–120°C (short-term) | Maintains rigidity | Oven & microwave reheating |
Water and Oil Resistance: The Science Behind Non-Leak Performance
Bagasse’s dense fiber network naturally provides a moderate barrier against moisture and oil.
During production, plates are thermo-pressed at high pressure, reducing porosity and sealing microscopic gaps. Some high-performance designs use a natural plant-based coating to enhance resistance to greasy foods.
Compared with paper or foam plates, bagasse tableware demonstrates:
-
2–3x longer resistance to oil penetration
-
4–5x greater moisture resistance under hot food conditions
-
Zero layer delamination when exposed to steam
These characteristics allow bagasse plates to safely hold curries, stir-fried noodles, sauces, and even soups.
Food Safety and Chemical Stability
For any food packaging, safety is as important as functionality.
Bagasse is a natural, food-grade material, free from petroleum-based chemicals. When properly manufactured, it contains no BPA, PFAS, heavy metals, or fluorescent agents.
It emits no toxic fumes when exposed to heat, ensuring safety even when used in microwaves.
Regulatory Certifications
Most high-quality bagasse products comply with:
-
FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) standards
-
EU Food Contact Regulations (EC No. 1935/2004)
-
LFGB (Germany Food Contact Law)
DASHAN’s bagasse trays and plates undergo strict QC checks and are batch-tested for heavy metal content, migration limits, and microbiological safety.
This commitment ensures that every product leaving the factory meets international food safety and hygiene standards.
Compostability and Environmental Impact
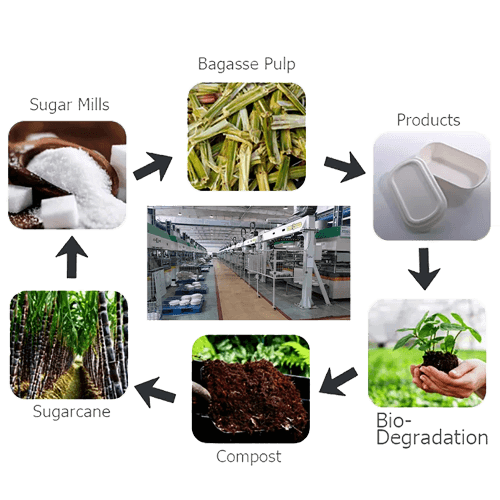

After use, bagasse plates can be composted in industrial facilities or home compost bins.
Under controlled conditions, they typically decompose within 45–90 days, returning to the soil as organic matter.
Compared to traditional plastics:
-
Bagasse reduces CO₂ emissions by over 60% during production.
-
Its carbon footprint is nearly neutral since sugarcane absorbs CO₂ during growth.
-
The material helps divert agricultural waste from burning, thus reducing air pollution.
By switching to bagasse, food businesses can significantly improve their sustainability profiles and meet consumer expectations for eco-friendly packaging.
Common Misconceptions About Bagasse Plates
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Bagasse plates become soggy with hot soup | High-density bagasse resists moisture for several hours |
| They can’t be microwaved | Safe for microwaves and ovens within recommended limits |
| Only suitable for dry foods | Effective for oily or saucy meals with zero leakage |
| Not strong enough for catering | Tested to handle large portion sizes and stacking loads |
Bagasse’s performance is comparable to PET and PP in practical foodservice environments while offering full compostability.
Practical Applications Across Industries
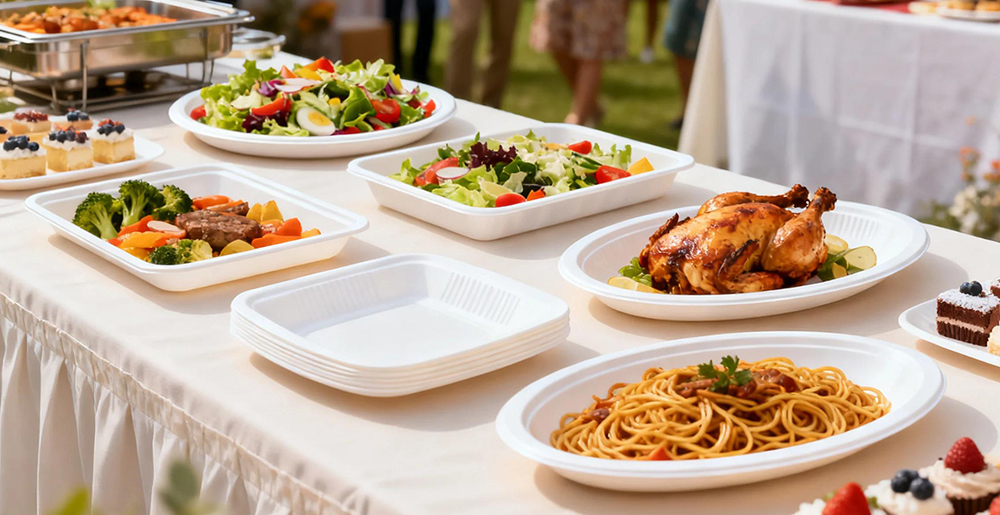

Bagasse plates and trays are now standard across:
-
Restaurants & Cafés – for dine-in and takeaway use
-
Catering Services & Airlines – lightweight, eco-safe serving options
-
Supermarkets – ready meal and salad packaging
-
Events & Festivals – disposable, biodegradable tableware
-
Frozen Food Suppliers – cold-resistant meal bases
DASHAN’s Expertise in Bagasse Tableware

With years of manufacturing experience, DASHAN combines advanced pulp-molding and thermoforming technologies to produce strong, safe, and elegant bagasse plates.
Each product line undergoes continuous testing for temperature tolerance, moisture barrier performance, and load strength.
DASHAN also provides custom OEM/ODM services—from mold design and embossing to export logistics—to serve clients in over 50 countries worldwide.
FAQ
1. Can bagasse plates hold hot soup?
Yes. Quality bagasse plates can safely handle hot liquids up to 100–120°C without deforming.
2. Are bagasse plates microwave safe?
Yes, they can be microwaved for up to 3 minutes (800W). Always avoid over-heating beyond recommended time.
3. Do bagasse plates leak with oily food?
No. DASHAN’s thermo-pressed bagasse plates maintain oil resistance for several hours.
4. Can bagasse plates be used for frozen desserts?
Yes. They remain stable at –20°C, perfect for ice cream or chilled dishes.
5. Are bagasse plates compostable at home?
Yes. Under natural composting conditions, they break down completely within 90 days.
Conclusion
Bagasse plates represent a perfect balance of durability, safety, and sustainability. They can handle both hot and cold dishes without leaking or deforming, meet stringent food safety standards, and return to nature through composting.
For businesses seeking a reliable eco-packaging solution, DASHAN’s bagasse tableware delivers proven performance backed by certified manufacturing and global expertise—making it the smart choice for the future of sustainable dining.
🔗 References
-
Hossam, Y. & Fahim, I. S. (2023).
“Towards a circular economy: fabrication and characterization of biodegradable plates from sugarcane waste.”
Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2023.1220324/full -
Liu, C., Xu, H., & Zhang, J. (2020).
“Biodegradable, hygienic, and compostable tableware from sugarcane bagasse.”
Journal of Cleaner Production, Elsevier.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590238520305580 -
Khoisnam, N. et al. (2024).
“Eco-Conscious Packaging: Exploring Sugarcane Bagasse Tableware.”
E3S Web of Conferences, 495, 01013.
https://www.e3s-conferences.org/articles/e3sconf/pdf/2024/86/e3sconf_rawmu2024_01013.pdf -
Zhu, Y., Wang, X., & Lin, Z. (2022).
“Performance evaluation of molded fiber packaging products derived from sugarcane bagasse.”
Packaging Technology and Science, Wiley Online Library.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/pts.2745 -
Sharma, A., Singh, B., & Dutta, P. (2021).
“Thermal and mechanical properties of eco-friendly bagasse-based molded food containers.”
Materials Today: Proceedings.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214785321009847 -
USDA (2023).
“Sugarcane Bagasse as a Renewable Source for Bioproducts and Packaging.”
United States Department of Agriculture BioPreferred Program.
https://www.biopreferred.gov/BioPreferred/faces/pages/ProductCategories.xhtml -
FAO (2024).
“The Future of Biodegradable Food Packaging Materials.”
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
https://www.fao.org/3/cc8207en/cc8207en.pdf -
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). (2023).
“Safety assessment of sugarcane bagasse food contact materials.”
EFSA Journal, Vol. 21(4), e08045.
https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8045 -
Singh, R. & Kumar, P. (2022).
“Moisture and oil resistance enhancement in molded bagasse tableware through mechanical densification.”
Journal of Polymers and the Environment.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10924-022-02478-8 -
Chen, H. & Li, W. (2023).
“Compostability evaluation of bagasse fiber products under simulated home and industrial composting conditions.”
Waste Management, Elsevier.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956053X23000987
Copyright Statement
© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.
All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,
and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this content
without written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information and
to upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.