Quick Summary
RPET Food Packaging is made from recycled PET bottles and containers through a closed-loop process of collection, sorting, cleaning, shredding, and pelletizing. This sustainable packaging reduces plastic waste, lowers carbon emissions, and supports a circular economy while remaining safe for direct food contact. Its versatility allows it to be used for cups, trays, clamshell boxes, and bottles in foodservice and retail. With growing consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions and stricter global regulations, RPET Food Packaging is emerging as a cost-effective, sustainable, and future-proof choice for businesses worldwide.
Introduction: Closing the Loop in Food Packaging
Plastic pollution remains one of the world’s most pressing environmental challenges. Every year, millions of tons of single-use packaging enter landfills or leak into oceans, creating long-term waste problems. Yet, in this crisis lies an opportunity—RPET Food Packaging is emerging as a key solution for building a circular economy in the food and beverage industry.
Unlike traditional plastics, RPET Food Packaging is made from recycled PET bottles and containers. This process gives waste a second life, reducing environmental impact while maintaining food safety. The result is a sustainable packaging solution trusted by restaurants, retailers, and brands worldwide.
This blog explores the recycling process behind RPET Food Packaging and highlights why it is becoming the preferred choice for modern businesses.

Part 1: The Recycling Process of RPET Food Packaging
Transforming waste into RPET Food Packaging requires a well-structured recycling system. The process involves six main stages:
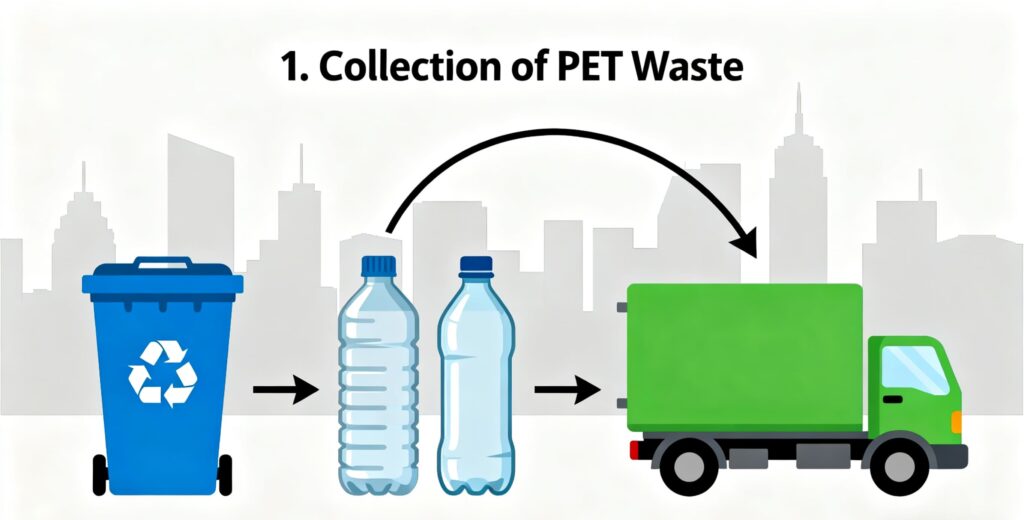
1. Collection of PET Waste
The journey begins with the collection of post-consumer PET bottles, cups, and trays. These are the building blocks of RPET Food Packaging. Municipal recycling programs, deposit return schemes, and private recycling systems ensure that PET waste is gathered at scale.
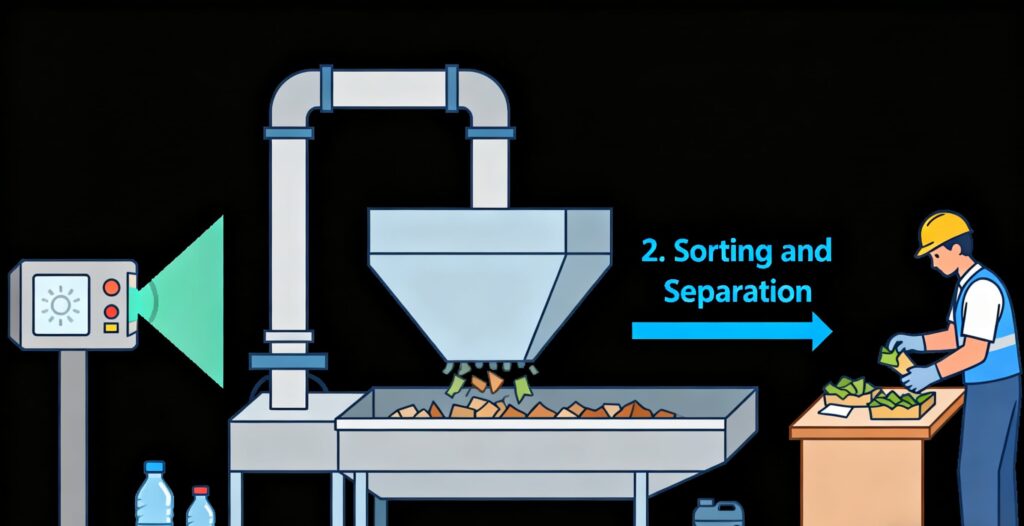
2. Sorting and Separation
At material recovery facilities, PET is separated from other plastics. Advanced systems such as infrared sensors, air classifiers, and manual checks ensure the waste destined for RPET Food Packaging is free from impurities.
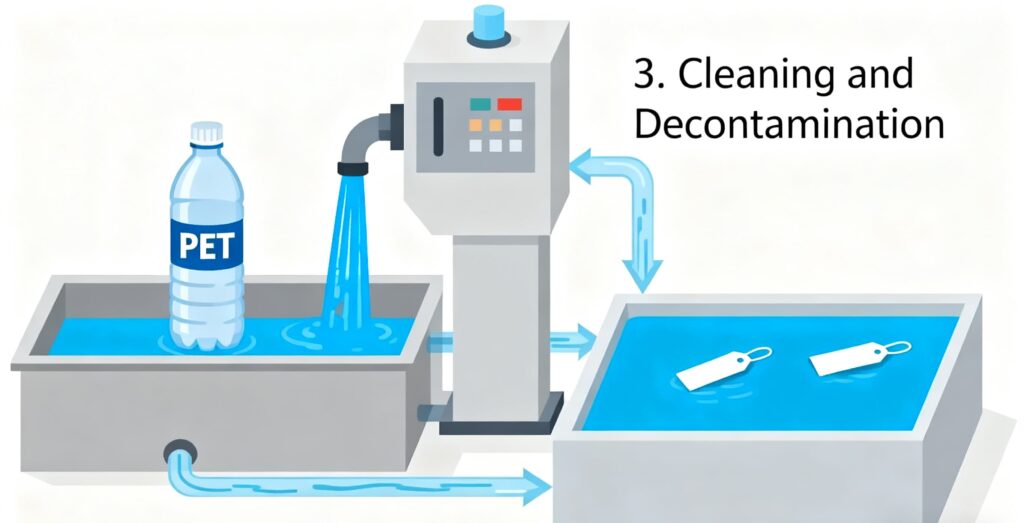
3. Cleaning and Decontamination
The PET goes through hot water washing, detergents, and flotation tanks to remove labels, adhesives, and food residues. This step is critical for creating food-grade RPET material that complies with strict safety standards for RPET Food Packaging.
4. Shredding into Flakes
Clean PET is shredded into flakes, which serve as the raw input for RPET Food Packaging. Flakes are easier to transport, process, and further purify.

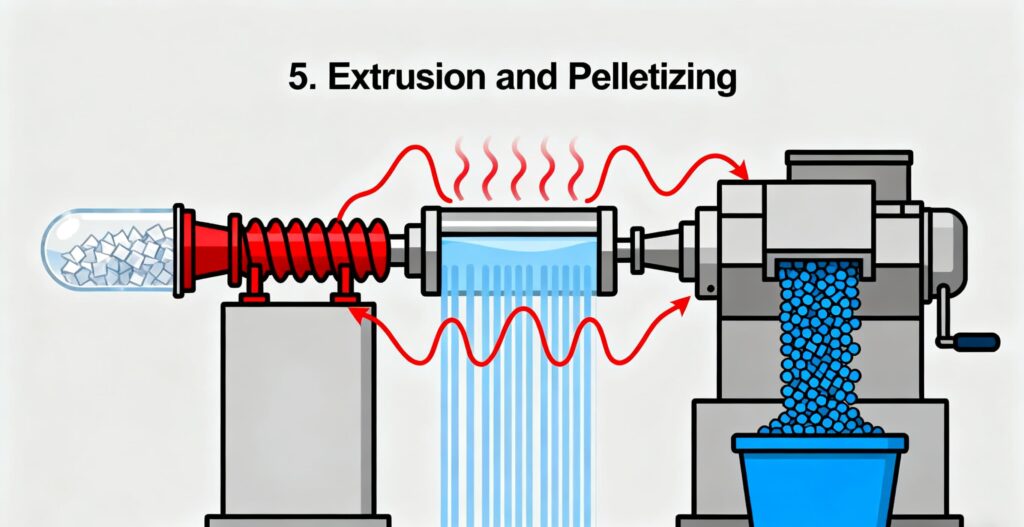
5. Extrusion and Pelletizing
Flakes are melted, purified, and converted into RPET pellets. These pellets are the foundation of RPET Food Packaging products like trays, bottles, and cups. Technologies such as solid-state polymerization help restore strength and quality, ensuring the packaging is durable.
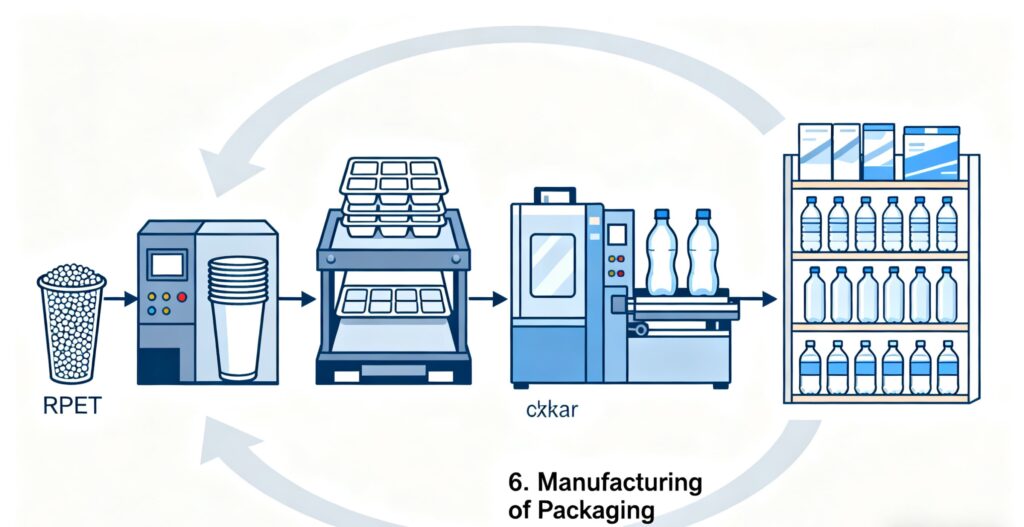
6. Manufacturing of Packaging
Finally, RPET pellets are molded through processes like thermoforming, injection molding, and blow molding to create cups, clamshell boxes, and trays. This stage completes the closed-loop system, turning waste into new RPET Food Packaging ready for consumers.
Part 2: The Benefits of RPET Food Packaging
The popularity of RPET Food Packaging is rising because it delivers benefits for the environment, businesses, and consumers alike.
1. Environmental Benefits
-
Waste Reduction: RPET Food Packaging prevents millions of tons of plastic from entering landfills or oceans.
-
Lower Carbon Emissions: Producing RPET uses up to 79% less energy compared to virgin plastic.
-
Supports Circular Economy: Continuous recycling creates a closed-loop packaging system.
2. Food Safety and Quality
Consumers often wonder if recycled plastic is safe. The answer is yes—RPET Food Packaging complies with global safety standards such as FDA and EFSA regulations. It ensures no harmful substances remain after recycling, making it completely safe for direct food contact.
3. Versatility in Design
From sushi trays to salad bowls, RPET Food Packaging can be manufactured in various shapes, sizes, and colors. Its transparency makes food look fresh, while tinted and metallic options (gold, silver, black) enhance presentation.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
Compared with biodegradable materials like PLA or bagasse, RPET Food Packaging remains one of the most cost-effective eco-friendly options. Its widespread availability keeps prices stable for businesses.
5. Consumer Appeal and Brand Reputation
Today’s eco-conscious customers prefer brands using recycled and recyclable packaging. RPET Food Packaging helps companies show responsibility, attract green-minded customers, and improve overall brand image.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Many governments are mandating the use of recycled plastic in packaging. By adopting RPET Food Packaging, companies can meet these requirements and avoid penalties while also preparing for stricter sustainability laws.
Part 3: Real-World Applications of RPET Food Packaging
RPET Food Packaging is widely used across foodservice, retail, and catering:
-
Cups and Lids: Ideal for smoothies, iced coffee, and soft drinks.
-
Clamshell Boxes: Perfect for fresh fruit, bakery goods, and takeaway meals.
-
Trays: Used for sushi, desserts, and ready-to-eat meals.
-
Bottles: Water, juice, and other beverages rely heavily on RPET.
For example, Xiamen Dashan specializes in customizable RPET Food Packaging designed for both durability and sustainability, making it a trusted partner for global food brands.
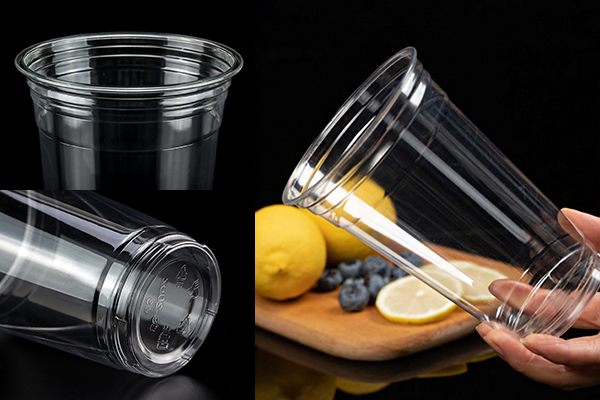

Part 4: Challenges and the Future of RPET Food Packaging
While RPET Food Packaging has clear advantages, challenges remain:
-
Recycling Infrastructure: Not all regions have efficient PET collection systems.
-
Quality Variation: Contamination in recycling can impact the quality of RPET.
-
Consumer Behavior: Effective recycling requires consumers to dispose of PET packaging properly.
The future looks promising, however. Chemical recycling and advanced decontamination technologies are making RPET Food Packaging even more reliable. Governments are also investing in recycling infrastructure to meet rising demand.
FAQ
-
What is RPET Food Packaging made from?
RPET Food Packaging is made from recycled PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) bottles and containers. The recycling process turns post-consumer plastic waste into new, food-safe packaging products such as cups, trays, and clamshell boxes. -
Is RPET Food Packaging safe for food contact?
Yes, RPET Food Packaging complies with international food safety regulations, such as those from the FDA and EFSA. The recycling process ensures that harmful substances are removed, making RPET safe for direct contact with food. -
How does RPET contribute to sustainability?
RPET helps reduce plastic waste by reusing PET material in the packaging production process. It lowers carbon emissions by up to 79% compared to virgin plastic and supports a circular economy by promoting continuous recycling and reducing landfill waste. -
Can RPET Food Packaging be customized?
Yes, RPET Food Packaging is highly versatile. It can be made in a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors, making it suitable for various food products. Options like tinted, metallic, and transparent designs can also enhance the presentation of food. -
What challenges does RPET Food Packaging face?
Some challenges include inconsistent recycling infrastructure, contamination in recycling streams, and consumer behavior related to proper disposal of PET. However, advancements in recycling technology and increased government investments are improving the quality and availability of RPET packaging.
Conclusion: Why RPET Food Packaging Matters
The recycling process of RPET Food Packaging transforms waste into valuable, food-safe packaging that supports a circular economy. It reduces waste, saves energy, and helps brands align with consumer expectations for sustainability.
As businesses adapt to green policies and rising eco-consciousness, RPET Food Packaging is no longer just an alternative—it’s the future of safe, smart, and sustainable food packaging.
References
-
European Commission. (2023). Directive (EU) 2019/904 on the reduction of the impact of certain plastic products on the environment.
👉 https://ec.europa.eu/environment/topics/plastics/single-use-plastics_en -
Ellen MacArthur Foundation. (2022). The Circular Economy and Plastics: Building a System that Works.
👉 https://ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/topics/plastics/overview -
National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). (2022). Recycling and Reuse of Plastics: Closing the Loop with RPET.
👉 https://www.nrel.gov/news/program/2022/recycling-plastics.html -
U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). (2023). Guidance for Industry: Use of Recycled Plastics in Food Packaging.
👉 https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/guidance-industry-use-recycled-plastics-food-packaging -
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). (2022). Recycled plastic in food packaging: Safety assessment and approvals.
👉 https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/recycled-plastic-food-packaging
Copyright Statement© 2025 Dashan Packing. All rights reserved.
This article is an original work created by the Dashan Packing editorial team.All text, data, and images are the result of our independent research, industry experience,and product development insights. Reproduction or redistribution of any part of this contentwithout written permission is strictly prohibited.
Dashan Packing is committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information andto upholding transparency, originality, and compliance with global intellectual property standards.